Porter’s Diamond Model analysis: Louis Vuitton and BMW
Learn about the business strategies used by Louis Vuitton and BMW from Porter’s Diamond Model analysis of these two successful and powerful organizations.
The Porter Diamond Model, also known as the Porter Diamond Theory of National Advantage is a business framework that describes a nation’s competitive advantage in the international market.
The model also highlights four factors that companies looking to expand their business internationally can take advantage of to achieve competitiveness in the market.
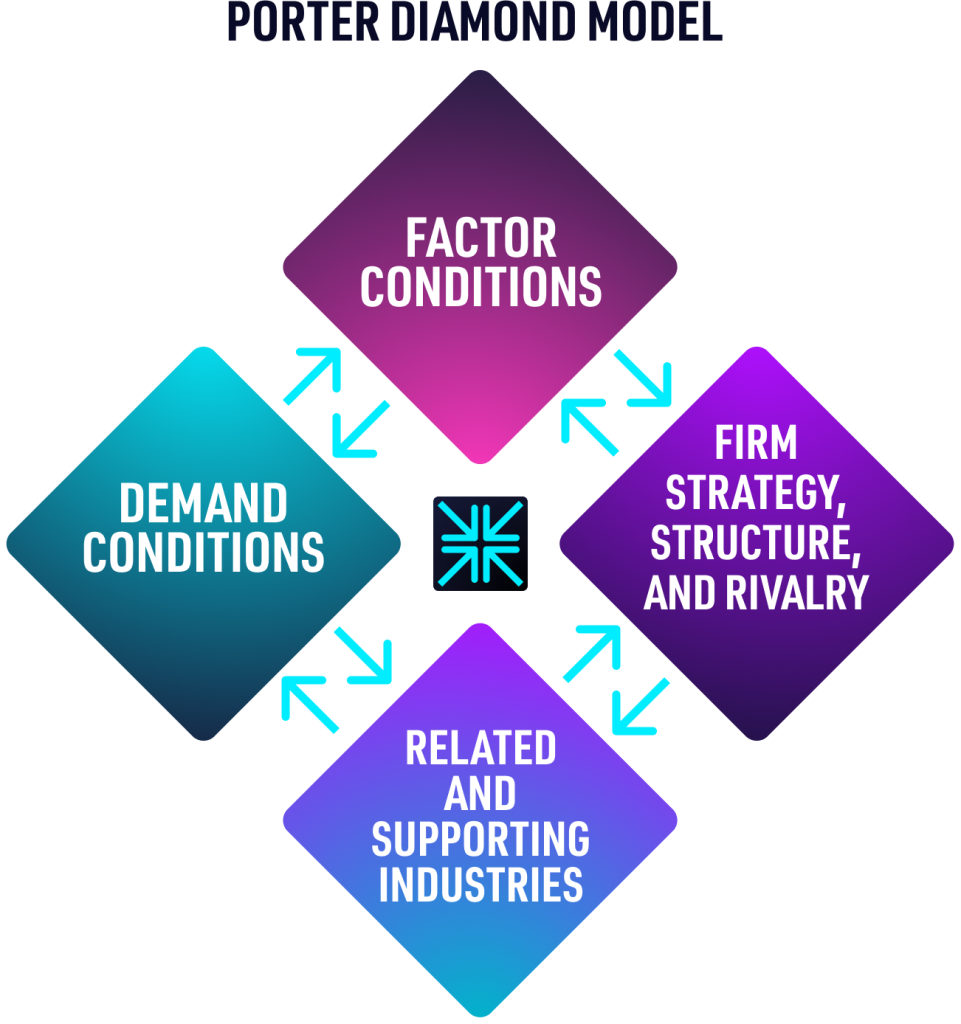
The Porter Diamond Model includes 4 attributes
The Porter Diamond Model analyzes a nation’s advantage against four broad attributes that each nation establishes and operates for its industries:
1.Factor Conditions
This attribute defines the nation’s position in factors of production, such as labour, land, natural resources, capital or infrastructure, necessary to compete in a given industry.
2. Demand Conditions
The second attribute of the Porter Diamond Model refers to the nature of home-market demand for the industry’s product or service.
3. Related and Supporting Industries
This attribute reveals the presence or absence in the nation of supplier industries and other related industries that are internationally competitive.
4. Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry
The Firm strategy, structure and rivalry attribute highlights the conditions in the nation governing how companies are created, organized, and managed, as well as the nature of the domestic competition.
For in-depth information on Porter’s Diamond Model, check out this article!
Theoretical knowledge is good but it’s only the starting point. Analyzing real-life examples is the best way to learn about a new business framework or model. It helps you put things in perspective.
For the purpose of this article, let’s look at two global brands and how the Porter Diamond Model is applied to them: Louis Vuitton and BMW.
Porter’s Diamond Model Analysis of Louis Vuitton

With a brand value of over $51 million in 2020, Louis Vuitton is the most valuable luxury brand in the world.
France is the company’s home base but since its inception more than 150 years ago, Louis Vuitton has expanded in 50 countries and has a retail network of over 4,910 stores worldwide.
What is the secret of Louis Vuitton’s success? Read Louis Vuitton: The story behind the brand.
Louis Vuitton: Factor and demand conditions
When you think of luxury, you think of France.
France is the world’s capital for luxury goods, haute-couture fashion, cosmetics, perfumes and accessories and the home for famous international houses such as Chanel, Dior, Givenchy, L’Oreal, Clarins, Lancome, Hermes, Celine, Louis Vuitton etc.
It’s not by chance that France has such a strong cluster of luxury brands.
The country’s luxury goods industry has a long history which began more than 500 years ago.
