The neuralink – Into the mind of Elon Musk
On this page:
- What is the neuralink, Elon Musk’s latest development?
- The neuralink monitors and stimulates brain activity
- Preparing for the first human implantation
- Medical and non-medical applications of the neuralink
- Is the neuralink the first step towards a Black Mirror-type of future?
- Hic sunt dracones or how we are adventuring into an unknown territory of human development
- Conclusion
What is the neuralink?
On August 29 2020, the world tuned in to see Elon Musk’s live presentation of Neuralink’s latest development, a brain implant.
Founded in 2016, Neuralink is a neural engineering company developing high bandwidth brain-machine interfaces.
The neuralink is a 23 mm wide and 8 mm thick coin-shaped device. The device is implanted by replacing a small portion of the skull then inserting the connecting electrodes in the brain. Since the skull is 10 mm thick, the device fits in seamlessly. I could have it right now, and you wouldn’t know. Maybe I do, jokes Elon. I’m sure many of the people watching the live feed wouldn’t have been surprised if he had.
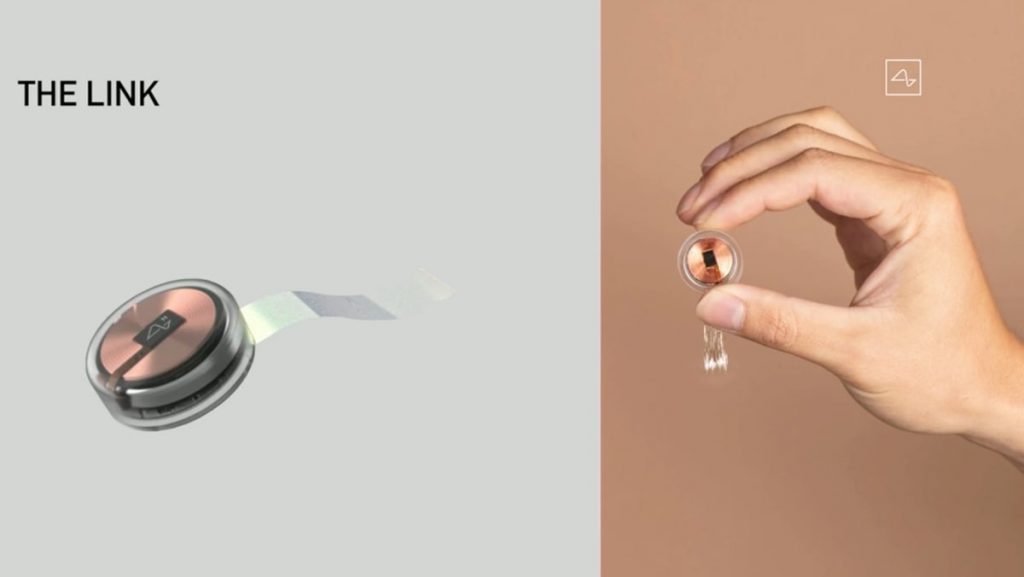

The brain implant developed by Neuralink
To get the device, the user undergoes a surgery performed by a surgical robot.
There is no bleeding or neural damage and the surgery takes about an hour. The user walks in the hospital in the morning and walks out a few hours later with the implanted device.
Should the user decide they no longer want to have the neuralink, the device is removed safely so that the user is still happy and healthy.
The neuralink monitors and stimulates brain activity
What does the neuralink do? What is its purpose? It’s like a Fitbit in your skull with tiny wires, Elon says.
Like any other sensor, the neuralink monitors health and measures temperature, blood pressure etc. It could warn its user of a heart attack or delight them with music.
During the live feed, Elon showed a demonstration of how the device reads one’s brain activity by showcasing Gertrude, the pig, whose neuralink connected with neurons in her snout. Every time she touched something with her snout, neural spikes fired to the neuralink which were turned into beeping sounds for everyone to hear.
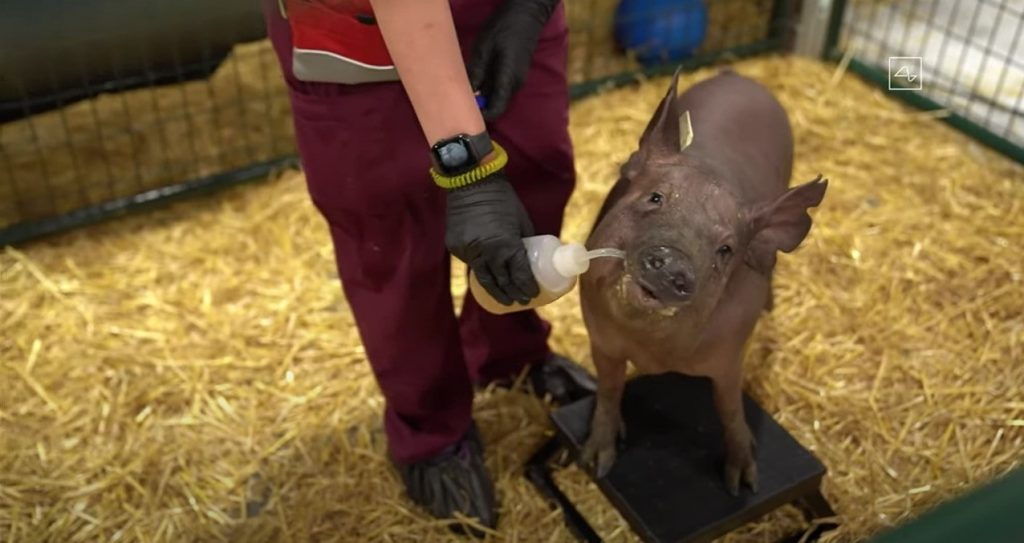

The neuralink isn’t limited to reading brain activity. It can also write it.
What does this mean?
It means the electrodes that have been inserted into the brain can stimulate various parts of the brain by controlling the electrical field. The device is connected to an app on the user’s smartphone so the user has complete control over the device over bluetooth.

