Top 10 smart cities in the world
What is a “smart city”? A “smart city” is an urban setting that applies technology to enhance the benefits and diminish the shortcomings of urbanisation for its citizens.
Here are the Top 10 smart cities in the world according to Smart City Observatory, an organization which produces the annual globally recognized Smart City Index report.
- SINGAPORE
- ZURICH
- OSLO
- TAIPEI CITY
- LAUSANNE
- HELSINKI
- COPENHAGEN
- GENEVA
- AUCKLAND
- BILBAO
Let’s see how each city is working toward sustainability!
As the world’s top smart city, SINGAPORE supports decarbonisation

- Set to achieve net-zero emissions
To achieve the new net-zero ambition, Singapore will raise the current carbon tax of S$5 per tonne to S$25 per tonne in 2024-2025, and S$45 per tonne in 2026-2027, with a view to reaching S$50 to S$80 per tonne by 2030 (source).
- Developing a services ecosystem to support decarbonisation
The Republic is scaling up its efforts to develop an international carbon trading marketplace and a services ecosystem to support decarbonisation.
The carbon exchange will be a digital platform for buyers and suppliers to trade large volumes of credits. It will cater primarily to large-scale buyers, including multinational corporations and institutional investors, and will provide the market with price transparency (source).
- Sustainability: squeezing value from waste
Around $220 million is being pumped into national research initiatives focusing on sustainability, in areas such as water technologies and projects that can squeeze value from waste.
Almost one-third, or $80 million, will go to research projects that look at how resources can be recovered from Singapore’s key waste streams – plastics, electronic waste and food (source).
ZURICH was voted the most pedestrian-friendly city

- Smart building management systems
Since 2015, the Green City demonstration project has been showing that smart building management systems are now a reality, with 13 buildings being run entirely on renewable energy of which 70% is produced on-site.
- Voted the most “pedestrian-friendly city”
Zurich’s smart city project places great emphasis on mobility by making public transport more attractive to users through its application “Zürimobil”, which provides real-time traffic information as well as walking and cycling alternatives.
- Online platform for residents
“Mein Konto”, the city’s e-administration platform. The platform provides residents with online access to information, events, administrative formalities, and more.
OSLO plans to ban gas car sales in 2025
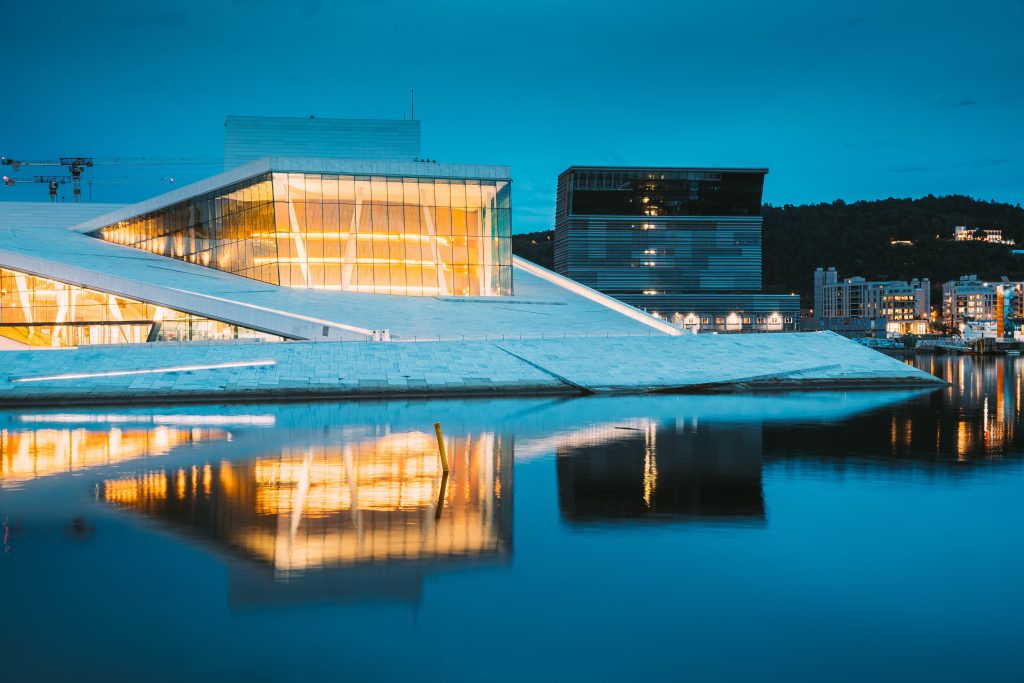

- Free public charging
Oslo provides inhabitants with free charging with renewable energy at all Level 2 charge points.
- Becoming a fossil-free city by 2030
Connectivity to nature is a central Norwegian value that underlies Oslo’s aspiration to be a green capital and its objective to become a fossil-free city by 2030.
- All public transport will be electrified by 2028
In recent years, there have been more people in Oslo travelling by public transport than by car. The goal is an accessible, green and cost-effective infrastructure. Reduced emissions are the overarching objective, with a view to both climate concerns and the health and well-being of the public.
- Norway plans to ban gas car sales in 2025
According to an analysis printed by the Norwegian Automobile Federation’s magazine, Motor, the downward trend in sales for gas cars has been so consistent and steep that the last new gas car sale in Norway could happen in April 2022 (source).
TAIPEI CITY uses smart illumination
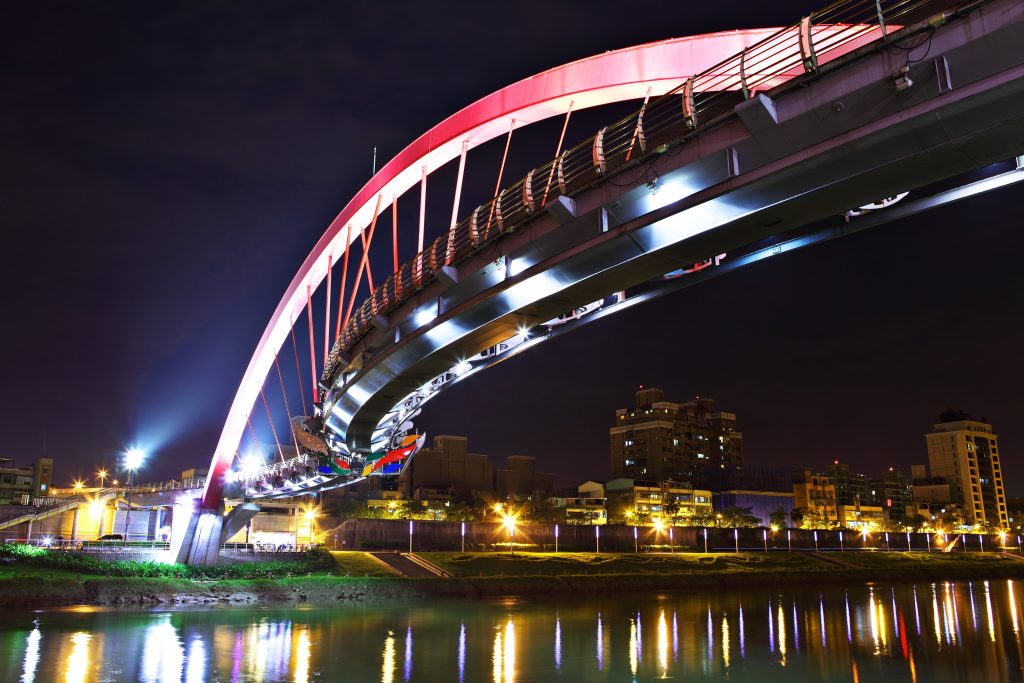