Eight hundred years ago, France was Europe’s silk centre with a booming silk industry.
King Louis XIV, the country’s most fashionable royalty recognized the importance of luxury goods to the national economy. Under his leadership, the country developed a powerful textile industry which in turn boosted trading and the country’s infrastructure.
Fast forward to the 21st century, France is synonymous with high fashion and luxury goods.
The fashion and luxury goods industry has a direct turnover of €150 billion. The share of French GDP generated by fashion is 2.7%. There are 1 million jobs in the fashion industry (source). The workforce in the industry is highly skilled. Experienced craftsmen or seamstresses sometimes receive an 18-month to 2-year training.
France was the perfect country for Louis Vuitton to be born in. The country provided the luxury brand with perfect factor conditions.
The French are known for their good taste and high fashion style so the brand had to work hard and innovate to meet the needs of such demanding customers (demand conditions).
This, in turn, helped them expand internationally and retain their competitive advantages.
With 37% of global sales, the Asian market is Louis Vuitton’s biggest revenue source.
Surveys show that 92% of Japanese women own a Louis Vuitton handbag and sales in China rose by more than 50% and in August last year when the brand reported record sales at its largest store in Shanghai.
Louis Vuitton: Related and Supporting Industries
The country also ranks high in the Related and Supporting Industries attribute for the luxury goods industry.
The industry’s development has been in close relationship with many subsectors such as textile and apparel, garments and embellishments, and sewing machinery. It’s an ecosystem whose members pressured each other to improve and innovate for mutual benefit.
Louis Vuitton: Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry
In France, the luxury goods industry is highly competitive.
With pressure from competitors, online sales increase and technology disruption, Louis Vuitton’s business strategy is to grow through acquisitions.
The brand is part of LVMH, the world’s largest conglomerate which came to be in 1987 when Louis Vuitton merged with champagne and cognac producer Moët Hennessy.
Over a period of 34 years, LVMH acquired more than 70 famous luxury brands. The latest acquisition is Tiffany & Co.
Porter’s Diamond Model Analysis of BMW
BMW: Factor and demand conditions
Germany played a major role in the history of the automotive industry.
It was Karl Benz, a German mechanical engineer who designed and, in 1885, built the world’s first practical automobile to be powered by an internal-combustion engine. Today, Germany is renowned for its powerful and innovative cars.
The largest industry sector in Germany is the automotive industry. Vehicles make up almost 17% of total exports.
The automobile industry generated roughly 426 billion euros in total sales in 2018.
With 882,000 manufacturing jobs in the automotive industry, Germany ranks first among European countries.
The country is a primary location for innovative car manufacturers and suppliers and is home to powerful brands such as BMW, Audi, Volkswagen, Mercedes etc.
One of the factors underlying German success is that the workforce is created. German students benefit from the country’s dual system of education where they combine vocational education with apprenticeships. This type of education supplies the country with a steady flow of highly skilled workers.
The German automotive industry benefits from a strong industrial core, first-class infrastructure, a highly-skilled workforce and cutting-edge research and development.
BMW has become a prestige global brand, operating 31 plants in 14 countries, including the largest car manufacturing plant in the world.
BMW has taken advantage of the factor conditions provided by the country. Ranked 2019’s 3rd most valuable car brand in the world, the company didn’t start as a car manufacturer, but as an aircraft engine manufacturer.
The brand’s success relies on its outstanding car design, technological innovation and workforce.
As the Porter Diamond Model recommends, the brand grows its own workforce. The BMW Manufacturer-Specific Advanced Training (MSAT) program provides students with extensive training on BMW vehicles thus preparing them to work for the company.
BMW: Related and Supporting Industries
BMW cars are high-quality automobiles.
The brand carefully selects suppliers in subsectors of the automotive industry such as parts and components, heating, ventilation, air conditioning, electronics etc. BMW depends upon a network of over 100 auto parts suppliers from all over the globe, though approximately 50% of its suppliers are either located in Germany or are subsidiaries of German-based companies (source).
BMW: Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry
BMW faces tough competition both domestically and internationally.
The company’s competitors are legacy brands much like itself.
On the local market, car automakers differentiate themselves through brand positioning.
In recent years, German car manufacturers have been struggling to adapt to new technological challenges (car connectivity, e-mobility), environmental challenges (green technology) and new entrants such as Tesla.
To stay ahead of the competition, BMW is using a competitive strategy which builds on market relevance, competitive services and research and development.
And it continues to make cars that consumers can emotionally relate to.
Attend the BUSINESS STRATEGY MASTERCLASS, on October 27 and learn future-proof business strategies for your organization from Costas Markides, Professor of Strategy & Entrepreneurship at London Business School.
Limited number of seats. Get your tickets today!

BUSINESS reSOURCES: Grow your business with Porter’s 5 Forces framework
On this page:
- What is Porter’s 5 Forces business framework?
- How to evaluate Porter’s 5 Forces (explained)
- 11 Benefits of applying Porter’s 5 Forces framework to grow your business
- 6 recommendations for a successful business strategy
What is Porter’s 5 Forces business framework?
Porter’s 5 forces is a holistic way of looking at any industry and understanding the structural underlining drivers of profitability and competition.
Porter’s 5 Forces framework is a valuable business tool that helps entrepreneurs shape their strategy to drive profitability.

Business strategist Michael E. Porter
The framework was created by Michael E. Porter, an economist, researcher, author and Harvard Business School professor. His expertise focuses on market competition and company strategy. His extensive research is widely recognized in governments, corporations, NGOs, and academic circles around the globe.
Strategy can be viewed as building defences against the competitive forces or as finding positions in the industry where the forces are weakest.