Technical specs of the neuralink/image source: teslarati.com
Preparing for the first human implantation
The company is now preparing for the first human implantation which could happen really soon.
In July 2020, the company received the FDA breakthrough device designation which is a voluntary programme designed for certain medical devices that provide effective treatment or diagnosis of life-threatening or irreversibly debilitating diseases or conditions. The neuralink is heading towards clinical studies.
How can neuralink improve the life of its user – medical and non-medical applications
Poets talk about giving away their heart as a symbol of their love for someone else. When we feel sad, we draw a bleeding heart as a representation of our emotions. But our emotions don’t form in the heart, they form in the brain. The heart is nothing more than a muscle pumping blood. The brain is where our conscious life happens. Our brain commands the body to move. We feel with our brain. We make decisions in our brain. We essentially live inside our brain. It is possible now to replace one’s heart (the first heart transplant was performed only fifty years ago) but not the brain.
Medical applications of the neuralink
At this stage, the neuralink stimulates surface layers of the brain where much of the low-level processing happens such as motor intentions, sensory information (hearing and visual processing etc).
Taking all this into account, the neuralink could restore movement and communication in people with spinal cord injuries essentially helping them walk and talk again.
It could also solve blindness, paralysis or hearing loss.
Or give people with severe spinal cord injury the ability to control computers and mobile devices directly with their brains.
In the not so distant future, the team at Neuralink plans to insert the electrodes into the deeper levels of the brain and potentially solve mental afflictions like depression, addiction or anxiety and other neurological disorders.
Non-medical applications of the neuralink
Is the neuralink applicable to the healthy? The answer is yes.
Neuralink’s long-term vision is to create BMIs (brain-machine interfaces) that are sufficiently safe and powerful that healthy individuals would want to have them.
What would a healthy person use neuralink for? Non-medical applications are yet to be discovered but gaming could be one of them.
Is the neuralink the first step towards a Black Mirror-type of future?
We’ve all watched the Black Mirror series and wondered if the next-generation technology featured in it will ever be available to people.
With the development of the neuralink, this technology is possible.
Here are just two examples of Black Mirror technology rendered possible by the neuralink:
- The grain, the implant featured in episode 3, Series 1 which allowed users to record everything they see and hear and playback their memories directly through their eye or to a video monitor.
- Arkangel, the monitoring system featured in episode 2, Series 4 which allowed a mother to track and monitor her daughter’s health and emotional state, and censor sights that may upset her such as blood or the dog she was afraid of.
When asked what he hoped the neuralink would achieve in the future, Matthew McDougall, the Head Neurosurgeon at Neuralink present at the live demonstration answered this: To limit human pain and suffering to a fraction of what it is today.
Elon’s team is made up of neuroscientists, neuro engineers, robot engineers, implant electronics developers, mechanical engineers, security specialists etc.
Every member mentioned a number of ways that they believe this device could help augment people including telepathy, saving, storing and replaying memories, Terminator-like displays, superhuman vision etc. Elon mentioned AI symbiosis.
The neuralink could provide users with a new way to tap and enhance their creativity. Scientists would learn a lot more about how the brain works and the mechanisms of neurological diseases. We could finally begin to understand the nature of consciousness.
Hic sunt dracones or how we are adventuring into an unknown territory of human development
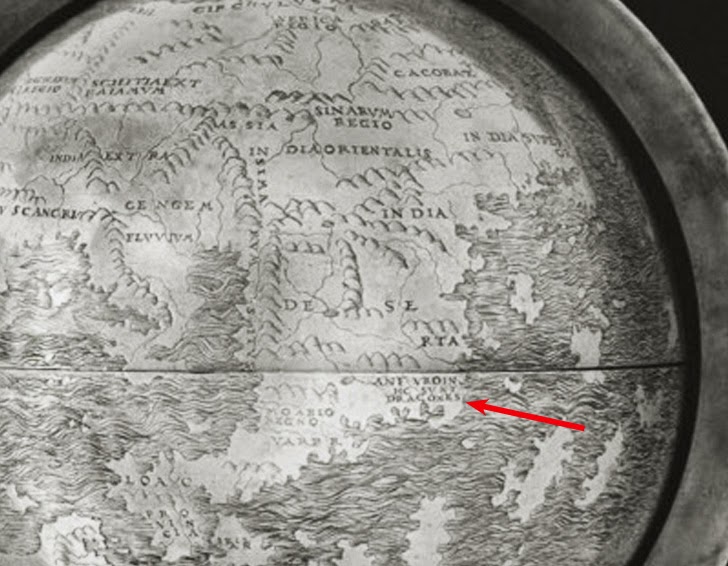

The Hunt-Lenox globe where you can read Hic sunt dracones/image source: International History Blog