- Narrowing the gap between rural and urban
Through the use of big data analysis, service integration, various real-time Apps and other applications, the goal of a smart and one government is gradually reached and the gap between urban and rural was narrowed via the incorporation of technology. (source)
- Building the smart city through the Smart City Wheel framework
The Wheel constitutes six categories: smart government, smart mobility, smart economy, smart environment, smart living and smart people. Each of the categories covers different indicators to examine a smart city.
- Smart street illumination
To lead the environment smarter, the smart illumination of LED street lights has been used and the cost-saving on electronic bills makes the project penniless.
LAUSANNE is building eco-neighbourhoods
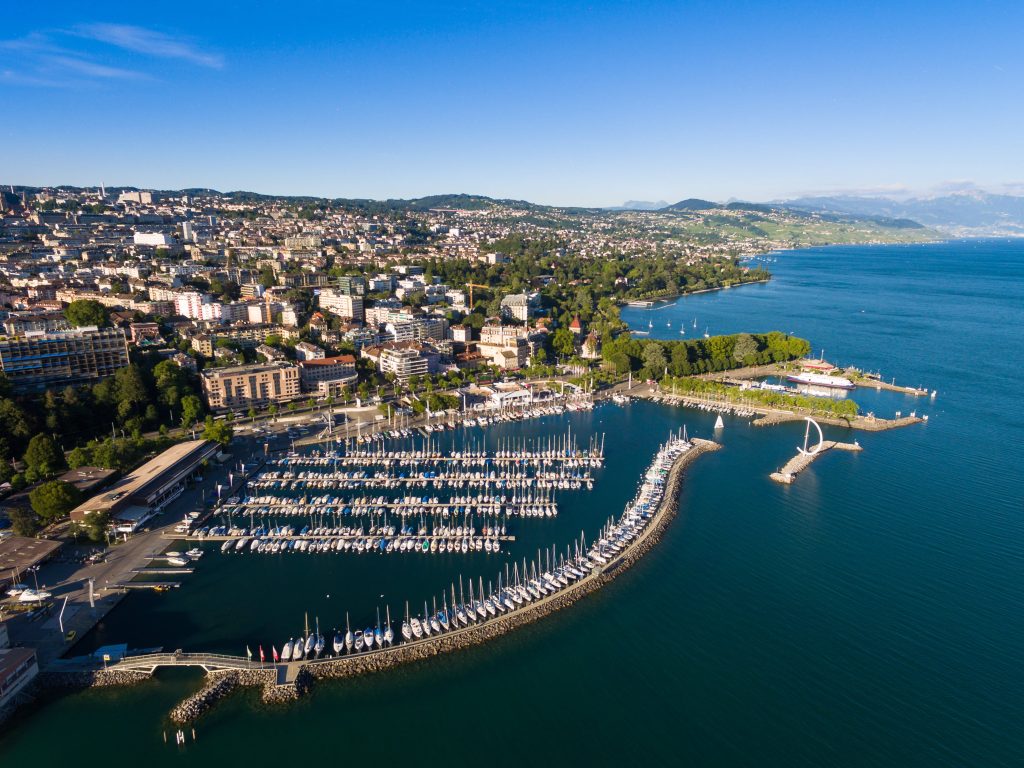

- Improving the quality of life, conserving resources and providing services more efficiently are the primary goals of Lausanne as one of the world’s top smart cities.
Success factors for advancing the Smart City movement in Switzerland are stronger networking and data platforms.
- Building eco-neighbourhoods
The city is building two large eco-neighbourhoods in the north and south of the city which are expected to have nearly 20,000 residents by 2022.
- M2, Switzerland’s first fully automatic metro
The metro line connects the south of the city to the north in 18 minutes. This main urban line is linked to the city’s bus network and the national rail system.
HELSINKI to become carbon neutral by 2035
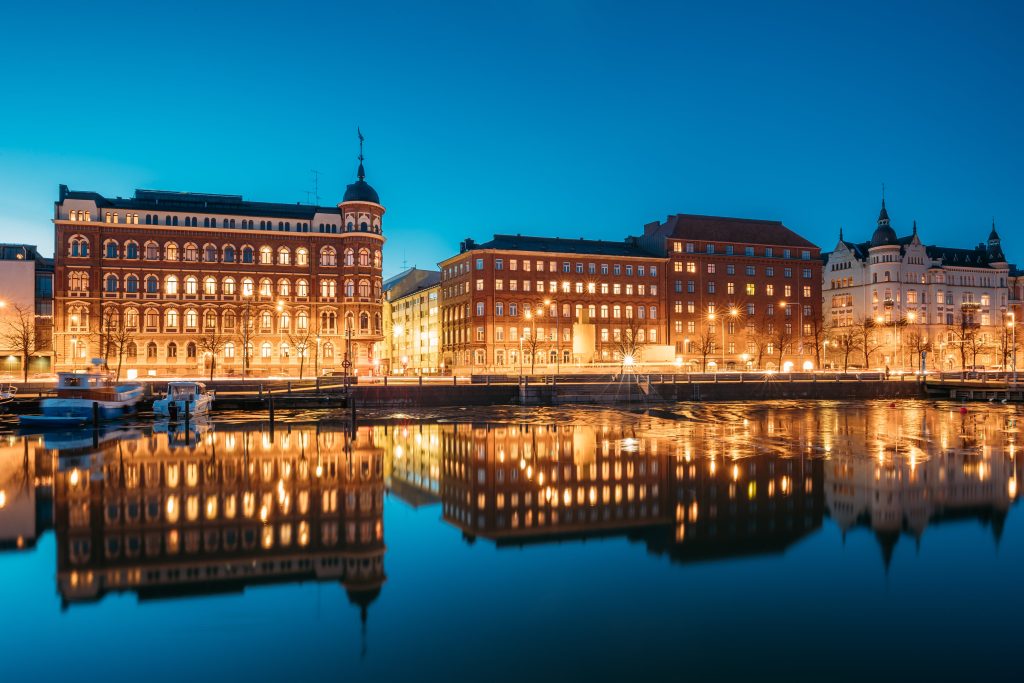

