This Origami Screen Turns Your Windows Into Solar Panels
This origami screen turns your windows into solar panels.
Check it out!
Join the Conversation
We’d love to hear what you have to say.
Get in touch with us on Facebook Group and Twitter.
Batteries, solar panels and the end of fossil fuels
A study published in January in the Journal of Sustainable Finance & Investment predicts that the combination of battery storage with renewable energy will make fossil fuels increasingly obsolete. The driving forces of this disruption include the “decline in retail renewable electricity prices,” along with plummeting costs of batteries. Fossil fuels are the most widely used source of energy because of base load power, which means they provide energy at all times, night and day. In contrast, renewables have faced the ‘intermittency’ challenge—the sun doesn’t always shine, and the wind doesn’t always blow.
But authors Jemma Green and Peter Newman of Curtin University in Australia show that as storage gets cheaper, renewables will become more competitive with fossil fuels on costs and reliability. By 2050, these irresistible technological and market forces could make oil, gas and coal seem too costly and cumbersome, leading renewables to account for “100 percent of global energy demand.”
source: energyathaas.com
According to Vicente Lopez-Ibor Mayor, chairman of Lightsource—the biggest solar energy company in Europe—there will be an immediate impact within just three years. Moreover, Mayor told Motherboard that the speed of technological improvement means solar storage is “going to be massively disruptive to the business-as-usual processes of oil, gas and coal.”
In three years, he said, it will “begin to transform” the electricity infrastructure of major cities. “Solar storage is pitched to become so cheap it will make relying on natural gas peaker plants pointless…It will lead to rapid adoption of solar by businesses, local governments, and households—not because people are environmentally conscious, but simply because it will make more economic sense.”
More on their approach you can read here.
The Powerwall system
While wind and solar power have made great strides in recent years, with renewables now accounting for 22% of electric energy generated, the issue that has held them back has been their transience. But now, the renewable power billionaire Elon Musk has just blown away that final defence. In an event held in California he introduced to the world his sleek new Powerwall – a wall-mounted energy storage unit that can hold 10 kilowatt hours of electric energy, and deliver it at an average of 2 kilowatts, all for US 3,500. That represents an electricity price (taking into account installation costs and inverters) of around US 500 per kWh – less than half current costs, as estimated by Deutsche Bank.
“That translates into delivered energy at around 6 cents per kWh for the householder, meaning that a domestic system plus storage would still come out ahead of coal-fired power delivered through the conventional grid,” explains iflscience.com.
Moreover, the reality is much closer than we might think as Musk is going to manufacture the batteries in the United States, at the “gigafactory” he is building just over the border from California in Nevada. And that while not staying and waiting for some totally new technology, but scaling up the tried and tested lithium-ion battery that he is already using for his electric vehicles.
The Powerwall system offering 10 kWh is targeted at domestic users. It is complemented by a commercial system termed the Powerpack offering 100 kWh storage, and a stack of 100 such units to form a 10 megawatt hour storage unit that can be used at the scale of small electricity grids. Whole communities could build micro-grid power supply systems around such a 10 MWh energy storage system, fed by renewable energy generation (wind power or rooftop solar power), at costs that just became super-competitive.
More than that, Musk declared that the entire electric power grid of the US could be replicated with just 160 million of these utility-scale energy storage units. And two billion of the utility-scale units could provide storage of 20 trillion kWh – electric power for the world.
Solar panels have repaid their fossil fuel debt
At the same time, another study says that thanks to the growing solar power capacity around the world, solar power has reached the break even point. The study from the Netherlands, published in Nature Communications, says that the power generated by solar photovoltaic panels over the last 40 years has offset the polluting energy used to produce them.
By the researchers’ calculations, for every doubling of global solar power capacity, the energy used to produce them fell by 12-13 percent and greenhouse gas emissions fell by 17-24 percent, depending on what material was used. Solar capacity has grown roughly 45 percent a year since 1975, reaching 230 gigawatts (GW) in 2015. By the end of 2016, there could be 300 GW installed.
“The researchers believe the break even point was likely hit about five years ago for both energy consumed and emissions meaning, at this point, global solar energy is having a net positive impact and will continue to increase that positive impact going forward. This feels like a major cause for celebration. If you’re a homeowner with solar panels, the researchers say that individual solar panels repay their fossil fuel debt several times over during their average 30-year lifespan,” wrote Megan Treacy for treehugger.com.