In medieval times, mapmakers described unexplored and therefore potentially dangerous territories by using the Latin phrase Hic sunt dracones translated as Here be dragons. It was a warning that essentially said We don’t know what’s out there, no other explorer has come that far so enter at your own risk.
With the neuralink, Elon and his team are venturing into the unknown, shaping the future of mankind. The neuralink is an incredible piece of advanced technology – the first brain to machine interface.
There are still many challenges that are yet to be solved, insulation (the human body is not a friendly environment) and security (protect the device from unwanted access) being two of the most important.
Conclusion
There’s no doubt about it: the neuralink was created with the very best of intentions.
But so was Facebook more than a decade ago. Today we are aware of its negative influence on human behaviour and society at large. Experts believe that the first step Facebook and any other social media platform should take towards a better future for its users is to generate revenue in a different way. The business model they are operating on now, in which they are paid to tweak the users’ behaviour has serious consequences in the real world.
How is Neuralink planning to generate revenue? Will the company have control over the devices? Could anyone else take control? Could users influence other users via the device with or without their consent? Could users connect and form one big network? What will the future look like?
We don’t know and it’s impossible to predict.
Our brains have been slow to catch up with exponentially advancing technology.
There’s no turning back. All we can do is tread carefully.
SpaceX Rockets Are Vital To The Future of Humankind. Here’s Why
SpaceX rockets will play a vital role in the future of humankind. We will evolve as a species thanks to the amazing rockets built by Elon Musk’s space company, there’s no doubt about it.
Read on to find out why.
Humans cannot survive on Earth indefinitely. We will go extinct if we do not become a spacefaring species.
Stephen Petranek, Author ‘How We’ll Live on Mars’
Elon Musk founded SpaceX in 2002 with one mission: to enable humans to go to Mars thus becoming a spacefaring civilization.
![]()
Spacefaring: having vehicles capable of travelling beyond the Earth’s atmosphere (Merriam-Webster)
![]()
When Elon Musk told people he had decided to enter the space industry business, they told him he was crazy and laughed at him.
But to make his dream come true, he knew he the key to getting to Mars was the reusability of rockets. So that’s what he set out to achieve.
What is reusability?
We reuse cars, we reuse planes, trains etc. Think of it: what if cars were of single-use? Would you have enough money to buy a new car every time you needed to drive someplace?
That’s why space programs are so expensive. Each Space Shuttle mission cost the US over $1 billion. Reusability is an economic principle but it wasn’t applicable to rockets until 2017. In the last decades, the US put its space program on pause due to its rising costs.
What does rocket reusability mean?
It means firing a rocket into orbit, launch a payload into space, bring the rocket down to land vertically, clean it, refuel it and send it back to space. It’s an incredibly complicated task from an engineering point of view. No other rockets in the history of human spaceflight ever achieved this. All previous rockets fired by NASA during the 1960s space program crashed into the ocean.
Right now it costs $60 million to launch a rocket. If we could re-use a rocket a thousand times the price goes down to $60K. Spaceflight would stop being expensive and walk into a new stage: commercial spaceflight.
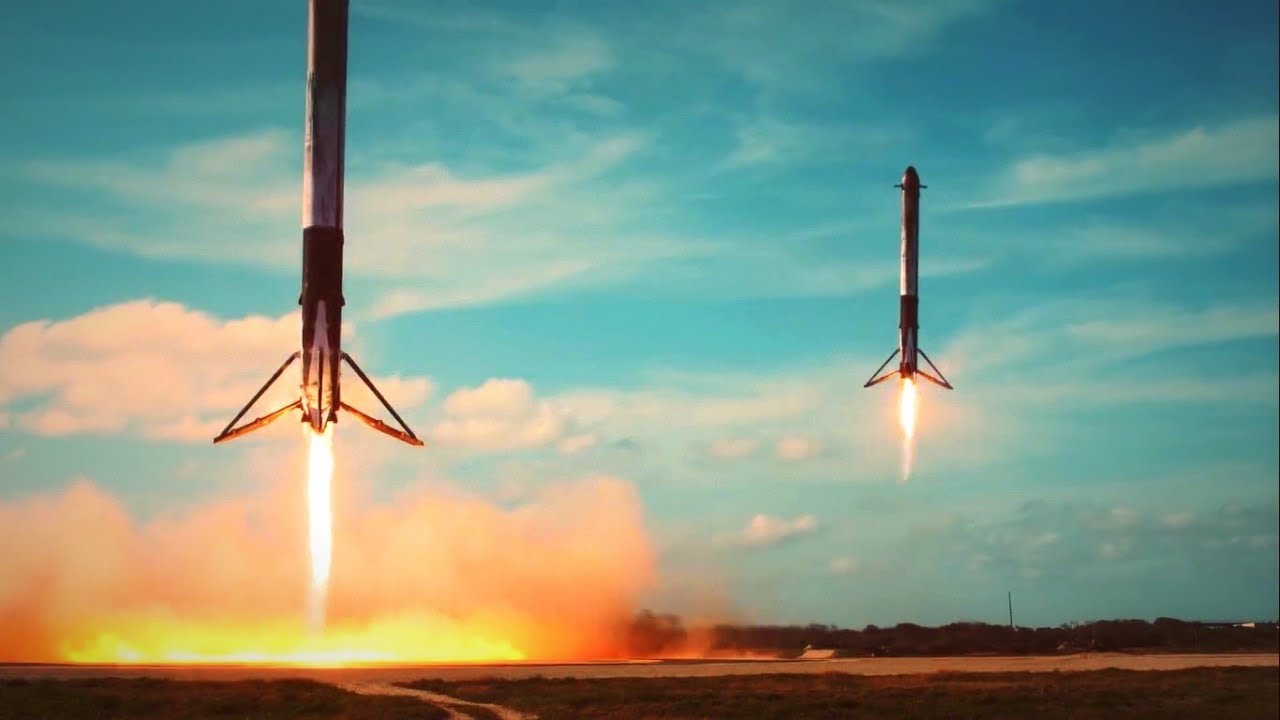
Vertical landing and reusability – a first in spaceflight history
To reuse a rocket first you need to have the rocket land vertically. Landing a rocket vertically on the ground after it’s been in space had never been done before. Falcon9 landed on the ground successfully in 2015.

Falcon 9 / source: teslarati.com
In 2017 SpaceX achieved the world’s first reflight of an orbital class rocket when the Falcon 9 returned to Earth for the second time.
It was an incredible achievement, a feat of engineering on its own! It’s the first step towards fulfilling Elon’s dream of establishing a human colony on Mars in his lifetime.
There are a thousand ways a rocket could fail and one way that it could succeed.
Elon Musk
Watch Falcon9 land after its second trip to space:
Benefits of rocket reusability
Rockets reusability ushered in many benefits:
- It drives costs down while raising revenue;
- SpaceX establishes itself as the first commercially viable space company;
- It democratizes spaceflight as Apple democratized the access to digital information and Kodak, photography;
- It revolutionizes space technology;
- It allows homo sapiens to set out to the next stage of evolution: becoming a spacefaring species, making sure we have a secured future.
SpaceX Facts and Numbers
- Founded in 2002;
- 100+ launches contracted;
- 6000+ employees;
- The only private company capable of returning a spacecraft from low Earth orbit (2010);
- Launched the first commercial spacecraft to deliver cargo to and from the International Space Station (2012);
- The first historic reflight of an orbital class rocket (2017);
- Launched Falcon Heavy, the world’s most powerful operational rocket by a factor of two (2018);
- Over $12 billion on contract;
- The Dragon mission will soon fly astronauts under NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
Falcon Heavy – Bigger and Bolder
Falcon 9 achieved vertical landing on Earth and paved the way for rockets reusability. It was time for SpaceX to go to the next level.
Enter Falcon Heavy – the most powerful launch vehicle since Saturn V.
The Falcon Heavy has the ability to lift more than the weight of a 747 jet loaded with passengers, crew, luggage and fuel.
The rocket is fitted with two reusable boosters and increased payload capacity making it the only vehicle able to transport the huge amount of supplies needed to establish a colony on Mars.
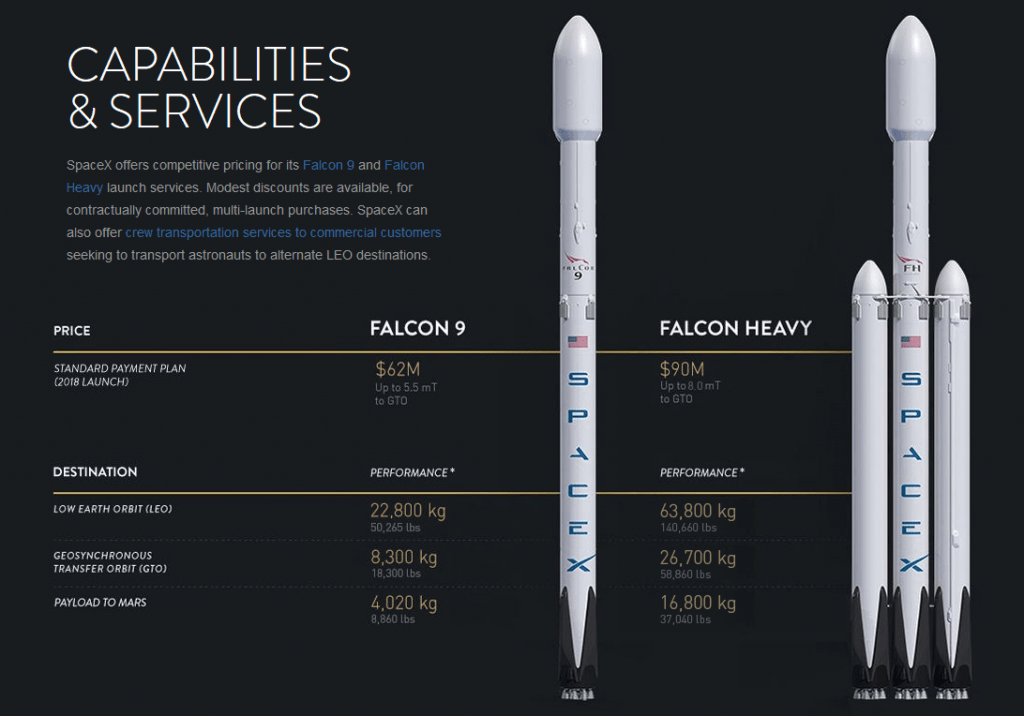
source: spacex.com
I see no better way of ending this article than to invite you to watch the vertical synchronous landing of Falcon Heavy’s boosters, an engineering feat previously deemed impossible:
Did you get goosebumps?
I did!
Learn More
Elon Musk: from living on $1/a day to building a spaceship company
Join the Conversation
We’d love to hear what you have to say.
Get in touch with us on Facebook Group and Twitter.
5 Success Tips From Top Tech CEOs
This article highlights 5 success tips with real-world applications from the top tech CEOs to help you tackle life’s challenges.
The world’s most successful businesspeople know a thing or two about success. Their expertise, however, goes beyond the boardroom. Reaching the top of your profession requires developing a range of talents and aptitudes for dealing with people and situations as well as products.
Here are 5 success tips from top tech CEOs:
1. Take Risks
I always did something I was a little not ready to do. I think that’s how you grow. When there’s that moment of ‘Wow, I’m not really sure I can do this,’ and you push through those moments, that’s when you have a breakthrough.
Marissa Mayer, Yahoo

