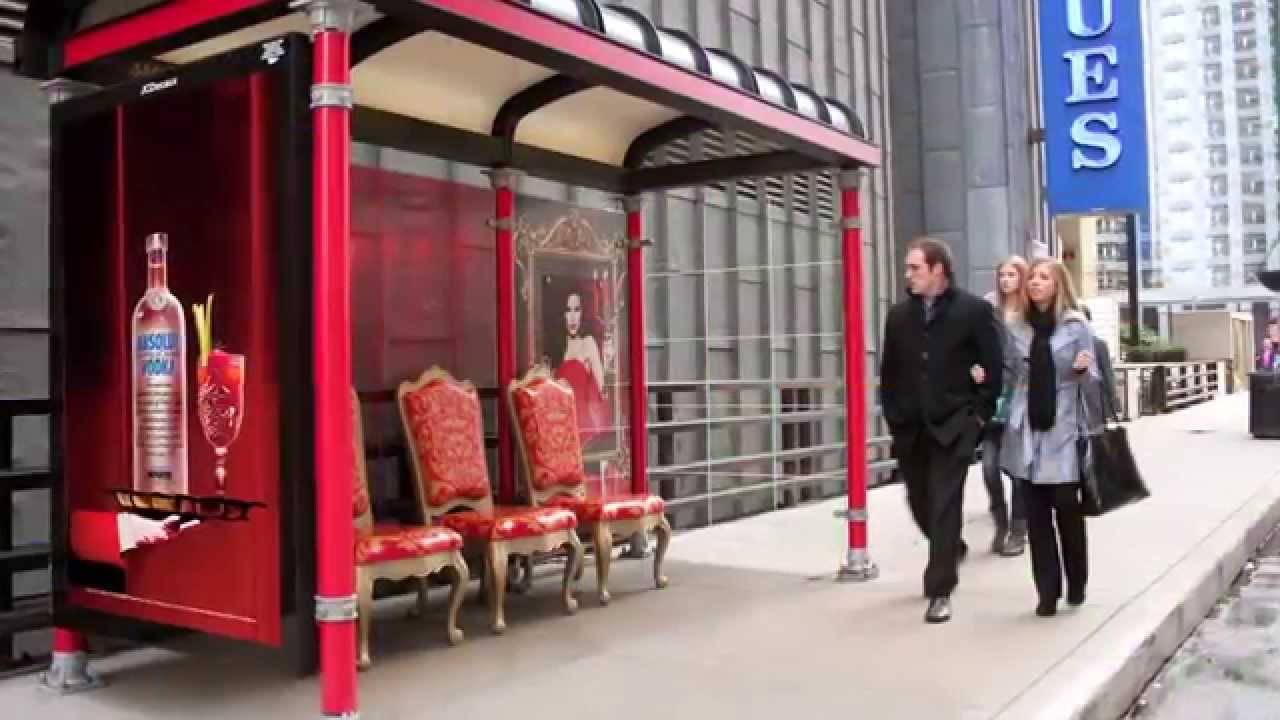
The digital out-of-home advertising is already blooming
The share of global advertising spend going to out-of-home (OOH) advertising remains stable at 6 percent, shows ‘Why Out Of Home Performs’, a joint study by Magna Intelligence and Rapport, IPG Mediabrand’s out-of-home agency, into OOH’s continued growth and impact. The report was based on findings from an analysis of the global OOH industry and OOH advertising in 70 countries. This is largely down to major investment in digital OOH (or DOOH), which is growing in every environment and has seen unit numbers jump 70,000 to 300,000 worldwide in two years, and revenue increase by 30 percent.
Digital OOH is boosting advertising revenues by creating more opportunities for marketers in premium locations like airports or malls, thus increasing the revenue per panel multiple times. Although digital units account for only 5% of the global OOH inventory, they already generate 14% of total advertising revenues. In fact, DOOH already accounts for 30% of revenues in some markets like the UK and Australia, and the global share is predicted to grow to 24% globally by 2021.
“With the explosive growth of digital-out-of-home (DOOH), the diversified lifestyle touch points it reaches, and the veritable mountain of mobile driven audience data, we are best positioned to accurately, and in real-time, track audiences and deliver contextually relevant messages through out-of-home media. OOH’s sustained growth on a global scale will further enable us to create engaging consumer experiences,” said Mike Cooper, Global CEO Rapport.
source: Campaign Asia
“The digital-out-of-home market is a return to advertising’s roots, quietly shifting the industry by way of re-imagining the classic advertising experience. Nearly $4.5 billion is expected to be spent on DOOH advertising in the U.S. by 2019, an increase of approximately $1.2 billion from 2016. Zenith forecasts that DOOH will grow faster globally than all other buying methods, and PricewaterhouseCoopers predicts that DOOH advertising revenues will overtake traditional media spend in 2020, growing at a rate of 15% a year for the next four years,” writes AdAge.com.