- One of the most functional cities in the world
Helsinki is a sum of many factors: availability of open data, early adoption of digital developments, commitment and cooperation between the whole ecosystem from citizens to companies and government (source).
- Ecological thinking
This smart city motivates its inhabitants to consume less, build sustainably and achieve ambitious climate goals.
- Becoming carbon-neutral by 2035
An open tool has been devised to track progress towards this goal. The tool gives information about the subcategories of traffic, construction, the use of buildings, consumption, procurement, sharing and circular economy initiatives, and the set of so-called “smart & clean” actions (source).
Over 1 million journeys are taken by bike in COPENHAGEN every day
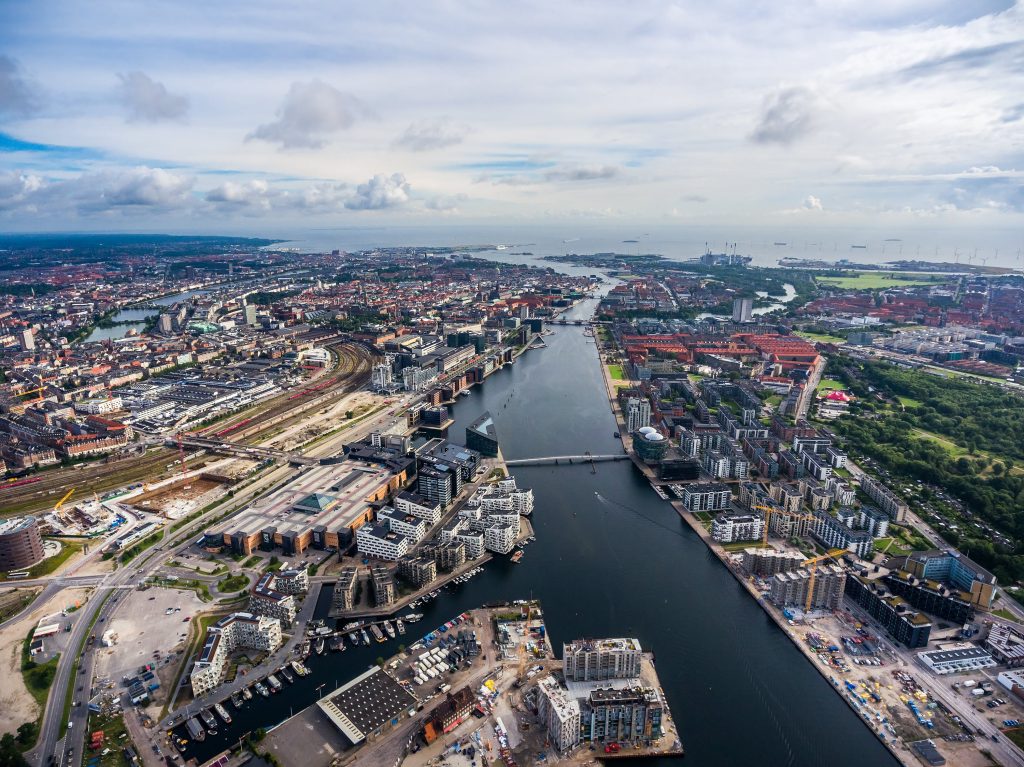

- Aims to become the world’s first carbon-neutral capital by 2025
Copenhagen’s aim to become carbon neutral by 2025 has spurred the development of a new intelligent traffic systems framework for the very near future. The framework builds on Copenhagen’s Climate Plan 2025, and one of its goals is to ensure that 75 per cent of all trips within the city should be taken by bike, public transport, or on foot (source).
- Free access to public data sources
A new government programme provides free access to public data sources with the aim to drive smart city innovation.
- Over 1 million journeys are taken by bike in Copenhagen every day
Continuous efforts are being made to provide better conditions for cyclists—for example, maintaining road surfaces, creating dedicated cycle paths, providing bike parking, and integrating bicycles into multimodal solutions (source).
- Smart street lights
Their main smart feature involves varying the luminosity that they produce. The lampposts detect the arrival of a cyclist and react by increasing the intensity of the light, before decreasing it as the cyclist moves away. So far, the scheme has produced a 76 per cent saving in the bill for public lighting (source).
GENEVA’s inhabitants recycle 39% of their waste
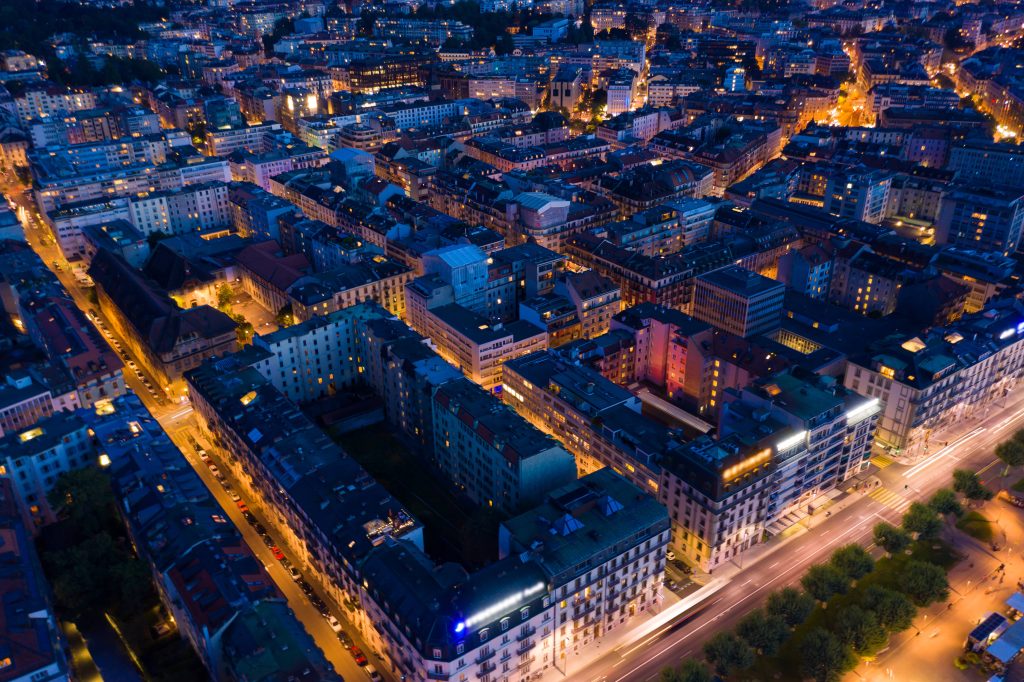