Marissa Mayer / theverge.com
Before Mayer’s tenure at Yahoo, she was “Employee Number 20” at a then little-known technology company called Google. As an information technology pioneer, she’s widely regarded as one of the most brilliant minds in the industry.
Mayer didn’t get where she was by playing it safe. Her decision to leave Google in 2012 made waves, but it was worth the risk: Mayer became the CEO of Yahoo, and later cofounded Lumi Labs, an artificial technology incubator after Verizon acquired Yahoo in 2017.
Takeaway
Pushing yourself outside your comfort zone is never easy. In business and in life, if you aren’t taking risks, you’re missing out on valuable opportunities.
2. Learn From Mistakes
Failure is an option here. If things are not failing, you are not innovating.
Elon Musk, Tesla

Elon Musk / bigspeak.com
Although it sounds counterintuitive, the majority of successful business leaders have failed along the way. From being ousted as the CEO of PayPal shortly after its merger to presiding over not one, but five spectacularly terrible rocket explosions, Musk is no stranger to failed business ventures.
The differentiating factor is that he kept innovating on his ideas as he gained experience, no matter how great the losses or how they were perceived.
Takeaway
In the long run, success isn’t defined by what you fail to do, but by your ability to learn and grow from each bump in the road. One winning idea can trump every single unsuccessful one.
3. Define Your Vision
A successful vision is aspirational, inspirational and specific.
Mark Hurd, Oracle

Mark Hurd / appleinsider.com
In Hurd’s book, The Value Factor, he talks about how a company’s access to information gives them a competitive edge, and how they translate that information into an executable strategy to drive their success. Vision is one of the cornerstones of business strategy. Software companies like Oracle know firsthand that aspirational visions can transform entire industries.
Takeaway
It’s okay for your vision to be ambitious, but it also must incentivize positive behaviour, and above all, it must be measurable. Setting time-specific goals are a great way to hold yourself accountable for hitting those milestones.
4. Collaborate
My model for business is The Beatles. They were four guys who kept each other’s kind of negative tendencies in check. They balanced each other and the total was greater than the sum of its parts. That’s how I see business: great things in business are never done by one person. They’re done by a team of people.
Steve Jobs, Apple

Steve Jobs / swisslet.com
Takeaway
Teamwork is an extraordinarily powerful interpersonal skill. Proving you can handle your own responsibilities and add value to a larger group is how promotions, raises, and other opportunities arise.
5. Be Receptive to Change
Lots of companies don’t succeed over time. What do they fundamentally do wrong? They usually miss the future.
Larry Page, Google

Larry Page / pikbee.me
Adaptability is another core element of business strategy, especially in the technology sector.
CEOs like Page are highly cognizant of the way products and platforms develop. In order to become what is arguably the most influential online force, Google had to transform to address its users’ needs, reflect modern technology consumption, and adapt to evolving information security trends.
Silicon Valley is chock full of stories of failed startups and companies that could have been the next best thing but couldn’t quite keep up with changing times.
Being flexible is integral to growing as an individual and a professional. You’ll be more likely to recognize opportunities as they arise and be able to shift priorities in order to take advantage of them.
Conclusion
The world’s top CEOs have become successful in business in part because they had a clear grasp on the professional and interpersonal skills necessary to succeed in today’s workforce. If you work on these elements of professional development, you too may find yourself the next CEO of a Fortune 500 company one day.
Join the Conversation
We’d love to hear what you have to say.
Get in touch with us on Facebook Group and Twitter.
Elon Musk: From Living On $1/Day To Building A Spaceship Company
This is the story of how Elon Musk went from living on $1/a day to building a spaceship company.