Michael E. Porter
How to evaluate Porter’s 5 Forces (explained)
1. Existing rivals
Evaluate the existing rivals by looking at the number of competitors. Are there many competitors? How do they rate in terms of size and power? Are they clearly differentiated or are their products almost identical?
What is the size of the competitors?
What is the industry growth rate: slow or fast?
Is product differentiation between competitors present?
What about exit barriers: are they high or low?
2. Buyers
The buyers are powerful and can influence the industry if they make purchases in large volumes.
Is the product undifferentiated? If that’s the case, the buyer will be price-sensitive and the digital environment allows the buyer to instantly compare prices and choose the cheapest.
Is there a large customer base? Do they have many alternatives to buy from? When the buyers are interested in high quality, they are not price-sensitive.
3. Suppliers
How much control does a supplier have over your business?
Does it influence your business by raising the cost of their products and lowering quality?
How many suppliers are in the industry? The fewer they are, the more powerful they are to control the industry and influence your profit margin.
Factors in determining supplier power: number of suppliers and concentration, switching costs, availability of substitutes, uniqueness of product, whether or not the industry is an important customer of the supplier and its availability to cut out the middle man.
4. Substitutes
Substitutes are alternative products that fulfil the same need by different means. In the airline industry, the substitutes are trains and cars.
Rule of thumb: don’t limit your analysis to your industry. Expand your approach to products that meet the same need but are in different industries.
How many alternatives to your product are on the market?
How can you rate the buyers’ willingness to switch and choose a substitute instead of your product?
What is the price-performance ratio of the substitutes?
5. New rivals
Is the entry barrier low or high?
If the entry barrier is low, which means requirements to enter the industry are affordable or readily accessible, then there are increasing chances of new entrants in great numbers. In this case, the threat is high.
There are six major sources of barriers to entry: economies of scale, product differentiation, capital requirements, cost disadvantages independent of size, access to distribution channels and government policy.
In a future envisioned by Elon Musk, people will fly from New York to Shanghai in a rocket, not an airplane and it will take only 10 minutes instead of 24 hours. The downside of this type of futuristic fast-travel may prove to have a high price.
A different way of fast and affordable transportation shines brightly in the near future: the hyperloop. Read about the hyperloop.
11 Benefits of applying Porter’s 5 Forces Business Framework
If you have a great idea, the next step is not product development, logo design, or assembling the best team.
If you’re contemplating starting a business, the first thing you should do is industry analysis and look at the competitor environment before anything else.
And that’s why Porter’s 5 Forces framework is of paramount importance to any entrepreneur: it helps to design a successful business strategy that will support the business to achieve its goals.
11 benefits of applying Porter’s 5 Forces Business Framework
- Evaluate the roots of long-term profitability in your industry.
- Discover the trends that are most likely to be significant in changing the game in the industry.
- Where are the constraints which if you can relax, it might allow you to find a really strong competitive position?
- Avoid getting trapped or tricked by the latest trend or technological sensation.
- Focus on the underlying fundamentals.
- Analyze your competition and how it is affecting the profit.
- Learn how to approach competition in your industry.
- Identify the structure of the industry.
- Find answers to the question How is the industry changing?
- Get the tools to understand industry dynamics.
- Position your business to find that spot in the industry where you can have a really good profit.
6 Recommendations for a successful business strategy
The goal of Porter’s business framework is not to find the weaknesses of your competitors in order to drive them out of the market.
As Michael Porter says, it’s not a zero-sum game. By applying this framework, you get valuable insights which in turn can help you identify a specific and unique way in which to delight your customers.
Your business can delight your customers in one way, the competitors can delight their customers in another way.
It’s a better strategy rather than engaging in price wars which is not a long-term strategy.
When creating your strategy based on insights gained by applying Porter’s 5 Forces framework, take into account the following recommendations:
- Choose a supplier group to buy from that exercises less power over your business;
- Perform buyer selection i.e. choose a buyer group to sell to that leverages a low power over your business;
- Your business can sell to powerful buyers if it partners with a low-cost supplier or the product is unique;
- When creating your strategy, factor in the substitutes that are subject to trends improving their price-performance tradeoff with the industry’s product;
- Devise a solution to not merely survive the forces, but change them;
- Keep a close eye on industry evolution.
The key to growth—even survival—is to stake out a position that is less vulnerable to attack from head-to-head opponents, whether established or new, and less vulnerable to erosion from the direction of buyers, suppliers, and substitute goods. Establishing such a position can take many forms—solidifying relationships with favourable customers, differentiating the product either substantively or psychologically through marketing, integrating forward or backwards, establishing technological leadership.
Michael E Porter
Conclusion
Porter’s 5 Forces Framework is a very robust framework, easily applicable to all industries, allowing entrepreneurs to position the business so as to be least vulnerable to the industry’s competitive forces.
Join the Conversation
We’d love to hear what you have to say.
Get in touch with us on our LinkedIn Page, Facebook Page, Twitter or TikTok.
Source: How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy by Michael E. Porter
Blue Ocean Strategy: How to differentiate from the competition
On this page:
- Definition of Blue Ocean Strategy – What is Blue Ocean Strategy? Who created Blue Ocean Strategy?
- Differences between Red Ocean Strategy and Blue Ocean Strategy in business and leadership
- 3 brands that have differentiated from the competition, generated new demand and found a new market
- How to create a blue ocean for your company through value innovation
What is Blue Ocean Strategy?
Every entrepreneur wishes their company was the only one in the market. No competitors, having all the customers to themselves. King of the castle ruling unchallenged over the country.
While for most entrepreneurs this dream is only wishful thinking, for some it’s reality.