- Thanks to its energy policy, Geneva is designed to be 100% renewable by 2050
The city implements tangible actions when building or renovating buildings within its territory in order to reduce dependency on fossil fuels and to increase the share of solar and geothermal energy.
- Responsible mobility
In 2015, road traffic was the main source of emissions of fine particles in Geneva. The city has implemented solutions to support mobility while protecting the inhabitants from disturbances resulting from traffic.
- The inhabitants of Geneva recycle 39% of their waste
Since 2016, the City has distributed 60,000 green bins and rolls of biodegradable bags to its inhabitants intended for organic kitchen waste with a view to promoting compost.
AUCKLAND is the world’s spongiest city
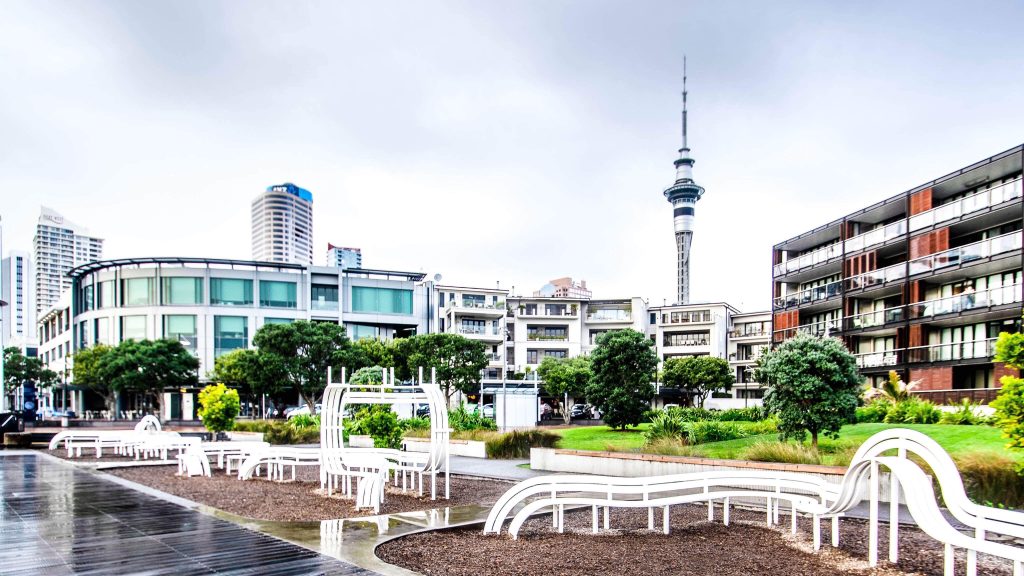

The term “sponge city” was first coined in 2013 by Professor Kongjian Yu of Peking University to describe cities that work with nature to absorb rainwater – instead of using concrete to channel it away.
According to engineering consultancy Arup, Auckland is the spongiest city in the world with a high percentage of green space and permeable local soil (source).
- World’s most liveable city per the 2021 Global Liveability Index by the Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU)
The ranking classifies 140 cities across five categories including stability, healthcare, culture and environment, education, and infrastructure (source).
- 43,000 streetlights converted to LED by Auckland Transport, saving NZ$36 million over 20 years (source).
BILBAO is an international benchmark in urban transformation
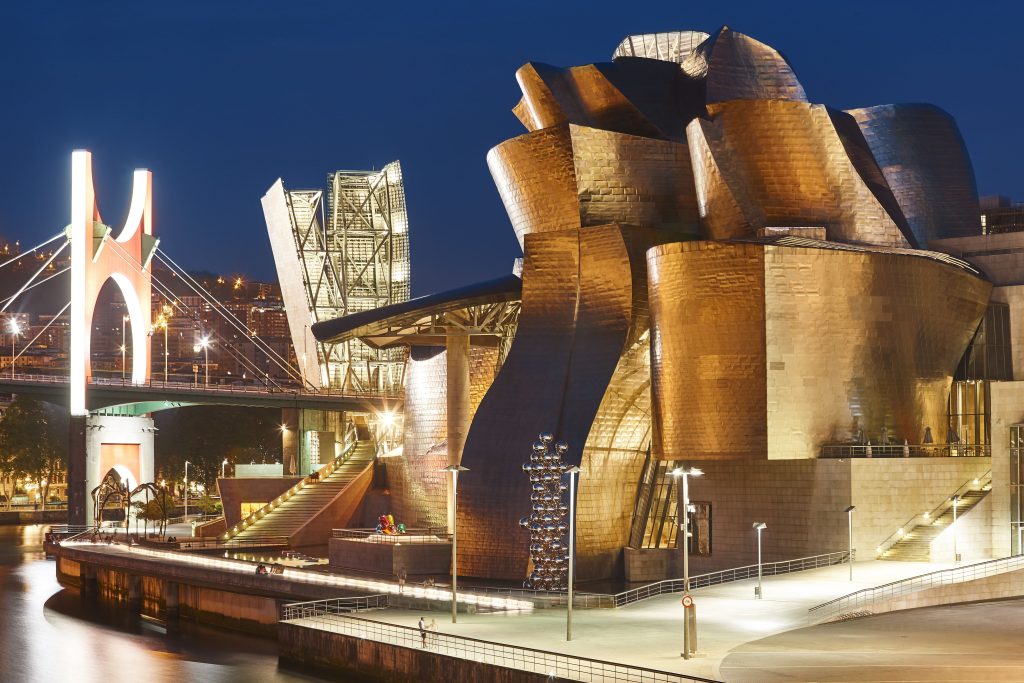

- Reduced pollution for citizens
The city established a maximum speed of 30km/h on all streets, making it the first city in the world with more than 300,000 inhabitants to adopt this measure. As a result, the city has managed to reduce pollution, providing a safer and healthier space for its citizens, and has managed to reduce traffic accidents by around 28 per cent (source).
Upgrading Our Cities With Smart Street Furniture

We rely on our smartphone to stay connected with friends, family and the world; we watch movies and browse the internet on a smart TV; we check the time but also the latest emails on a smartwatch. Everything around us is getting smart!
In a previous article, I wrote about the 5G technology and how it has the power to transform our cities into smart cities.
We are not there yet, but here is the first step towards the future: smart street furniture.

linkedin.com
Include is a European hardware company producing smart street furniture. The company’s R&D team works on the development of both hardware and software solutions, which means they have the capacity to develop any IoT or solar powered solution for smart cities.

Steora, the smart bench/include.eu
Mission
We believe that technology is a driver of equality and inclusion. Our mission is to find undiscovered potential around us, and use it to create amazing technology products, designed to improve the lives of urban users.
Include