The young man is looking at his new car being delivered outside his office: a $1 million silver McLaren F1. He’s in the street, admiring his new sports car together with his girlfriend and a CNN filming crew.
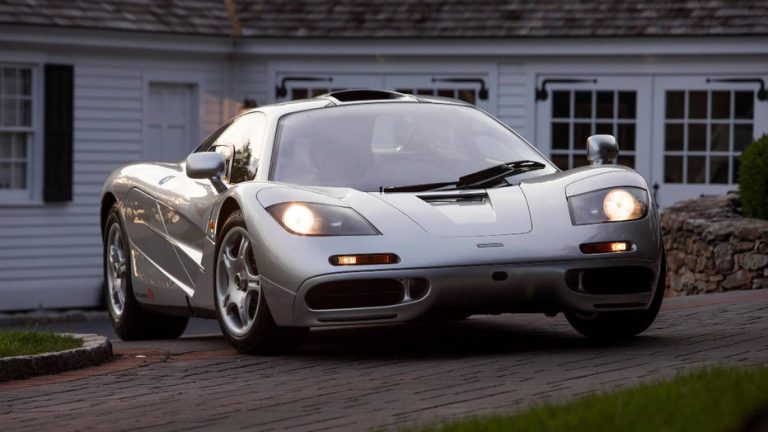

He is being interviewed for a documentary featuring Silicon Valley multi-millionaire entrepreneurs. He’s wearing a camel coloured jacket and black pants which are both too large for his frame, sporting a weird haircut. He may look like a boy wearing his father’s clothes, but this young man has sold his software company for $340 million to a giant computer corporation only a year earlier. He proudly tells the CNN journalist that there are 62 McLaren cars in the world and now he owns one of them. His girlfriend gives her opinion on his new car:
It’s decadent.
Back in his office, sitting in a brown leather armchair, the young man eloquently tells the journalist how he was one of the entrepreneurs who had foreseen the booming success of this new thing: the internet.
Most people thought the internet was a fad.
But he was not most people. Unlike most children, he didn’t enjoy his childhood, he survived it. He was severely bullied in school and coming back home, he didn’t receive much care or empathy from his stern father.

As a young child, he sought refuge in reading. There were days when he would read for 10 hours straight. He read every book in his father’s house no matter the genre: biographies, fantasies and science-fiction.
As a young adult, to avoid serving in the mandatory military service, he moved to Canada where his family from his mother’s side lived. Life wasn’t much easier there. He supported himself by working odd jobs. At one point when he was 17 he tested to see how much he could save by living on $1 a day. The result? He saved $30 eating hotdogs and orange juice.

He was living a hard life, but he didn’t let that interfere with his education. He received his American citizenship and went to California to study business and physics. After he graduated he went to Stanford University in California to pursue a PhD in energy physics. He dropped out of Stanford to ride the internet wave.
While the CNN journalist mentions he received $22 million for the sale of his first company, the young man remembers how he made his first five hundred bucks – by selling a computer game called Blastar he had made when he was only 12 years old.

source: retrothing.com
This young man’s successful life was influenced by one auspicious moment: when he saw a Commodore VIC-20 computer in a shopping window. He was 9 years old and used his allowance to buy it. He learned how to program by reading textbooks on the subject.
He tells the journalist that he could have bought one of the islands in the Bahamas and live carefree for the rest of his life. Instead of that, he was more interested in creating a new company. So he took all his net worth and re-invested it in his new internet company he had created with the purpose of transforming the traditional banking industry.
The real payoff is the sense of satisfaction of having created the company that I sold.

source: radioadelaide.org.au
The young man in my story is Elon Musk.
The year is 1999 and the company he is talking about is X.com which will lately become PayPal. Before PayPal was followed by SpaceX, Tesla Motors and The Boring Company.
As of December 2018, his net worth currently stands at $23 billion.
Some say he is the mad genius of our time, others say he is a visionary looking to change the future of mankind.
He’s certainly had his ups and downs, and more is yet to come.
And it all started … when education happened.
Elon Musk is a world-changer. The next one could be YOU!
Are you a #worldchanger?
Come to BRAND MINDS 2020!
Here are our first confirmed speakers; we will be announcing more speakers in the coming months so stay tuned!
Malcolm Gladwell, Martin Lindstrom and Michio Kaku

This is the third article in our World-Changers Stories Series. Read the previous stories here:
- The $8 Billion Company built by this World-Changer
- The story of a 1.5 Billion User App Built by this World-Changer
sources:
medium.com/the-mission/from-trauma-to-triumph-c4e1f3fc259
startalkradio.net/show/the-future-of-humanity-with-elon-musk/
What Books has Elon Musk Read?
Earlier this month, Elon Musk broke the internet when he took one puff of cannabis while being interviewed on radio.
In August, Arianna Huffington wrote an open letter where she called him out on working 120-hour weeks, thus “demonstrating a wildly outdated, anti-scientific and horribly inefficient way of using human energy.” Working long-hours and sleeping too little is business as usual for Elon – he’s done it while a college student, he’s doing it as CEO of Tesla and SpaceX.
Some say he should set a better example for his employees, others say he should be allowed to be himself: “let the man be an individual” (Neil DeGrasse Tyson)
Elon Musk is a brilliant man with the whole world watching over his shoulder.
But how did he become the visionary tech entrepreneur he is today?
I was raised by books. Books, and then my parents.
Elon had a traumatic childhood: he was heavily bullied in school and his father was harsh on him and his brothers. So it’s understandable how as a young boy, he took refuge in reading. Interviewed by CNBC about his childhood, Elon said he was raised by books – he would spend even 10 hours a day reading.
Here are 13 books Elon Musk has mentioned reading, which we organised into 4 categories: fantasy and heroes, biographies/autobiographies, science-fiction, futurism and AI.
Fantasy and heroes
The heroes of the books that I read always felt a duty to save the world.
1.The Lord of the Rings trilogy
2. Game of Thrones series
Biographies and Autobiographies
3. Benjamin Franklin – An American Life
4. Screw Business as Usual: Turning Capitalism into a Force for Good (Richard Branson)
5. Catherine the Great: Portrait of a Woman
6. Einstein: His Life and Universe
Science Fiction
7. The Foundation series (Isaac Asimov)
The lesson I drew from the works of Isaac Asimov, science fiction writer, is you should try to take the set of actions that are likely to prolong civilization, minimize the probability of a dark age and reduce the length of a dark age if there is one.
8. Dune series (Frank Herbert)
9. The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy (Douglas Adams)
Futurism and AI
10. The Culture series (Iain M. Banks)

Compelling picture of a grand, semi-utopian galactic future. Hopefully not too optimistic about AI.
11. Life 3.0: Being Human in the Age of Artificial Intelligence (Max Tegmark)

AI will be the best or worst thing ever for humanity, so let’s get it right.
12. Our Final Invention: Artificial Intelligence and the End of the Human Era (James Barrat)