According to MAGNA, OOH advertising is now a $29 billion market, responsible for approximately 6% of the $500 billion global advertising spending. However, OOH market share increases to 10% to 12% in some countries, including France and Russia, compared with other media categories including Internet, TV, print and radio. OOH market share has remained stable in the last five years, hovering around 6%. However, as part of its increasing importance in the media mix, OOH market share has increased from 8% to 10% of traditional media advertising spend, which includes TV, print, radio and out-of-home, among other categories.
MAGNA Intelligence, in partnership with Rapport, conducted an in-depth survey in 22 key markets including Argentina, Australia, Belgium, Canada, China, Denmark, France, Germany, India, Italy, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, Netherlands, Norway, Philippines, Russia, Singapore, Spain, Thailand, United Kingdom and the United States. The objective of the survey was to assess OOH advertising’s sustained growth and impact during a period where offline marketing budgets are stagnating and other media categories are struggling.
Moreover, MAGNA showed in another study launched in June, that in the USA, Out-of-Home (OOH) advertising is expected to grow +2% to $7.9 billion in 2017, including cinema. MAGNA reduces its 2017 growth forecast following weak first quarter advertising sales, which grew by just +0.3% in a sudden slowdown, as seven of the last eight quarters had shown year-over-year growth of +3% or more. The 1Q17 stagnation occurred as a result of several key verticals reducing spend, including both automotive and food & beverage, which both experienced double-digit declines. This offset the continued growth from tech brands (e.g. Google, Apple, Hulu and Netflix) that have driven OOH sales over the last two years.
The DOOH market encapsulates everything from digital billboards to screens in elevators to screens on jukeboxes. Unlike internet or mobile advertising, it allows advertisers to reach target audiences in a specific, real-world context. Instead of interrupting an internet user’s online experience with an ad, it’s focused on marketing to consumers when they are “on the go” in public places or in transit. Due to its specifications, the technology has the opportunity to give to its target the message in a format that’s automated, dynamic and interactive.
“The DOOH space presents a major opportunity for creatives, technologists and consumers alike. We see DOOH’s effectiveness in the numbers: the 2016 Nielsen OOH ad study found 91% of U.S. residents age 16 or older, who have traveled in a vehicle in the past month, noticed some form of OOH, and 79% noticed OOH in the past week. The same Nielsen digital billboards study found 71% of digital billboard viewers find those ads to stand out more than online ads. Ultimately, the emerging digital-out-of-home market is groundbreaking in its interactive technology, but it’s also a return to advertising’s roots and the original purpose around advertising: to provide an engaging and useful service to the public,” writes AdAge.
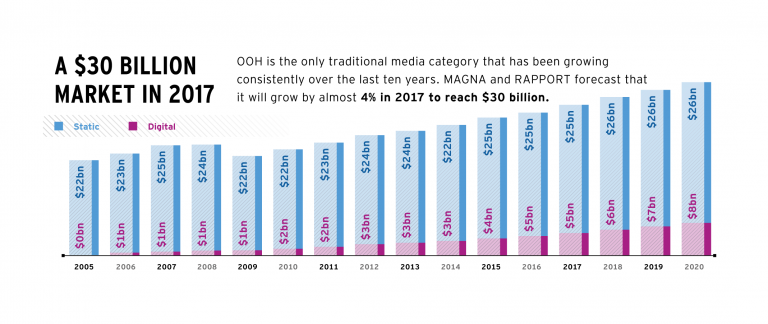
Globally, in 2016, the OOH market was worth $28 billion in net advertising, according to Magna’s report, and is predicted to grow by 4 percent per year to reach $33 billion by 2021. Behind this growth is an ever-more concentrated supply-side market, in which the top international OOH media owners are continuing to expand their influence: the six main global vendors (in order of 2016 revenue size, JCDecaux, Clear Channel, Outfront, Lamar, Stroer and Exterior) now control almost 40 percent of the whole market. By 2021, the report predicts small, but significant changes, in the environments most used for OOH. Use of billboards, currently the top revenue-generating segment and performing particularly well in India, Russia and the US, will drop 4 percent from 45 to 41 in the next five years. Street furniture and transit, meanwhile, are due to grow, respectively, from 31 to 34 percent and from 14 to 15 percent as local authorities become more willing to partner with OOH vendors. A series of major contracts—typically over 10 years long—in big cities are also in the process of renewal, the first time this has happened in the era of DOOH and programmatic opportunities, which partly explains DOOH’s recent giant revenue leap.