include.eu
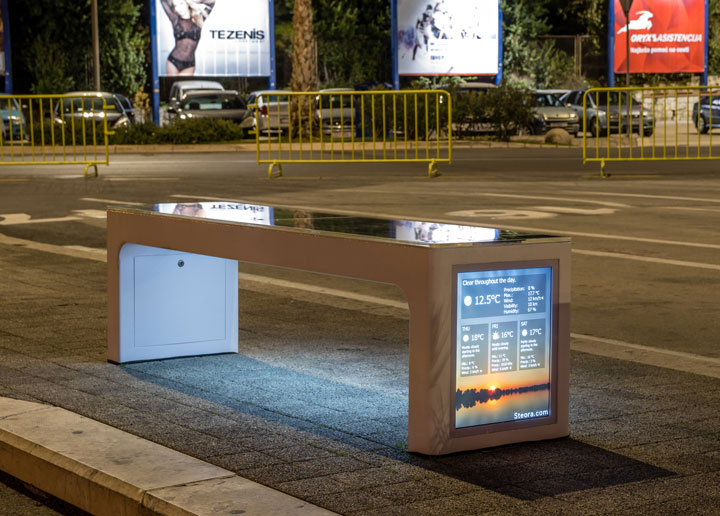
Steora – The Smart Bench
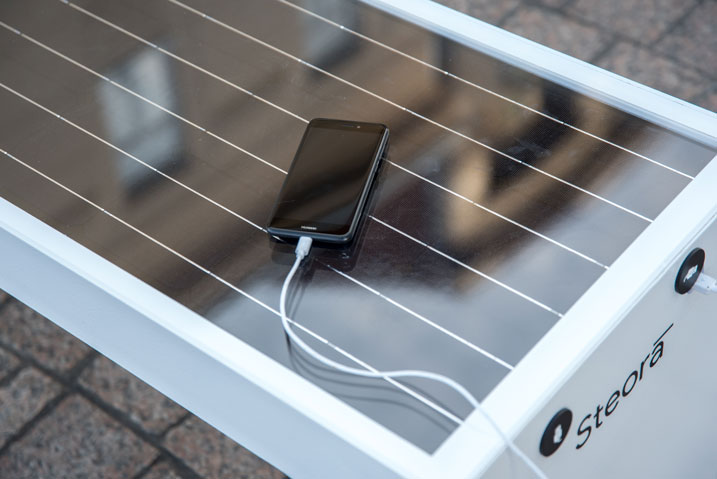
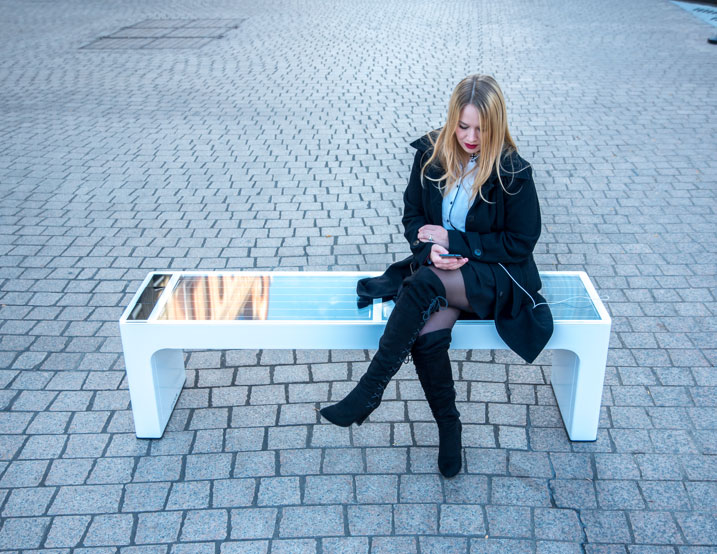
With its simple, balanced design and convenient size, Steora can be installed to substitute regular street benches, bringing a touch of modern aesthetic to outdoor spaces together with solar-powered Wi-Fi hotspot and charging stations.
Technical specifications of Steora:
- Fitted with Photovoltaic modules;
- Wireless charging;
- Battery pack capacity: 72Ah;
- USB charging: 2 ports;
- Internet technology: 4G LTE / Speed: up to 150Mbps / Range: 4 – 20 meters;
- Various sensors: temperature, humidity, Energy production & consumption, Internet connections counter & data traffic usage, Battery status, Rain sensor – powers the bench off in case of heavy rain, System sensor – analyzes every device inside the bench;
- Cooling system;
- Ambient light: 2 meters range;
- LCD display;
- CCTV.

include.eu
Benefits of Steora, the smart bench:
- self-sustaining green solar energy;
- wireless charging;
- superfast internet connection;
- outdoor advertising;
- area lighting;
- seat cooling.
Include by the numbers
- The company was founded in 2014 by Ivan Mrvoš, a young Croatian innovator;
- The first smart bench was launched in 2015 and sold almost 100 units in the first year;
- To date, the company sold over 1000 benches in 42 markets around the world.
Awards
For its innovative products, the company was awarded the StartUp of The Year, Best Smart City Solution and Best IoT Solution at the 2017 Central European Startup Awards.
Forbes 30 under 30 included Ivan Mrvoš on its 2019 Europe list at the Manufacturing & Industry category.
Join the Conversation
We’d love to hear what you have to say.
Get in touch with us on Facebook Group and Twitter.
5G and The 4th Industrial Revolution
5G is the next generation of mobile internet connectivity. Experts say 5G connectivity not only means outstanding network reliability but also a major change of how we live and work – the 4th Industrial Revolution.