13. Superintelligence: Paths, Dangers, Strategies (Nick Bostrom)

Worth reading Superintelligence by Bostrom. We need to be super careful with AI. Potentially more dangerous than nukes.
Conclusion
These books (and other technical books) have shaped Elon’s forward-thinking and helped him dream big.
As an introvert, biographies and autobiographies of scientists and inventors may have supported him in building the level of self-confidence and self-worth he needed to trust in himself first.
Although he is working with cutting-edge AI technology, the world should feel relieved that Elon Musk is taking a cautionary approach and is not an indiscriminate supporter of AI.
Batteries, solar panels and the end of fossil fuels
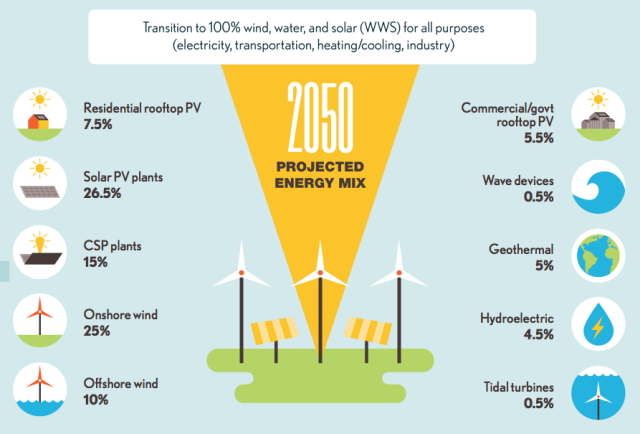
A study published in January in the Journal of Sustainable Finance & Investment predicts that the combination of battery storage with renewable energy will make fossil fuels increasingly obsolete. The driving forces of this disruption include the “decline in retail renewable electricity prices,” along with plummeting costs of batteries. Fossil fuels are the most widely used source of energy because of base load power, which means they provide energy at all times, night and day. In contrast, renewables have faced the ‘intermittency’ challenge—the sun doesn’t always shine, and the wind doesn’t always blow.
But authors Jemma Green and Peter Newman of Curtin University in Australia show that as storage gets cheaper, renewables will become more competitive with fossil fuels on costs and reliability. By 2050, these irresistible technological and market forces could make oil, gas and coal seem too costly and cumbersome, leading renewables to account for “100 percent of global energy demand.”
source: energyathaas.com
According to Vicente Lopez-Ibor Mayor, chairman of Lightsource—the biggest solar energy company in Europe—there will be an immediate impact within just three years. Moreover, Mayor told Motherboard that the speed of technological improvement means solar storage is “going to be massively disruptive to the business-as-usual processes of oil, gas and coal.”
In three years, he said, it will “begin to transform” the electricity infrastructure of major cities. “Solar storage is pitched to become so cheap it will make relying on natural gas peaker plants pointless…It will lead to rapid adoption of solar by businesses, local governments, and households—not because people are environmentally conscious, but simply because it will make more economic sense.”
More on their approach you can read here.
The Powerwall system
While wind and solar power have made great strides in recent years, with renewables now accounting for 22% of electric energy generated, the issue that has held them back has been their transience. But now, the renewable power billionaire Elon Musk has just blown away that final defence. In an event held in California he introduced to the world his sleek new Powerwall – a wall-mounted energy storage unit that can hold 10 kilowatt hours of electric energy, and deliver it at an average of 2 kilowatts, all for US 3,500. That represents an electricity price (taking into account installation costs and inverters) of around US 500 per kWh – less than half current costs, as estimated by Deutsche Bank.
“That translates into delivered energy at around 6 cents per kWh for the householder, meaning that a domestic system plus storage would still come out ahead of coal-fired power delivered through the conventional grid,” explains iflscience.com.
Moreover, the reality is much closer than we might think as Musk is going to manufacture the batteries in the United States, at the “gigafactory” he is building just over the border from California in Nevada. And that while not staying and waiting for some totally new technology, but scaling up the tried and tested lithium-ion battery that he is already using for his electric vehicles.
The Powerwall system offering 10 kWh is targeted at domestic users. It is complemented by a commercial system termed the Powerpack offering 100 kWh storage, and a stack of 100 such units to form a 10 megawatt hour storage unit that can be used at the scale of small electricity grids. Whole communities could build micro-grid power supply systems around such a 10 MWh energy storage system, fed by renewable energy generation (wind power or rooftop solar power), at costs that just became super-competitive.
More than that, Musk declared that the entire electric power grid of the US could be replicated with just 160 million of these utility-scale energy storage units. And two billion of the utility-scale units could provide storage of 20 trillion kWh – electric power for the world.
Solar panels have repaid their fossil fuel debt
At the same time, another study says that thanks to the growing solar power capacity around the world, solar power has reached the break even point. The study from the Netherlands, published in Nature Communications, says that the power generated by solar photovoltaic panels over the last 40 years has offset the polluting energy used to produce them.
By the researchers’ calculations, for every doubling of global solar power capacity, the energy used to produce them fell by 12-13 percent and greenhouse gas emissions fell by 17-24 percent, depending on what material was used. Solar capacity has grown roughly 45 percent a year since 1975, reaching 230 gigawatts (GW) in 2015. By the end of 2016, there could be 300 GW installed.
“The researchers believe the break even point was likely hit about five years ago for both energy consumed and emissions meaning, at this point, global solar energy is having a net positive impact and will continue to increase that positive impact going forward. This feels like a major cause for celebration. If you’re a homeowner with solar panels, the researchers say that individual solar panels repay their fossil fuel debt several times over during their average 30-year lifespan,” wrote Megan Treacy for treehugger.com.
Inspirational people to watch in 2017
Inspiration is what drives us to be better and better each day, to look up to people that give us the courage to try something new, to discover and push our limits. It’s also one of the talents that few people carry with them, a quality that makes them really special. We chose for you certain persons, from different fields of activity, that we believe represent an inspiration for today and the years to come.
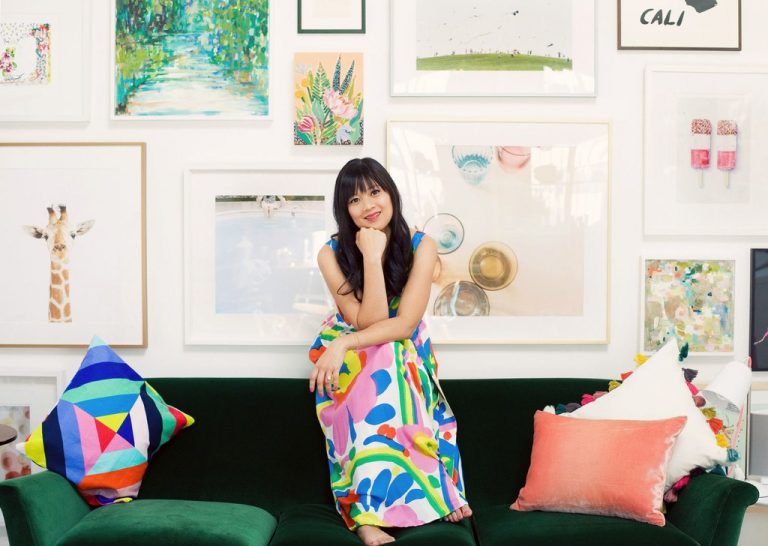