These entrepreneurs (and we will talk about three of them later) have led their companies to great success by applying Blue Ocean Strategy.
Blue ocean strategy is the simultaneous pursuit of differentiation and low cost to open up a new market space and create new demand. It is about creating and capturing uncontested market space, thereby making the competition irrelevant. It is based on the view that market boundaries and industry structure are not a given and can be reconstructed by the actions and beliefs of industry players.
Who created the Blue Ocean Strategy?
Blue Ocean Strategy was created by management thinkers Chan Kim and Renée Mauborgne.

Chan Kim and Renée Mauborgne (image source: blueoceanstrategy.com)
Both Chan and Renée are Professors of Strategy at INSEAD, one of the world’s top business schools, and co-directors of the INSEAD Blue Ocean Strategy Institute in France.
In 2005, Chan Kim and Renée Mauborgne co-authored Blue Ocean Strategy. The book shows the results of a study of 150 strategic moves spanning more than 100 years across 30 industries. The authors’ conclusion is that lasting success comes not from battling competitors but from creating blue oceans – untapped new market spaces ripe for growth.

Since its first edition, Blue Ocean Strategy has been revised and expanded in 2015 and has become a bestseller with over 4 million copies sold in 46 languages.
The book is recognized as one of the most iconic and impactful strategy books ever written and is the recipient of numerous distinguished awards. Both authors received widespread recognition for their work in the form of various awards and distinctions.
Apart from their careers in academia, Chan and Renée have been employed in an advisory capacity by prestigious organizations. Kim is an advisory member for the European Union and serves as an advisor to several countries and Renée served on President Barack Obama’s Board of Advisors on Historically Black Colleges and Universities (HBCUs) for the president’s two terms.
In 2019, Thinkers50 named Chan Kim and Renée Mauborgne the #1 Business Thinkers in the World.

How to grow your business with 1 strategy framework
Differences between Red Ocean Strategy and Blue Ocean in business and leadership
In Blue Ocean Strategy, red ocean is a metaphor for the known market space encompassing all the industries in existence today. Remember the documentaries that showed the audience what happens when a large number of sharks feed at the same time, in the same place? It’s called a shark feeding frenzy event and it turns the ocean water red with the blood of the fish the sharks are feeding on.
Blue ocean is the metaphor for the unknown market space and all the industries that are not in existence today. It’s the unchartered land that courageous explorers venture in to discover unimaginable riches and opportunities.
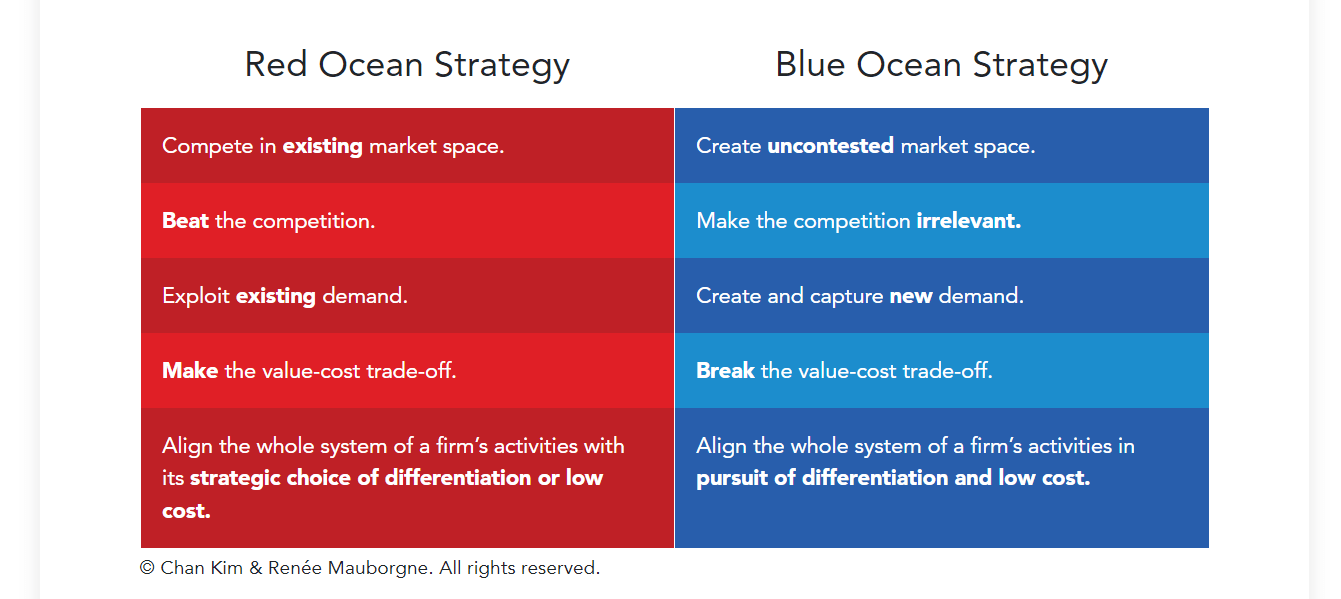
- Red ocean strategy is about competition
- Blue ocean strategy is about creating new demand
- Red ocean strategy is a market-competing strategy where profit and growth decline while competition increases
- Blue ocean strategy is taking the opportunity to grow rapidly and profitably
- Red ocean strategy competes over customers
- Blue ocean strategy turn non-customers into customers
- Conventional leadership focuses on the cognitive and behavioural skills of leaders
- Blue ocean leadership focuses on actions and activities tied to market realities
- Conventional leadership has resulted in 87% global average in employee disengagement
- Blue ocean leadership’s goal is to unlock unrealized talent and energy in the organization fast and at low cost
3 Brands that have differentiated from the competition, generated new demand and found a new market
Cirque du Soleil

image source: Cirque du Soleil@Facebook
Founded in 1984 in Canada, Cirque du Soleil is an entertainment company and the largest contemporary circus producer in the world.