How will the house of 2025 look like?
The word of the future is smart. Even in the housing and design department. And as the technology is evolving at a huge rate, we wonder how it will look like in the future.
If the third industrial revolution was about using electronics and information technology to change economic systems and the way we live, the fourth will be characterized by disruptions stemming from a merger of the digital and physical worlds.
According to Yoshiaki Fujimori, President & CEO of the LIXIL Group Corporation for weforum.org, what we are seeing now with the emergence of the fourth industrial revolution is the development of cognitive architecture, which enables our living spaces to be tailored for personal and family preferences. This is set to have a profound effect on our quality of life.
“The home will become a natural, intuitive, extension of you. Rather than the occupant adapting to the home, we’ve entered an exciting new phase where the home works for those who live inside it. Development of AI, robotics and other advanced technologies for applications within the living space has been underway for some time, but are gaining increased attention,” said Yoshiaki.
Kevin Foreman, quoted by wired.com, believes that homes will soon become intelligent enough to distinguish between family members and guests within physical spaces and adapt to individual needs based on biometrics like fingerprints, body temperatures and even the rhythm of our own heartbeats. Therefore, in the very near future as you walk through your home, a small device worn around the wrist will authenticate your identity by pairing itself to your specific heartbeat, allowing your home to automatically adjust the lighting, room temperature and play custom music based on personalized preferences and pre-configured profiles.
Meanwhile, companies such as Nest are creating connected products that recognize homeowners’ preferences and adjust settings like temperature automatically or via an app.
In the same way that primary energy use in the home shifted from lighting to more complex devices and appliances, Internet traffic is following a similar pattern. Professor Klaus Schwab’s report on the Fourth Industrial Revolution predicts that the tipping point will be when over 50% of internet traffic delivered to homes is for appliances and devices as opposed to entertainment and communication, and that we can expect this tipping point to have occurred by 2025.
Here are some of the aspects that will make our lives easier:
Robots everywhere
According to the specialists, home appliances will become more self-aware, an example being the iRobot Roomba 780 which can be set to vacuum on a schedule, find its way around furniture, and even stay within a specific zone. In 15 years, devices for cleaning windows, sweeping the floor, and even making minor repairs will do their work inconspicuously. Yet, even the predictive technology in your home – using less energy during one week because the weather forecast says you will need more heat for an upcoming cold spell – has robotic intelligence.
Moreover, the journalists from http://www.plymouthherald.co.uk believe that in 15 years the companion robots will be available as part of team of collaborating robots. They will be able to monitor the wellbeing of their elderly charges, remind them to take their medicines, call relatives or cariers in an emergency, and perform simple tasks. Their owners will be able to give them shopping lists – by voice or by computer tablet – which the companions will convey via a “warden” robot who will pass it on to the outside robot, which will do the shopping. Your children might also benefit by having a “teacher” robot to help with the homework.
Solar photovoltaics on every roof
Over 15 per cent of houses in Australia already have rooftop solar installed, and forecasts show by the 2020s, solar and wind will be the cheapest way of producing electricity. Companies are already combining satellite imagery with algorithms to understand the savings you can make from your rooftop. And given the massive cost reductions of 99 per cent since 1970, and 80 per cent since 2008, it’s easy to foresee that solar photovoltaics will be ubiquitous by 2025.
Still according to plymouthherald, by 2030 the mantra will become “Energy, energy, energy”. Many new buildings will be carbon-neutral, meaning they will produce all of the energy they need without burning fossil fuels, and will even export electricity.
Merlin Hyman, chief executive of Regen SW, said: “For most of us our regular bill is the only time we think much about how we use energy in our homes. However, with the introduction of smart meters that is set to change. In the future we will be flexible to use energy when it is cheapest – for example charging electric cars overnight, or heating our water during the day. We may even export power back to the grid from batteries in the house if there is a surge of demand and a high price.”
Everyone will have to adapt to the future of energy – and that includes the suppliers. Nigel Turvey from Western Power Distribution predicts that the growth of renewable energy will really take off after 2025.