The connectivity benefits of 5G will make businesses more efficient and give consumers access to more information faster than ever before. Super-connected autonomous cars, smart communities, industrial IoT, immersive education—they all will rely on 5G.
Verizon
How is 5G superior to our current 4G connectivity?
Here are the most important features and benefits of 5G:
- Increased Speed: 5G is approximately 20 times faster than 4G;
- Increased Download speed: 5G offers a minimum peak download of 20 Gb/s while 4G pokes along at only 1 Gb/s;
- Lower Latency: 5G provides below 1-ms latency compared with 30 – 70 ms for 4G.
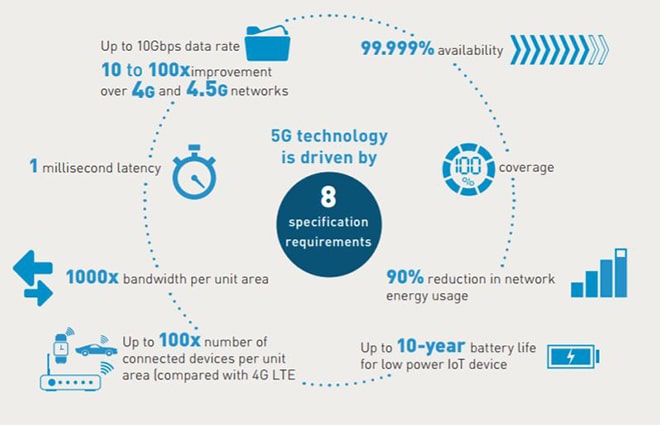
image source: gemalto.com
Superior speed and increased download speed mean IoT will finally be made possible and smart cities will emerge.
Lower latency makes 5G-enabled technology highly suitable for critical applications that require rapid responsiveness, such as remote vehicle control.
5G isn’t just another iteration of wireless innovation.
Ronan Dunne, Executive Vice President and Group President, Verizon Wireless
Is 5G setting the world on the path to the 4th Industrial Revolution?
5G represents a massive upscale of network technology. It will provide data transfer rates many times faster than a blink of an eye, high bandwidth and greater opportunities for connectivity and reliability.
But according to Ronan Dunne, 5G doesn’t upgrade incrementally, but exponentially which supports the advent of the 4th industrial revolution.
5G will improve many industries and make new developments possible like the following:
- Social VR;
- AR in sports;
- Smart cities applications;
- Connected cars.
Social VR is The Next VR development
No matter the latest tech developments in regards to medium or tools, what we humans look for is interaction with others. This is the case for VR also. According to Verizon, 78% of survey respondents who have used VR said they wanted to interact with other people in the virtual environment. That’s why social VR is a new development in VR in recent years.
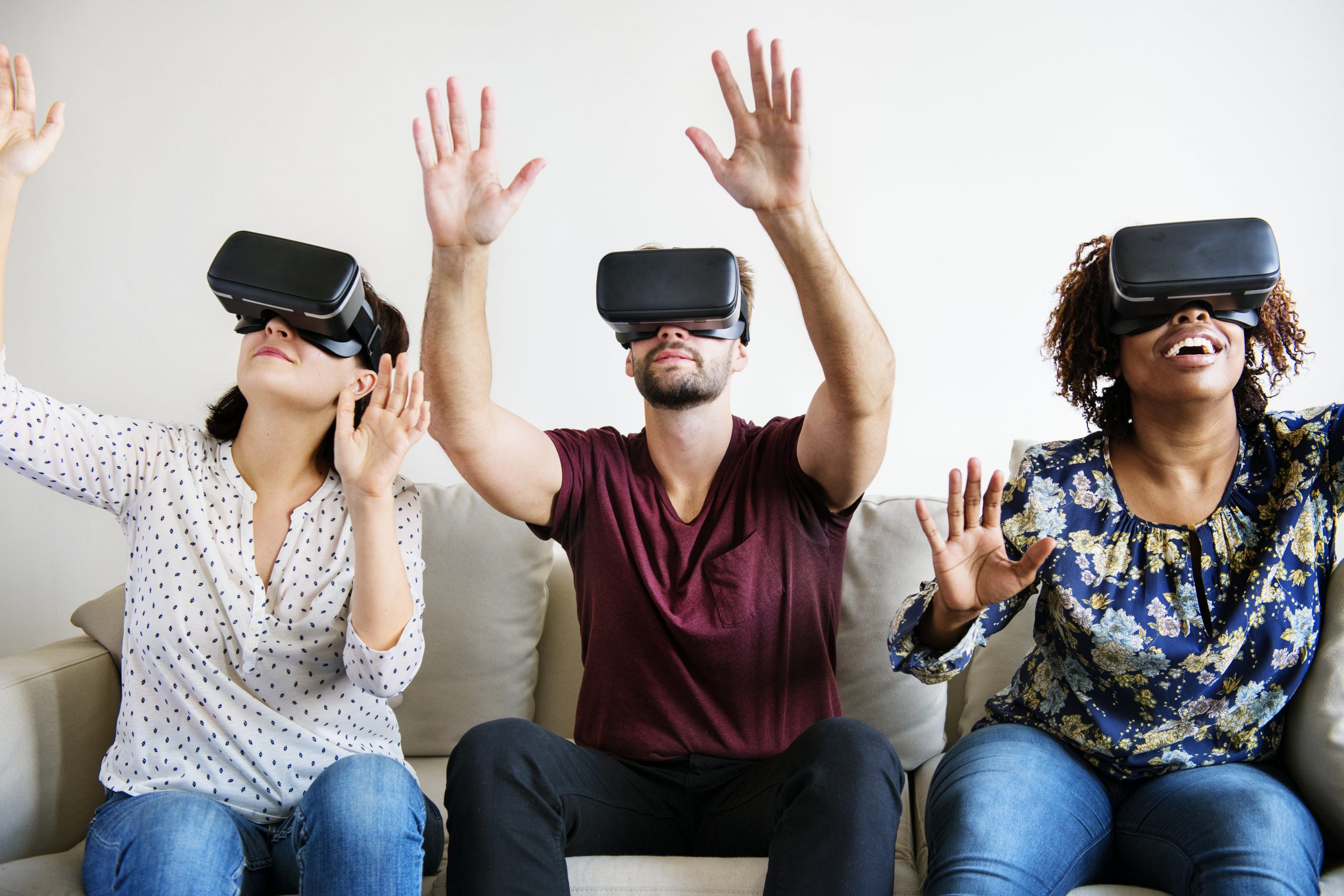

Social VR is when users create or visit virtual environments in the company of friends, hang out in clubs, get together at parties or at the movies. 5G will help make the VR experience feel more and more real; it will usher in a world where VR becomes our primary communication system.
AR for sports – Making sports experiences more fun for younger audiences
The average fan’s age is over 40 and major sports leagues are looking for ways to attract, engage and retain younger audiences. 5G promises to take sports experiences to a whole new level and make it more exciting for fans in their twenties or younger.
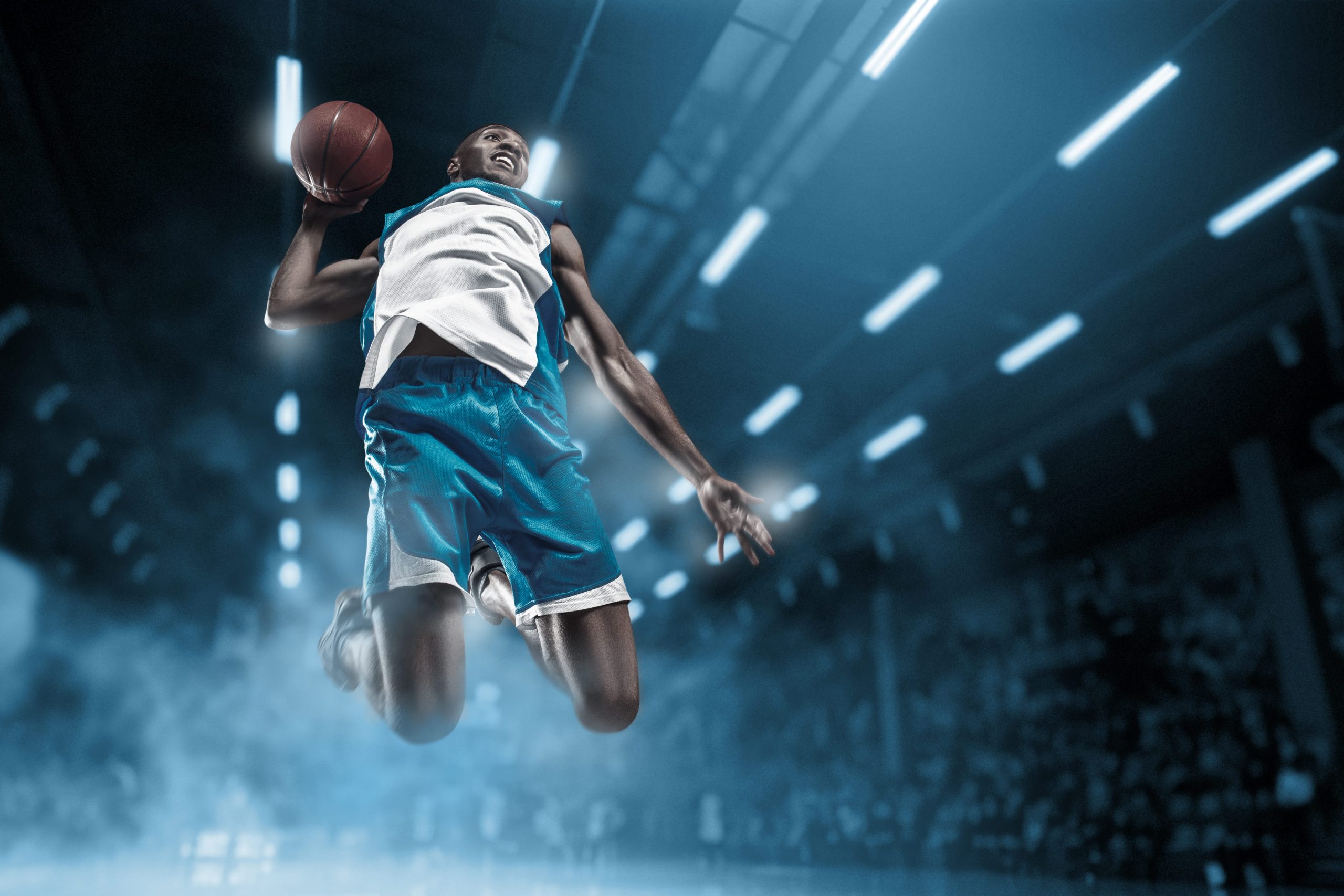