There’s circus in the company name but the performances are not your usual live animal children focused shows.
By taking out live animal acts from their performances and focusing on creating storyline-based shows with live music and amazing acrobats, Cirque du Soleil has created a new market space and new demand: circus entertainment for adults.
More than 180 million spectators have seen a Cirque du Soleil production since 1984 worldwide. The company generates annual revenue of approximately $1 billion and its creations have received numerous prizes and distinctions, including seven Primetime Emmy Awards and a star on the Hollywood Walk of Fame.
Uber & Airbnb
Both Uber and Airbnb are great examples of the blue ocean strategy.

Airbnb launched in 2008, Uber – one year later.
Although operating in the hospitality industry, Airbnb doesn’t own any property, it manages an online travel platform. By allowing homeowners to monetize their spaces and travellers to book them instead of hotels, Airbnb has found a new market, a big one.
The numbers speak for themselves: 7+ million listings worldwide, 2+ million people staying on Airbnb per night on average, 750+ million all-time Airbnb guest arrivals. In Q1 of 2019, Airbnb registered $9.4 billion in the total booking value.

Although Uber is operating in the people moving industry, it is not a taxi company, but a ridesharing service.
The latest stats say there are 21 million trips a day taken by 111 million monthly active platform consumers located in over 900 cities across 69 countries. In 2019, the company registered $65 billion in gross bookings across all platforms.
How to create a blue ocean for your company through value innovation
Value innovation is one of Blue Ocean Strategy’s tools and is defined as the simultaneous pursuit of differentiation and low cost, creating a leap in value for both buyers and the company.

10 questions to increase employee retention
The concept of Value Innovation is the cornerstone of the market-creating strategy.
Because value to buyers comes from the offering’s utility minus its price, and because value to the company is generated from the offering’s price minus its cost, value innovation is achieved only when the whole system of utility, price, and cost is aligned.
Chan Kim and Renee Mauborgne
But how does one achieve value innovation?
To achieve value innovation, the company looks at two factors: cost savings and buyer value.
The company makes cost savings by eliminating and reducing the factors an industry competes on and lifts buyer value by raising and creating elements the industry has never offered.
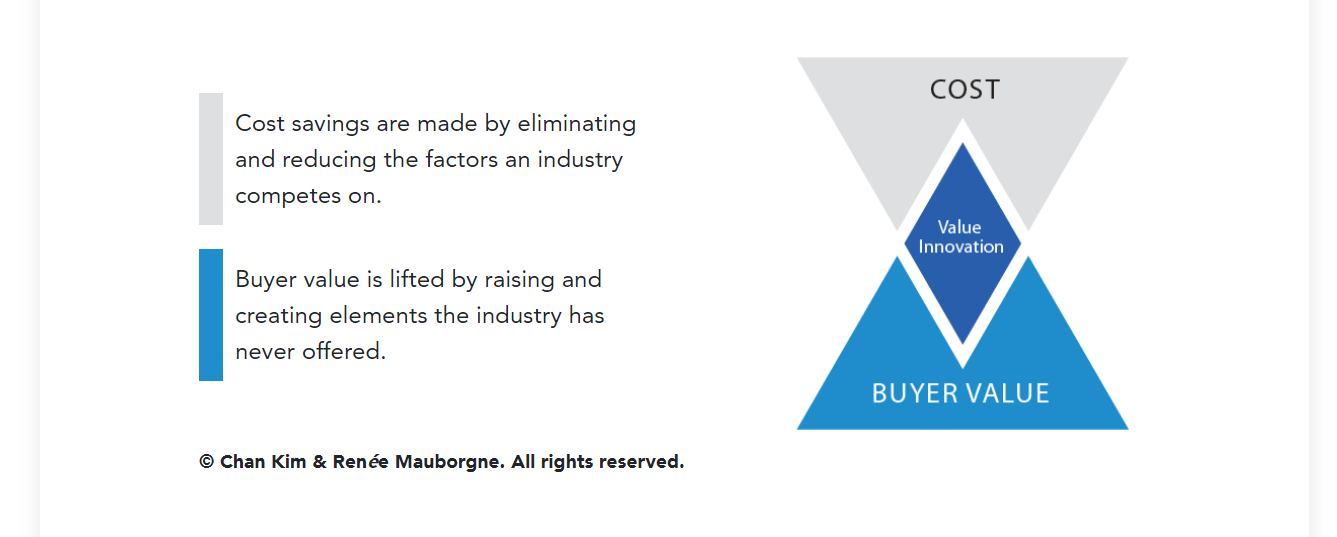
Many businesspeople believe that lowering costs and increasing value is a trade-off. It’s either creating greater value for customers at a higher cost or creating reasonable value at a lower cost. Blue Ocean Strategy allows companies to pursue differentiation and low cost simultaneously.