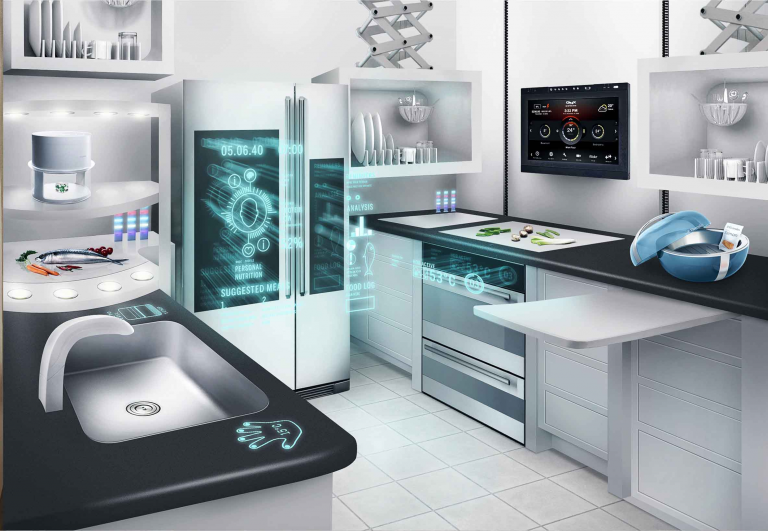
Smart appliances
In the house of tomorrow everything will be connected through technology and the new, smart appliances are a big part of it. The interaction with the user will be easy and smooth, they will increasingly be able to learn what you want and to have it on hand.

source: Emaze
The old-fashioned light switch will eventually disappear, and we will control lighting using smartphone or touchscreen panels – or even voice-activation. Smart thermostats like NEST and Hive allow you manage every minute of your home’s heating schedule from a smartphone, tablet or computer. So coming home from a holiday to a cold house will be a thing of the past.
The days of the chip-stop on the way home when you’re too tired to cook may be numbered too. Your fridge, connected to the Internet of Things, will not even need to ask you for a shopping list: it can tell when you’re running low, and place an order with the supermarket. This technology is actually here in some countries, not in the far-away future.
When it comes to novelties, ” June” is a smart oven, expected to ship this year. Its intelligent system can recognize the dish and know exactly how to cook it to perfection. June can be controlled with your iPhone or iPad, and you can monitor cooking with a live video stream.
Moreover, the appliances in one’s house will operate autonomously and interact with each other and even today one still has to load the washing machine, by 2030 one will just walk away, leaving the machine to decide how dirty the clothes are, and when to switch on to take advantage of the cheapest and most plentiful electricity.
Smart living & content
Virtual reality can turn couch potatoes into globetrotters. And they won’t even have to get up to hunt for a DVD: centralized streaming will give instant access to entertainment. The TV set will no longer dominate the living room: ultra-thin OLED displays will allow us to stick our TV screen to the wall, and holographics will bring characters right into the room.
The future home will be intelligent enough to predict what you want to do with content. Dell spokesperson Chad Andrews told TechRadar about a concept where media knows more about the playback device that we can even conceive today: adaptive music, movies, and photos that change shape and size (and color profiles) based on whether you are viewing them in the living room on an HDTV or on a tablet in your office. Data centers will predict the media you want to use and provide that media in the proper formats and sizes. Moreover, the number of screens in the future home will increase exponentially. To avoid overload, the visual information will integrate better into appliances, mirrors, and even the tools and household items you use. There might be flexible display on your cleaning detergent with instructions for use, or a display in the garage that reminds you about home maintenance.
Speech enabled
Whether you are a fan of Apple Siri or not, one thing is clear: speech tech has finally hit the mainstream. Your home will understand what you say. Already, Samsung and others are developing smart televisions that understand spoken commands. In the future, your home will respond to voice requests for the news, sports, and entertainment. More importantly, your home will use advanced algorithms that determine when you are speaking to the home or to your spouse – sensing a change in your tone, or interpreting a phrase that must be an instruction to change the house temperature. How about that level of smart?
Knowing you better that you know yourself
The future home will be smart enough to know what you want – sometimes even before you want it. Ford has already started experimenting with the Google prediction engine to guess where you want to go at certain times of the day. Your house will also know your preferences: when you start a movie, the lights will dim to the level you normally use. Moisture sensors in your lawn will learn how much you use a sprinkler system and adjust patterns accordingly.