The crown jewel of this graphic designer’s online empire, which also includes her popular lifestyle blog, is Pinterest, where Cho has 12.8 million followers. As the most-followed person on the platform, she’s now able to garner big partnerships, including a photo-documented road trip sponsored by Toyota and new lines of baby clothes and nursery and home décor for Target. Last year she was tapped to design the souvenir eggs for the 2016 White House Easter Egg Roll. As if that weren’t enough, Joy is a best-selling author, has a thriving YouTube channel, consults with leading companies.
More about her you can read here.
Felix Arvid Ulf Kjellberg (a.k.a. PewDiePie)

The Swedish gamer (born Felix Kjellberg) has a record of 42.7 million subscribers on YouTube, giving him a reach bigger than most TV networks. He recently struck a deal with Disney’s Maker Studios to produce original content for RevelMode, a new virtual network. PewDiePie’s net worth has grown steadily since 2010, clearing over $9 million a year since he started posting videos to YouTube.
For proof that a single tweet can change the world, look no further than Sept. 2, when Bouckaert, the Emergencies Director for Human Rights Watch, shared a photo of Alan Kurdi, a 3-year-old Syrian-Kurdish refugee, lying dead on a Turkish beach. Within hours, the image (taken by Turkish photographer Nilüfer Demir from the Dogan News Agency) had gone viral, drawing attention to the human toll of Europe’s migrant crisis—and perhaps even hastening a response. Two days after Bouckaert’s tweet, the U.K. agreed to accept thousands more refugees.

He has testified about war crimes before the United States Senate, the Council of Europe, and at the Yugoslav Tribunal (ICTY) in The Hague, and has written opinion pieces for papers around the world. His work has been profiled in Rolling Stone, The Washington Post, The Stanford Lawyer, and The Santa Barbara Independent Newspaper. Most recently, Bouckaert was awarded an honorary doctorate by the Catholic University of Louvain for his work on human rights.
Engineer, physician, best selling author and brilliant entrepreneur. He’s best known for being the Founder and Executive Chairman of the XPRIZE Foundation (best known for its $10 million Ansari XPRIZE for private spaceflight.) and Singular University (whose mission is to educate leaders to apply exponential technologies to address the biggest challenges we face today).
Dr. Peter H. Diamandis is an international pioneer in the fields of innovation, incentive competitions and commercial space. In 2014 he was named one of “The World’s 50 Greatest Leaders” – by Fortune Magazine. Diamandis is also the Co-Founder and Vice-Chairman of Human Longevity Inc. (HLI), a genomics and cell therapy-based diagnostic and therapeutic company focused on extending the healthy human lifespan. In the field of commercial space, Diamandis is Co-Founder/Co-Chairman of Planetary Resources, a company designing spacecraft to enable the detection and prospecting of asteroid for precious materials. He is also the Co-Founder of Space Adventures and Zero-Gravity Corporation.
Diamandis is the New York Times Bestselling author of Abundance – The Future Is Better Than You Think and BOLD – How to go Big, Create Wealth & Impact the World. He earned an undergraduate degree in Molecular Genetics and a graduate degree in Aerospace Engineering from MIT, and received his M.D. from Harvard Medical School.
He turned his 10k Facebook group into 3M+ members, he’s written 3 New York Times bestselling books and Larry King calls him one of the worlds’ top trainers. He started from scratch after surviving a horrible car crash. As he saw the end near, he realized we’d all be asked 3 questions at the end of our lives. Did we live? Did we love fully? And did we make a difference, did we matter? With those 3 questions he left his corporate job and claimed a path to become a speaker, author, coach and trainer to inspire others with his message to live, love and matter. He now runs a multiple 8 figure business that inspires tens of millions of people on a weekly basis.
Brendon is one of the leading high performance coach and one of the most watched, quoted and followed personal development trainers in history. A Top 100 Most Followed Public Figure on Facebook, over 50,000,000 people watched his videos in the last 12 months and more than 1,000,000 students have completed his online courses and video series, making him “one of the most successful online instructors in history” (Oprah.com) and “the reigning world heavy-weight personal development educator” (Entrepreneur.com).
Forbes crowned him the “Ultimate thinking machine”. Ray Kurzweil is an inventor, futurist, computer scientist, founder of Singularity University, author and director of engineering at Google. He has been described as “the restless genius” by The Wall Street Journal, and “the ultimate thinking machine” by Forbes. Inc. magazine ranked him #8 among entrepreneurs in the United States, calling him the “rightful heir to Thomas Edison,” and PBS selected Ray as one of 16 “revolutionaries who made America,” along with other inventors of the past two centuries. He is considered one of the world’s leading inventors, thinkers, and futurists, with a 30-year track record of accurate predictions.

Kurzweil was the principal inventor of the first CCD flatbed scanner, the first omni-font optical character recognition, the first print-to-speech reading machine for the blind, the first text-to-speech synthesizer, the first music synthesizer capable of recreating the grand piano and other orchestral instruments, and the first commercially marketed large-vocabulary speech recognition.
Sergey Brin
Sergey Brin created Google with Larry Page, the two becoming billionaires as Google developed into the world’s most popular search engine and a media giant. After raising $1 million from family, friends and other investors, the pair launched the company in 1998. Google has since become the world’s most popular search engine, receiving an average of more than a trillion searches a day in 2016. On August 10, 2015, Brin and Page announced that Google and its divisions were being restructured under the umbrella of a new parent company called Alphabet, with Brin and Page serving as Alphabet’s respective president and CEO.
In November 2016, Brin was ranked No. 13 on Forbes‘ “Billionaires” list, and No. 10 among U.S. billionaires who made the list. According to Forbes.com, as of November 2016, Brin’s net worth was $37.9 billion. As director of special projects at Google, Brin shared the company’s day-to-day responsibilities with Page, who served as Google’s CEO, and Eric Schmidt, executive chairman of the company.
Elon Musk became a multimillionaire in his late 20s when he sold his start-up company, Zip2, to a division of Compaq Computers. He achieved more success by founding X.com in 1999, SpaceX in 2002 and Tesla Motors in 2003. Musk made headlines in May 2012, when SpaceX launched a rocket that would send the first commercial vehicle to the International Space Station. He bolstered his portfolio with the purchase of SolarCity in 2016, and cemented his standing as a leader of industry by taking on an advisory role in the early days of President Donald Trump‘s administration.
Angela is assistant dean of the Samberg Institute for Teaching Excellence at Columbia Business School and a former McKinsey consultant. Looking at the investing landscape, she was appalled at the lack of women investing and felt it was limiting the innovation economy. She founded 37 Angels, an angel investment network that trains women to invest in early stage start-ups. The network fund Angela is a sought-after expert on CNBC, Bloomberg TV, and Fox Business Network and is regularly featured in media outlets such as Huffington Post, Forbes, and Fast Company. Entrepreneur Magazine recognized Angela as one of Six Innovative Women to Watch in 2015, and Alley Watch named her as one of 100 NYC Tech Influencers You Need to Know.
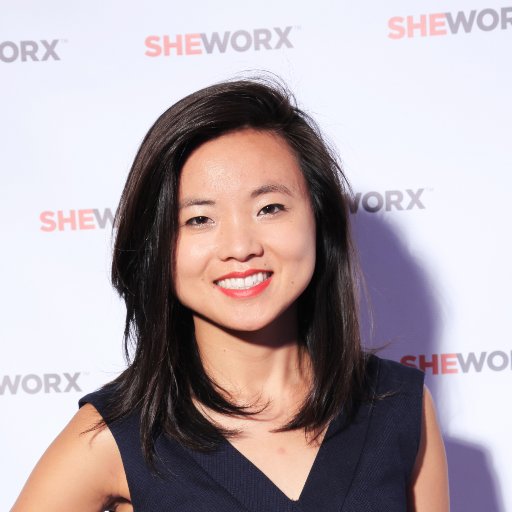