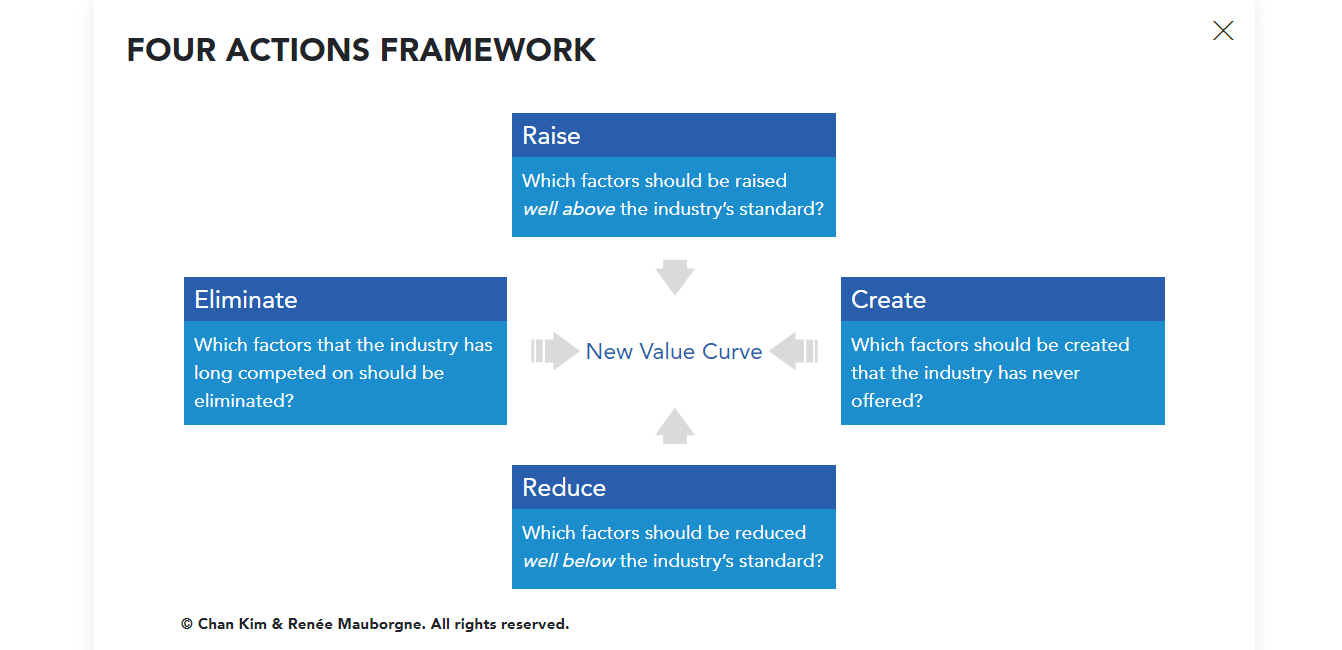
A great starting point for achieving value innovation is to answer the following questions devised by Chan Kim and Renee Mauborgne in the Four Actions Framework:
- Which of the factors that the industry takes for granted should be eliminated?
- Which factors should be reduced well below the industry’s standard?
- What factors should be raised well above the industry’s standard?
- What factors should be created that the industry has never offered?
In conclusion, to find your blue ocean, namely to tap into a new market, you need to perform an innovative leap in customer value at lower costs thus making the competition irrelevant.
Join the Conversation
We’d love to hear what you have to say.
Get in touch with us on our LinkedIn Group, Facebook Group or Twitter.
10 Less Known Facebook Features That Help Marketers
The most loved and used social media platform is changing so fast that is hard to keep track of all of its novelties. Social media specialists are spending more and more time online reading and trying all about the new changes in order to bring them and explain them to their clients and followers.
This is the main reason we decided to focus today on Facebook and show you some of the most important features you, as a marketer, shouldn’t forget to focus on when it comes to your business Facebook page. Especially because they tend to be forgotten, while they have an important role of their own. In no particular order, here they are:
- The download your Facebook history for business analytics option. You will have your entire Facebook history at your disposal, finding: review all the posts, photos, and videos you’ve shared; your messages and chat conversations; past info from the About section of your profile; ads you’ve clicked on; historical data, facial recognition data,etc.
-
- Travel agencies and tourism boards could let people explore certain places in VR before buying their tickets.
- Real estate companies could let potential buyers look at houses in VR before actually visiting the houses.
- Furniture companies could let customers “try out” furniture in their homes before purchasing.
- Clothes retailers could let customers “try out” clothes and chat with friends about them before buying, or even let them customize their avatars with their clothes.
- Education institutions and online learning platforms could let students attend classes together.
- What do I want to achieve with the marketing research?
- Do I need help with it? / Do we need to hire a research company?
- How can I reach my target?
- What other organizations have asked and answered comparable question to ones I have?
- What experts have insights into the questions we want to answer?
- Are there industry associations with ideas on answers or research methods to make us smarter?
- Are there other organization’s surveying our audience that might allow us to include some questions?
- Could I propose a joint research project with another organization to satisfy our mutual needs?
- Are there university programs where students can conduct research for us?
- Is the target market winning anything out of my business?
- Is the target market easy to be managed or how hard is it to be managed?
- Whom is my main competition?
- Primary research focuses on gathering data from analyzing current sales and the effectiveness of current practices. It also takes competitors’ plans into account, giving you information about your competition. The pieces of information will be received following: interviews (qualitative and quantitative), surveys, questionnaires (online or by mail), focus groups.
Facebook Spaces is a virtual reality (VR) app developed by Facebook that lets you invite and interact with up to 3 of your Facebook friends using a VR device. Right now, you can download Facebook Spaces for Oculus Rift or HTC Vive . Once you open Facebook Spaces in VR, you’ll be asked to take off your headset and log into your Facebook account.
For brands’ representatives this feature can be easily used, as Buffer Social says:
3. Free Images for Ads
When you create a Facebook ad, you can choose from a searchable database of thousands of free stock images from within the Facebook image library.
