The global exoskeleton market projected to grow to $4.2billion by 2027
According to the latest report, the global exoskeleton market is projected to grow to $4.2billion by 2027 at a CAGR of 26.3%.
- What is an exoskeleton?
- Benefits and types of exoskeletons;
- The exoskeleton market: an overview;
- Key factors driving the growth of the exoskeleton market;
- Key restraining factors of the exoskeleton market.
What is an exoskeleton?
According to exoskeletonreport.com, exoskeletons are wearable devices that work in tandem with the user.
They are placed on the user’s body and act as amplifiers that augment, reinforce or restore human performance.
Exoskeletons can be made out of metal, carbon fibre or soft and elastic parts.
They can be powered and equipped with sensors, they can be mobile or fixed/suspended, and they can cover the entire body, or just a specific body segment.
Exoskeletons are biomechatronic devices or wearable robots.
Building an exoskeleton requires the combination of many specialities like mechanics, electronics, robotics, biology, engineering, information technology etc.
Exoskeletons can also be referred to as robotic suit, powered armour, exo-frame or exosuit, wearable machine, power jacket, etc.
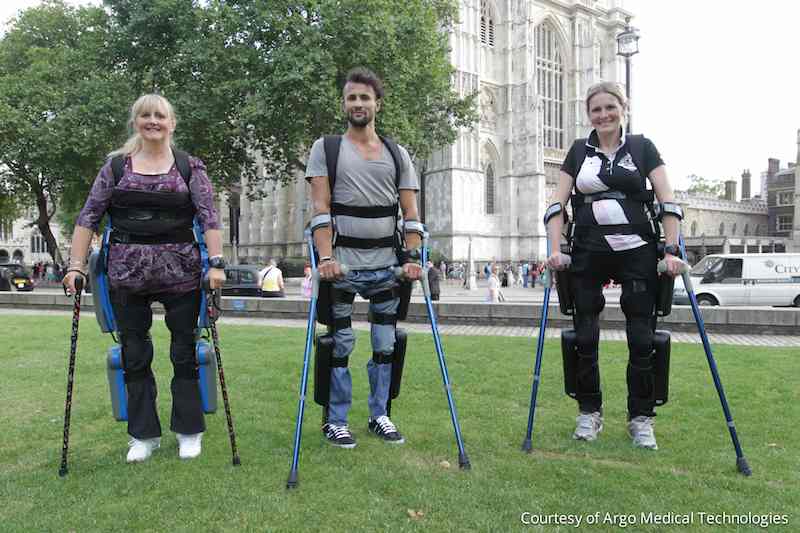
Robotic exoskeletons developed by ReWalk (source: goodnewsnetwork.org)
Benefits and types of exoskeletons
The benefits of exoskeletons are numerous.
In industrial applications, exoskeletons improve the productivity and safety of workers.
In healthcare, nurses wear exoskeleton vests to fulfil the special requirements of patient care. They are at high risk of work-related musculoskeletal disorders mainly caused by overexertion from lifting and moving patients (i.e., patient handling).
Military personnel wear exoskeletons to move heavy supplies and equipment.
Based on the technology drive used, there are 7 types of exoskeletons:
Pneumatic Actuator, Hydraulic, Electric Servo, Electric Actuator, Fully Mechanical, Shape Memory Alloy Actuator and Fuel Cell.
Here are three examples of the latest commercial robotic exoskeletons:
The WIITE is a powered lower-body exoskeleton designed for a person with a complete spinal cord injury. The exoskeleton allows the person to stand up, walk, and ski tour.