Yin Lin, along with co-founder Lisa Wang, is the force behind SheWorx, a global collective of female entrepreneurs with programs in New York, Los Angeles, London, Singapore, and Tel Aviv. SheWorx has been recognized as the leading female entrepreneur event series, having launched in 6 global cities, reached over 20,000 women, and curated 100 dynamic round tables and summits providing women with actionable business strategies and access to top mentors and investors. Previously, she co-founded a design and development agency that consulted early stage startups to build out their brand and technology at their most critical juncture. Clients that have leveraged their expertise have gone on to raise over $ 27M in venture funding. She was an associate Techstars, one of the most selective technology accelerators in the world.
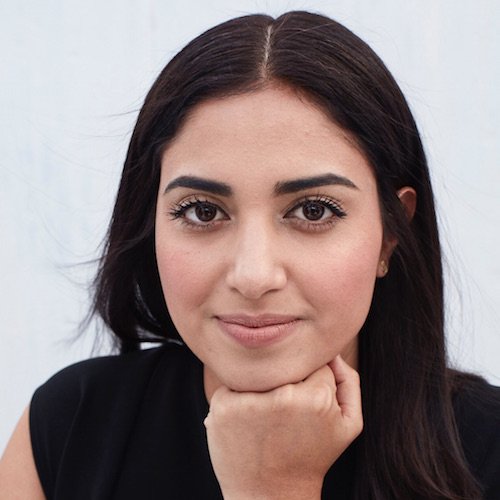

Tanya Menendez started researching the problem of technology’s hurting rural jobs in Oaxaca, Mexico, while at college. Later, working with Matthew Burnett at the Brooklyn Bakery, she came up with the idea of a platform for entrepreneurs who make things. She and Matthew started Makers Row, which helps small manufacturers get the software, community, and production materials they need to keep up with change.
Maker’s Row has industry leading investors like Alexis Ohanian, Joanne Wilson, Comcast Ventures, Index Ventures, Kapor Capital, Expansion Capital and Melo7. To date, Maker’s Row has raised over $2.5M in venture capital. In 2015, Tanya was included in Forbes’ 30 Under 30, and has been named Business Insider’s Coolest People in Tech and one of PopMechanic’s 25 Makers Who Are Reinventing the American Dream.
Based in Houston, Carolyn took a look at the burgeoning numbers of startup accelerator and incubators and saw something magical missing–women. She founded the Circular Board, the world’s first and largest digital accelerator for women entrepreneurs.
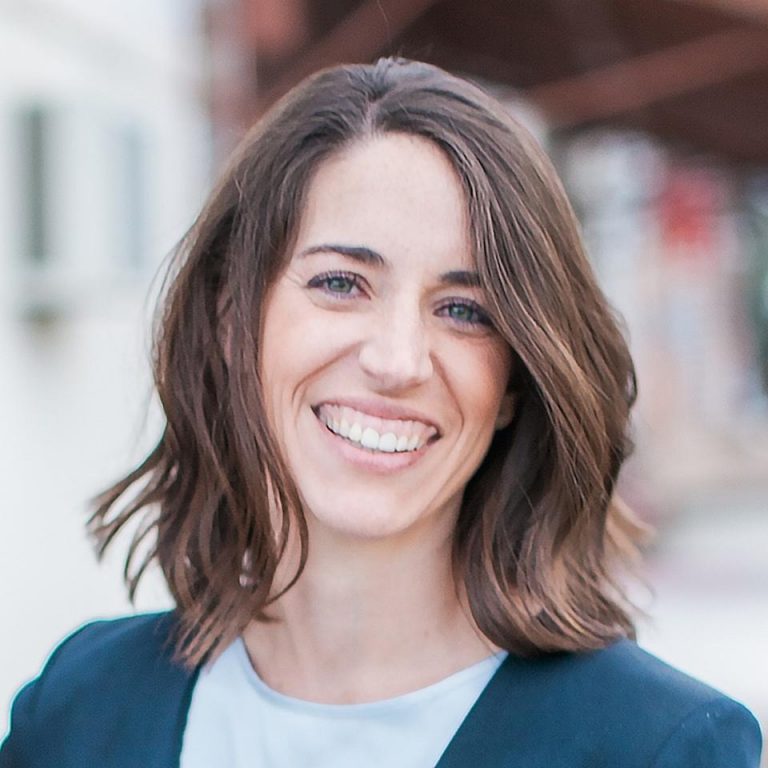

She currently is a board member for the Texas A&M Mays College of Business, a member of the Dell Women’s Entrepreneur Network, a United Nations Global Accelerator delegate, and TEDx speaker. Other honors include an American Express Micro to Millions award, Sam Walton Emerging Entrepreneur, and Entrepreneur Magazine 2016 “Woman to Watch.” She has been featured in Entrepreneur, Huffington Post, Fortune, Time, MSNBC and other national publications.
Reshma Shetty, co-founder, Ginkgo Bioworks
Reshma Shetty has raised over $151 million to re-engineer technology through cells. Reshma has been active in synthetic biology for over 10 years and co-organized the first international conference in the field: Synthetic Biology 1.0. In 2008, Forbes magazine named Shetty one of Eight People Inventing the Future and in 2011, Fast Company named her one of 100 Most Creative People in Business. Reshma holds a Ph.D. in Biological Engineering from MIT.