4. Prioritize Who to See First
Changing your news feed preferences gives you control over what appears in your news feed. To choose which posts you want to see first in your news feed, click the arrow in the upper-right corner of the page and choose News Feed Preferences from the drop-down menu. Then click Prioritize Who to See First. This feature allows you to select from both personal profiles and business pages that you’re following so their updates get visibility in your news feed. You can also choose to unfollow people so you stop seeing their updates without unfriending them. If you find that your news feed is too full of updates from groups, you can also mute them by unfollowing updates from them.
5. The Camera Effects Platform
This feature allows you to use trackers, data, animation and more to create interactive, shareable effects that respond to people and objects in their surroundings. Through the platform developers can create frames, masks, and special effects for the Facebook camera. The two main products on this platform are Frame Studio and AR Studio.
It’s the place where people can browse and find Messenger bots, nearby places and businesses to message. Organized by category, recent activity and featured experiences, Discover complements existing entry points, including advertising to Messenger Codes, me.me links and plugins. The Discover tab can be located in the lower right-hand corner of the Messenger home screen and will enable users to browse recently visited businesses, featured experiences as well as bots and Pages. The bots are categorized and listed under various categories for easier access.
Facebook has also added chat extensions to the Messenger app that allow multiple people to chat with the same business at the same time. This allows users to directly add a bot to a group thread and share the conversation with other users in the group. Moreover, The Discover tab works with new parametric Messenger Codes, where people can scan such codes through the Messenger camera and link to a specific brand or business.
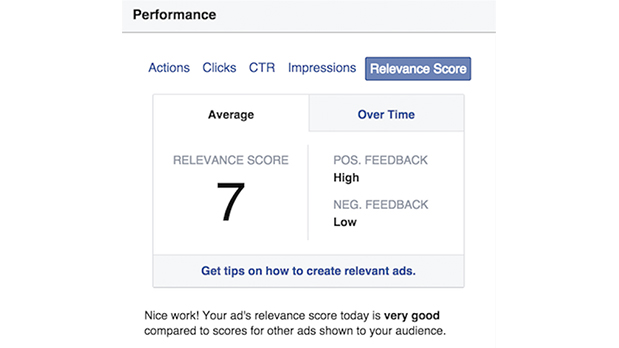
7. Relevance Score
Relevance Score metric is a measure of your Facebook ad’s effectiveness and the equivalent of Google’s AdWords Quality Score, in their ad reporting dashboard. This new score is an important ad quality signal that will affect both your ad delivery and the cost you pay for your Facebook campaigns. Facebook will use feedback from ad viewers to determine this score on a scale of 1 to 10, with 10 being the highest possible score.
According to Facebook’s statements, the new feature can lower the cost of reaching people (the higher an ad’s relevance score is, the less it will cost to be delivered). Moreover, bid matters too. “For instance, if two ads are aimed at the same audience, there’s no guarantee that the ad with an excellent relevance score and low bid will beat the ad with a good relevance score and high bid. But, overall, having strong relevance scores will help advertisers see more efficient delivery through our system. It can help advertisers test ad creative options before running a campaign. Advertisers can test different combinations of image and copy with different audiences, and learn which combinations offer the highest relevance scores”.
At the same time, the feature promises to help optimize campaigns already in progress. While ad campaigns are running, advertisers can monitor their relevance scores.
8. Smart Replies for Pages
Facebook intends to help small businesses automate some of the customer support processes. Using AI, Smart Replies helps Page owners to respond to the most frequently asked questions that they receive, such as business hours, directions, and contact details. “The AI would grab information from the Pages, detect the questions asked, and reply with the appropriate information. It can help free up some of your time for you to create high-quality content and engage with your audience on social media. As the AI would grab information from your Page, it’ll be great to keep your Page information updated,” wrote Social Buffer.
9. Competition monitor
On Facebook Insights the Posts’ area, you will find “Top Posts from Pages You Watch”. There you can track other pages, from partners, competitors to friends. You can take a look at the metrics and spot the likes, posts and engagement on these pages. Moreover, Facebook will suggest you some pages to follow. You can also type in the names of brands you want to check out and add them to the list.
10. The Auto-optimization Rules
You can set up four different consequences if the conditions have been met: turn off the ad campaign, ad set or ad; send notifications to the ad manager; adjust budgets and manual bids. In order to set up an automated rule set, select a campaign, ad set or Facebook ad and go to the editing panel (Icon on the right side of the reporting table). Next, click on the “Create Rule” button to create a new rule set. You can create rules by selecting some conditions and telling Facebook what to do once the conditions are met.
Main questions before planning a marketing research
A marketing research done right needs planning and the important and right questions asked on time.Therefore, we decided to show you some of the questions we believed you should make sure you ask yourself,your department and your business,prior to starting a marketing research.
Marketing research done right
Either you start a new business, launch a new project / product / service or you just want to stay ahead of your competition, a strong and smart marketing research will give you the necessary advantage over the competition. Moreover, in this ever-changing and moving market, with the technology changing it day by day and with consumers always up-to- date and in control of the situation, research becomes more and more important daily. Therefore, market research is a key component of any good product team management process, sales and marketing strategy, or business growth strategy.
“Marketing research can give a business a picture of what kinds of new products and services may bring a profit. For products and services already available, marketing research can tell companies whether they are meeting their customers’ needs and expectations. By researching the answers to specific questions, small-business owners can learn whether they need to change their package design or tweak their delivery methods–and even whether they should consider offering additional services,” writes entrepreneur.com.
Research deserves its important place in a business activity and should be treated accordingly. We are presenting you some of the steps you must take in order to make sure your research is done right.