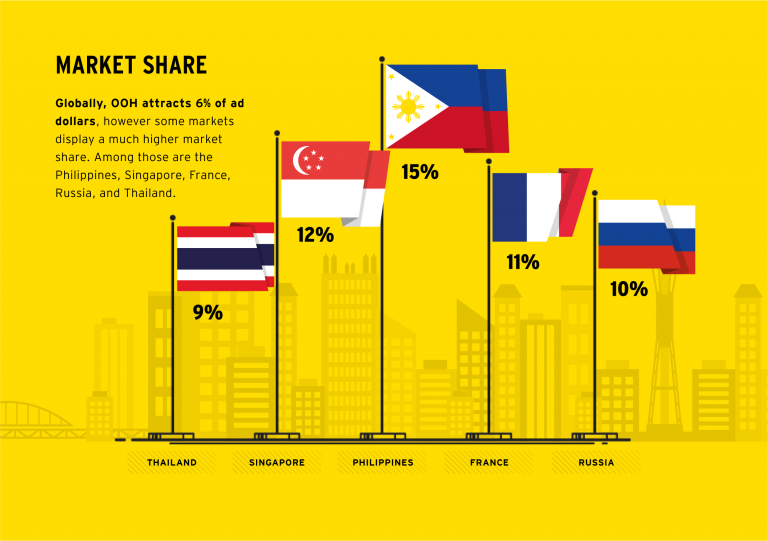
According to APAC, while the US is the largest OOH market, valued at $7.1 billion last year, APAC countries Japan ($4.7 billion) and China ($3.1 billion) come in at second and third position and per capita spending on OOH amounts to a record $38 per year in Japan, compared to $22 in the US. Singapore spends the second highest amount per capita at $36 a year. In the Philippines, meanwhile, OOH accounts for one of the highest percentage shares of overall ad spend in the world, at 15 percent compared to the global share of 6 percent. Singapore (12 percent) and Thailand (9 percent) also exceed the worldwide average.
Singapore’s OOH ads have the highest reach range of any other APAC market, with a penetration of 70 to 80 percent of the relevant population, due to its concentrated levels of urbanisation. Australia’s have the second highest, reaching 60 to 70 percent, but neither matches the reach of OOH ads in Argentina, which are considered seen by a huge 85 to 95 percent of the population.
In Australia, DOOH represents more than a third of total OOH spend, which the report attributes to a sophisticated advertising market and a population relatively concentrated in a few urban centers.
In China, the total OOH spend about matches other markets, it is one of the top five global markets in terms of penetration of digital, led by the transit segment. By 2021, MAGNA predicts that digital growth will have doubled, while OOH growth will be stagnating, partly due to lack of interest in non-digital inventory.
“OOH’s natural convergence with other digital media has hurt most other ad forms. OOH complements digital media by amplifying and enhancing it. This phenomenon has brought additional ad revenue to OOH, while most other media have experienced revenue losses as a result of the growth in digital.OOH has benefited from other new technologies, too, such as social media and mobile. Many OOH media campaigns are now picked up on social media, which greatly amplifies the total viewership. When consumers are on mobile devices, OOH is typically one of the last ad forms they’re exposed to just before important path-to-purchase decisions,” explained Steve Nicklin, Vice President of Marketing, OAAA, for billboardinsider.com.
The innovative opportunities provided by the digital platform have provided the OOH industry with new thinking and new ideas. Moreover, in the USA, as shown by the USA Touchpoints/RealityMine study, OOH and Today’s Mobile Consumer, consumers spend more time with OOH than any other form of advertising media except TV. The findings are supported by the 2016 Nielsen OOH ad study that found that 91% of US residents age 16 or older, who have traveled in a vehicle in the past month, noticed some form of OOH, and 79% have noticed OOH in the past week. Their research also discovered impressive levels of engagement, with 82% of billboard viewers reporting they look at the advertising message at least some of the time; and over one-third looking at the billboard ad each time or almost each time they noticed one. The Nielsen digital billboards study found 71% of digital billboard viewers find them to stand out more than online ads.
OOH is expanding to brand new environments. Digital screens have allowed OOH advertising vendors to penetration niche environment allowing to reach young urban population that is otherwise hard to reach by traditional media: offices, elevators, taxi, gyms, bars, retail etc. The “Digital Place-Based” segment offers targeting capabilities and programmatic opportunities. Moreover, OOH becomes addressable and experiments with programmatic. Initially developed to automate the trading of online display ads, the programmatic technologies are now being used in to buy and optimize ad campaigns on connected DOOH units.
Programmatic techniques not only optimize the workflow of media-buying but help brands deliver the right ad in the right place and at the right time, using consumer data and mobile location data. Giving advertisers the ability to plan, buy, optimize and measure the effectiveness of their outdoor campaigns through an online platform represents the natural evolution of OOH’s technology-driven transformation with many vendors developing Private Marketplaces (PMP).
Besides that, DOOH is going social. “There are two main avenues DOOH is being used to complement social campaigns, either through integration or through content creation,” says Neil Morris, founder and CEO of UK-based creative production house Grand Visual.