The goal of all major sports leagues is to have people buy tickets and come to the stadiums. 5G-enabled AR might just be the solution.
From AR games during timeouts, participation in game quizzes and polls to AR portals which will allow fans to virtually walk into the locker rooms, on the field or into a player interview.
5G will also prove useful for improving how the audience is experiencing real-time sports matches:
The high bandwidth of 5G will also allow fans to upload their view of the game so they can switch between feeds from the cameras in the stadium to feeds from the fans point of view.
Verizon
It’s all about providing a personalized experience of the game and a personalized way to watch the game.
Smart cities – Smart society
5G has the power to lead our cities into the future. In this future, our cities will develop economically; they will be environmentally sustainable and will rise on the foundations of competitiveness, economic progress and security, social cohesion and innovation.

These smart cities will be seeds from which the smart society will bloom. A society that improves the quality of life for residents, businesses and visitors altogether.
5G could impact almost every aspect of city operations and service delivery: power and water grids, trash collection, transit, public health and education, pollution and disaster management.
Smart cities benefits:
- Smart traffic management;
- Smart grids;
- Smart homes;
- Smart healthcare and security;
- Smart transportation.
Connected cars are already here
What is a connected car?
A connected car is a car which is equipped with internet access and a wireless local area network.
Car connectivity has developed in two directions: vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) connectivity and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) connectivity.
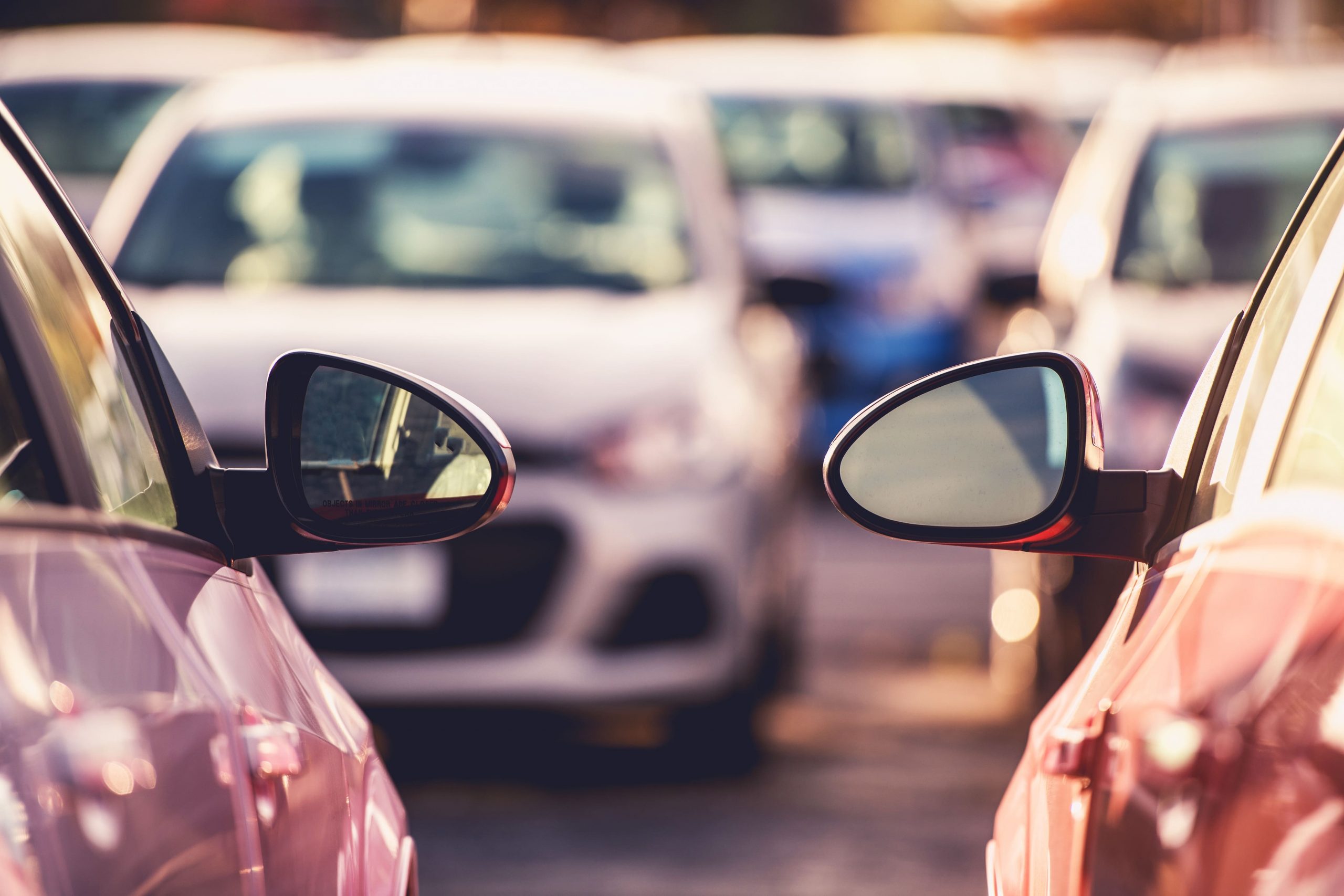