source: AdWeek
2. Secondary research. Analyzing the data that has already been published. and that can help you identify competitors, establish benchmarks and identify target segments. Your segments are the people who fall into your targeted demographic–people who live a certain lifestyle, exhibit particular behavioral patterns or fall into a predetermined age group.
3. Study the Economy: Just like the history is important in knowing and understanding who we are as a culture and what we will be in the future, showing what we can expect, so is knowing and understanding the economy helping your business grow. You can better understand reports about some of the most important big factors affecting the industry you’re in and the customers you hope will spend their money on your products or services.
Being up-to-date with the economics world will help you know how to adjust your business, prevent difficult situations and choose the right time to expand.
4. Read Business and Industry Publications: Whatever your industry, there’s likely a trade group or research firm out there compiling industry statistics and trends that are all insights into your business. Join your industry trade group or follow key industry thought their leaders on social media and media (their TV, print, online appearances). Being part of the industry and its insights will help you find out detailed industry statistics and trends that can help you better understand the past, present and future of companies like yours.
5. Look Elsewhere: Take example from successful local and international businesses. A similar business on the opposite end of the country may give you some great promotional ideas, or an international market could start complaining about rising commodity prices before they affect you directly.
6. Hire a smart internal researcher and a good research agency. Your researcher will be able to present you monthly reports regarding the market and your consumers, while the agency will be a key element when making an important move on the market. They will for sure make the difference.
More ideas and steps you can find here.
The best media mix for your brand in 2017
The media market is changing under our eyes, each year bringing something new. It’s more than obvious that, even if you are representing a smaller brand, it’s not enough to rely on a website or social media page alone if you want to be competitive in the marketplace. Moreover, the media channels that used to work very good for you two or three years ago may very well not be the best ones to use anymore.
According to Initiative and their report Media Fact Book 2016, in Romania the TV continued to be in 2015 the rising engine of the media market, having a push of volumes of 7 percent compared to 2014 and reaching the EUR 212 million margin. Other channels that grew were the online (a boost of 12 percent and reaching EUR 57 million) and the radio (a 5 percent boost, until EUR 19 million). The OOH remained stable at EUR 28 million. Moreover, Initiative estimated that the media market would reach in 2016 EUR 351 million this year, following a 6 percent growth. The evolution on each channel is similar to the one in 2015 – the TV market will grow with 6 percent, the online with 12, the radio with 5, while the OOH will remain the same and the print would continue to drop still with 10 percent. In this context, the approaching of the digital next to the TV in the consumers’ preferences are, the amplitude that the mobile took, the influence of the multi-screening or the forever bigger importance of the content’s quality has over the rise of the media budgets.

source: Linkedin
With a well-chosen media mix, you can build the kind of name recognition and buzz for your company that isn’t possible with single-pronged approach. A mixture of owned, paid and earned media will help ensure your marketing efforts are reaching your target audience.
Consumers want brands that are useful and accessible, and most of all, entertaining. Marketers will continue to pull out all the stops to counter declining ad receptivity. In 2017, we’ll see more branded content and less regular advertising. Get ready for more native content, short and long form video, branded filters, and emoji and PR stunts. But it won’t end here. The specialists forsee that the marketers will forge ahead with new technologies such as 360 video, augmented reality, virtual reality and artificial intelligence (chatbots performing customer service and sales functions), making the landscape ripe for new creativity. Marketers will also closely monitor effectiveness as studies start to show which formats consumers find annoying and intrusive, particularly on mobile.
These advancements create new challenges for marketers. Far from a controlled consumer view of a brand (TV, outdoor, instore), marketers will face multiplatform, multi-device, in and out of walled gardens, all differently experienced by every consumer. Geotargeting will be seen as a commercial opportunity and Snapchat itself is using geofilters to let people know where to find a Snapbot vending booth. Brands will move quickly into customized/personalized creative content, delivered in a targeted way via programmatic buying. We will see more sequential content as marketers consider using retargeting for a more strategic and persuasive catenation of consumer messages.
In a media landscape of ongoing dramatic change, advertisers will more aggressively adopt multiple media alternatives to reach and connect with their audiences throughout 2017. Synergies will become more important than any single channel and the collective weight of all channels put together. Marketers will be focused on understanding the role each media plays within a broader plan and how they rub off to produce synergistic effects. The concept of synergies has been around for some time but what has changed is the planning aspect and the application of a discipline to the selection of channels to maximize its impact. Cross media studies conducted by Kantar Millward Brown show that globally 25% of media effectiveness has been attributed to synergies, and nearly 40% in APAC. These numbers are not only growing but increasingly we are seeing non-TV synergies emerging as advertisers and agencies start to get their heads around this. The two broad parameters needed to leverage synergies are – creative synchronization and media duplication and phasing.

source: Digital Land
„A “big idea” is important for creative synchronization to occur, but it’s also about adapting the message to the medium and following a common theme across a campaign. For example, it’s unlikely that a 30 second TV ad will work as well on YouTube or Facebook because these media have different characteristics. But they offer opportunities for forming different kinds of relationships that meet consumer needs at different times and occasions. Optimising media duplication and phasing can go a long way in driving synergies but as a first step, marketers will need to ensure that every medium has a role to play within the broader media mix. Roles will be in terms of driving ‘reach and or frequency’ or various aspects of how people think, feel and make decisions about the brand,” said Straford Rodrigues, Media & Digital Director, APAC at Kantar Millward Brown.
Therefore, every brand needs to create its media plan accordingly to its target, expectations and business plan. The strategy is more important than ever: setting clear objectives, finding the right opportunities, integrating your message and your true content, exploring, creating, producing and measuring.
Apart from the media planning itself, don’t forget the fact that the content is the KING and it needs to be as powerful, sincere and creative as possible.