Less known things that might surprise you about technology in general
One of the first Computer Science Ph.Ds was earned by a nun
Sister Mary Kenneth Keller, born in Ohio in 1914, entered the Sisters of Charity in 1932 and professed her vows in 1940. She went on to study at DePaul University, where she received a B.S. in Mathematics and an M.S. in Mathematics and Physics. n 1965, she became the first American woman to earn a Ph.D. in Computer Science. Afterwards, Sister Keller founded the computer science department at Clarke College in Iowa, which she directed for 20 years. She was passionate about providing access and information to everyone, not just computer scientists. She also envisioned a world in which computers made people smarter and learned to think on their own.
Changing fonts can save printer ink
Some say that if you use a ‘lighter’ font (with a lighter stroke), you’ll use slightly less ink per page. Based on the assumption that you’re only printing with inkjet printers that use the old style cartridges (not ink tanks, and not toner based laser printers), you’ll likely save about 10 per cent ink by switching to one of the lighter fonts.
QWERTY was designed to slow you down

There are actually two theories to this. The first one starts to make sense when you look at manual typewriters. If someone typed too fast, the keys would jam. QWERTY placed common alphabets at a distance from each other and slowed typists down. Another theory is that telegraph operators designed the QWERTY layout because it was easier (and faster) to decipher Morse code.
92 per cent of the world’s currency is digital

This means that most of the money you earn, transact with, use to buy goods/services and so on exists only on computers and hard drives. Only an estimated 8 per cent of currency globally is physical money. Banks store electronically too and the 92 per cent includes all kinds of transactions done using credit/debit cards and wire transfers.
Russia built a computer that ran on water, in 1936
Before the miniaturization of transistors, computers had a much more visible system of counting: things like gears, pivots, beads and levers were often used and they needed some sort of power source to function. Vladimir Lukyanov built something like this in 1936, but he used water to create a computer that solved partial differential equations. In images of the Lukyanov computer, you’ll see a complex system of interconnected tubes filled with water. It was also called a Water Integrator and was originally designed to solve the problem of cracking in concrete. It’s now found in Moscow’s Polytechnic Museum.
The first mouse was made of wood

It was created by Doug Engelbart, with the assistance of Bill English, during the 1960’s and was patented on November 17, 1970. According to computerhope.com, the mouse was originally referred to as an “X-Y Position Indicator for a Display System” and was first used with the Xerox Alto computer system in 1973. Using the mouse, Douglas was able to demonstrate moving a mouse cursor on the Alto computer in The Mother of All Demos. However, because of its lack of success, the first widely used mouse is the mouse found on the Apple Lisa computer.
A killer may have gone free due to using Firefox
The Florida sheriff’s office that investigated Caylee Anthony’s death confirmed that it overlooked a computer search for suffocation methods made from the little girl’s home on the day she was last seen alive. WKMG reports that sheriff’s investigators pulled 17 vague entries only from the computer’s Internet Explorer browser, not the Mozilla Firefox browser commonly used by Casey Anthony. More than 1,200 Firefox entries, including the suffocation search, were overlooked.
The data can be corrupted by high-energy particles coming from the space
According to makesenseof.com, some scientists have suggested that Toyota’s unintended acceleration fiasco may have been caused by the interference of cosmic rays combined with inadequate fail-safes for recovering from randomly introduced errors. For most PC users, however, invaders from outer space are not the most likely source of trouble. Good ole-fashioned human error is a more common cause. Corruption usually occurs because of user error (deleting or modifying files that shouldn’t be tampered with), malicious activity (malware) or routine degradation and failure of storage media (mechanical and solid state drives).
The first ever webpage still exists at its place
Invented by Tim Berners Lee, the first website went live at research lab CERN in 1990. Created by 60-year-old British computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee in 1990, while he was a researcher at the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), the website still exists today. The site’s address is info.cern.ch, and provides information about the world wide web – the platform that sits on top of the Internet, where documents and pages on the Internet can be accessed by URLs, and connected to each other via hyperlinks.

And, on a lighter tone…
- In 2012, at least 17 newborn girls were named Siri
- A red panda is native to the Himalayas and southwestern China. Translated, the English word for red panda is “Firefox,” which is where the browser gets its name.
- The world’s first camera took eight hours to snap a photo.
- About 1 out of 8 married couples actually met each other on the Internet.
- There is a factory in Japan which can run unsupervised for 30 days at a time — it’s almost entirely manned by robots.
- In Mexico City, there are special bins that offer free wifi to people who properly dispose of their dog poop.
- On an average day, a typist’s hands fingers travel 12.6 miles.
- The first banner advertising was used in 1994.
- Two hundred and twenty million tons of old computers and other technology devices are trashed in the United States each year.