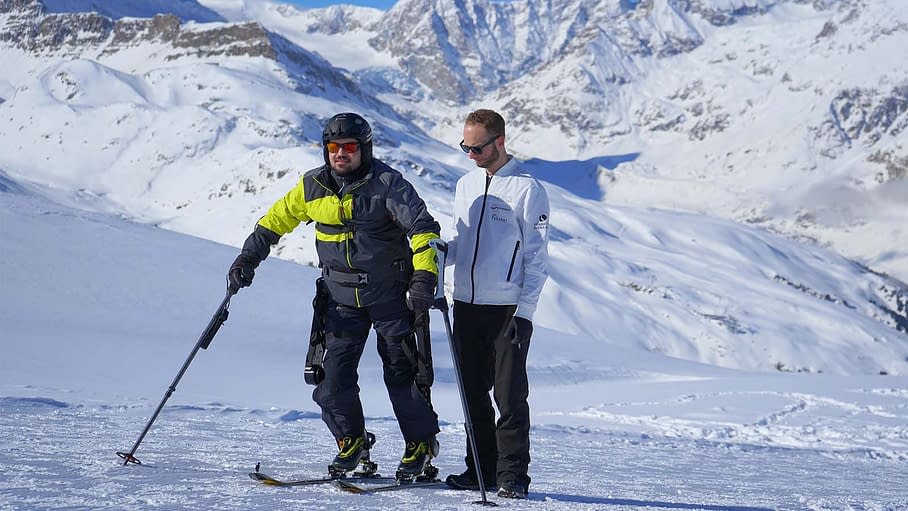

WIITE, the Powered Exoskeleton For Ski Touring by TWIICE (source: exoskeletonreport.com)
Vex is a wearable robot vest created by Hyundai Motor Group. The exoskeleton provides neck, back and shoulder muscles support to workers.
Sarcos Guardian is a full-body battery-powered exoskeleton. The exoskeleton augments operator strength and boosts productivity while dramatically reducing injuries.
The exoskeleton market: an overview
The global exoskeleton market size is anticipated to reach $4.2 billion by 2027.
North America dominated the market with a value of $297.8 million in 2019 owing to the availability of favourable reimbursement policies and increasing investments in robotics.
The fastest-growing market is in the Asia Pacific. The countries in this region, such as China, India, and South Korea, are among the most technologically developing countries across the globe.
Mobile exoskeletons accounted for a major share of 61.8% in 2019 owing to the introduction of innovative mobile systems for various industrial applications.
Due to the increased costs of the mobile exoskeletons, patients switch to stationary exoskeletons; this makes stationary exoskeletons the fastest-growing segment in the market.
In 2019, electric actuators dominated the global exoskeleton market with a share of 32.1% in terms of revenue, as they are cost-effective in comparison with the other drive types. Electric actuators are mechanical devices used to convert electricity into kinetic energy.
Usage of fuel cell-powered exoskeleton is increasing in military applications as they provide longer operation hours.
The industrial application is expected to hold the highest share in the market.
The powered segment of exoskeletons is expected to grow significantly over the forecast period.

Honda walking assist device (source: thenewstack.io)
Key factors driving the exoskeleton market
![]() Growing adoption of exoskeletons in healthcare;
Growing adoption of exoskeletons in healthcare;
![]() Growing adoption of exoskeletons in non-healthcare settings (industrial, commercial, military);
Growing adoption of exoskeletons in non-healthcare settings (industrial, commercial, military);
![]() Reimbursement coverage;
Reimbursement coverage;
![]() Increasing prevalence of spinal cord injuries (SCIs);
Increasing prevalence of spinal cord injuries (SCIs);
![]() Development in robotics;
Development in robotics;
![]() Introduction of innovative mobile exoskeleton by manufacturers for the ageing and disabled population;
Introduction of innovative mobile exoskeleton by manufacturers for the ageing and disabled population;
![]() Presence of a wide variety of commercialized electric actuators;
Presence of a wide variety of commercialized electric actuators;
![]() Compact in size, light in weight, and its flexibility to operate in the home as well;
Compact in size, light in weight, and its flexibility to operate in the home as well;
![]() Increase in geriatric population;
Increase in geriatric population;
![]() Increasing prevalence of stroke.
Increasing prevalence of stroke.
Key restraining factors of the exoskeleton market
![]() Massive investments required at the initial stage to procure exoskeletons.
Massive investments required at the initial stage to procure exoskeletons.
![]() Associated costs (installation, integration of solutions, training fees, after-sales services, maintenance costs).
Associated costs (installation, integration of solutions, training fees, after-sales services, maintenance costs).
![]() Many insurance providers don’t provide cover for robotics-based therapies.
Many insurance providers don’t provide cover for robotics-based therapies.
Source: GrandViewResearch
Join the Conversation
We’d love to hear what you have to say.
Get in touch with us on our LinkedIn Page, Facebook Page, Twitter or TikTok.