V2V means vehicles communicating with others on the roads so drivers are made aware of the location of the other participants within traffic, their destination and speed. The benefits of this type of connectivity are many: advanced warning of traffic build-up, opportunities for drivers to adapt their driving etc. All benefits converge to a safer traffic environment and faster journey.
V2X means everything on the roads is connected: vehicles are connected with each other but also with traffic lights, the roads themselves, lampposts etc. Everything is fitted with sensors which will collect data on everything: the traffic, the condition of the roads, weather, air quality, parking spaces, etc. The collected data can be used to: automatically change the timing of traffic lights to speed up or slow down in order to avoid or reduce congestion, identify roads in need of repair etc.
[bctt tweet=”To make the 4th Industrial Revolution possible, 4G is simply not enough, but 5G has what it takes.” username=”brand_minds”]
Join the Conversation
We’d love to hear what you have to say.
Get in touch with us on Facebook Group and Twitter.
sources:
verizon.com/about/our-company/5g/what-5g
verizon.com/about/our-company/fourth-industrial-revolution/social-vr-new-way-form-relationships
verizon.com/about/our-company/fourth-industrial-revolution/5g-changing-future-sports
verizon.com/about/our-company/fourth-industrial-revolution/powering-fourth-industrial-revolution-5g
5g.co.uk/guides/5g-and-the-connected-car/
How will the city of the future look like?
Big data, Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), robots, drones, autonomous green vehicles, 3D / 4D printing, renewable energy, virtual reality (VR),leap motion, eye controlled technology are just part of the present and new technologies that are here or will be here in the near future to influence our lives.
The cities are evolving as well, by becoming Smart Cities. From Singapore to Amsterdam and Barcelona, from Dubai to Stockholm,from New York to Manchester and even Alba Iulia in Romania, information and communication technology is used to enhance quality, performance and interactivity of urban services, to reduce costs and resource consumption and to increase contact between citizens and government. Smart city applications are developed to manage urban flows and allow for real-time responses.
The smart city concept integrates information and communication technology and various physical devices connected to the network (IoT) to optimize the efficiency of city operations and services and connect to citizens. Smart city technology allows city officials to interact directly with both community and city infrastructure and to monitor what is happening in the city and how the city is evolving.
According to the IESE Cities in Motion Index 2017, quoted by Forbes, which analyses all aspects that make up sustainability and quality of life in 180 key world cities, New York is again the smartest city in the world, followed by London and Paris.
To compile the index, the authors analyze 79 indicators across 10 different dimensions of urban life: the economy, technology, human capital, social cohesion, international outreach, the environment, mobility and transportation, urban planning, public administration and governance. The results show that almost all of the dimension measured in the ranking are led by European and North American cities. The exception is technology, where Taipei rules.
In top 10 are present three other American cities (Boston 4th, San Francisco 5th, and Washington, D.C. 6th), two other European cities (Berlin 9th and Amsterdam 10th), and two Asian (Seoul 7th and Tokyo 8th).
Moreover, according to CityMetric, Singapore is also a leading example of a smart city, and is constantly evolving its “city brain,” a backbone of technologies used to help control pollution, monitor traffic, allocate parking, communicate with citizens, and even issue traffic fines. “The behavioral aspect is not to be overlooked. Singapore’s “brain” is attempting to modify human behavior – for example, one system rewards drivers for using recommended mapped routes, and punishes those who do not. Ultimately, Singapore’s planners hope to discourage driving, and guide most commuters to making greater use of public transportation. The city is planning for 100m “smart objects” including smart traffic lights, lamp posts, sensors, and cameras on its roadways, which will be used to monitor and enforce laws,” wrote Fast Future for CityMetric.
But how will those smart cities look in the future and what can we expect from them and the specialists living and creating in them? “The number of smart cities around the world is expected to grow exponentially over the next few years and by 2050, 70 per cent of the world’s population will be living in smart cities,” believes Nick Ismail in his piece for information-age.com.
Moreover, it appears that 2030 will bring the introduction of Connected street lights, which will stream data between millions of devices and improve city services such as light, traffic, air quality, public safety and parking. Lighting technology will be at the heart of urban life in 2030 as well, helping deliver more sustainable and better-connected smart cities. “And if that wasn’t enough, by 2050 take-aways will be delivered by drones, replacing motorbikes and cars. One pizza manufacturer has already tested drone delivery and some predict these automated flying machines will fill the skies replacing the couriers of today,” adds Ismail.
5 IoT Trends for 2018
1.Connected Industry
Companies in a wide variety of industries can use the massive amounts of contextual data provided by IoT devices. This will help them to improve manufacturing processes, fine-tune management strategies, and monitor factory/ construction equipment. The trend will be visible in industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, agriculture, fleet management and automotive.
“While much of the attention has been place on acquiring as much raw data as possible, then analyzing it and presenting it to key decision makers, a shift in emphasis is now a foot in that the location and time of data acquisition is becoming just as important as secure communication and the data itself. This shift in emphasis toward more ‘context rich’ data presents exciting opportunities for application developers and system designers in IoT application arenas. For example, instead of simply detecting a dangerous bump or pothole in the road using tire pressure or suspension monitoring sensors, the data can be combined and communicated with precise location data so other trucks in a fleet can avoid that spot and avert fleet‑wide damage,” writes electronicspecifier.com.
Fleet management companies will be able to track mileage, monitor the number of stops taken, and find the current location of their trucks. They can also monitor gas levels, and even detect dangers on the road.
In agriculture, the industrial IoT can help secure the global food supply. With an expected 9.1 billion global inhabitants by 2050, using connected sensors to track temperature, soil conditions, sunlight and humidity, can provide the data needed to ensure optimal use of land. Then accurate location services and timely information communication can guide harvesters to ensure those crops are harvested quickly and efficiently at the optimum time.
2. Smart energy
“With much of global conversation focused on energy consumption, Smart Energy IoT projects will help both commercial buildings and households to better monitor their energy use. Smart streetlights powered by cost-effective and energy-efficient LED lights will help cities lower their environmental impact,” writes excellentwebworld.com.
Moreover, according to the website, Smart Meters will help households and commercial buildings to monitor their overall energy consumption and lower the overall pollution levels of a city, while also helping to detect power outages sooner than ever before.
IoT solutions can be implemented as narrowly as at the circuit level, and by leveraging and analyzing that data with AI, decision-makers can pull actionable information to significantly reduce waste and further optimize business operations. AI also enables real-time alerts and notifications as well as the automation of key functions, such as climate control and lighting. The power of IoT comes from the granular data it provides. Installing sensors on your existing devices enables them to communicate information about conditions like energy usage, pressure, temperature, etc.
3. Smart Supply Chain
A Smart Supply Chain is necessary for companies using AI and Smart data collection technologies, being qualified to “decode” and implement the information collected. It can also ensure that each individual operation within a company is using smart technology. This helps to keep things consistent.
Smart Supply Chains can help to fill in the gaps in production when workers are unavailable. This means that brands can produce more in less time. Additionally, these Smart Supply Chains often possess targeted skill sets that not every worker has. This technology will also help companies to make better use of their storage space, avoid over-production, and help to monitor inventory.
4. ADN Voice Technology
IoT projects that offer voice-led Operating Systems will soon become a part of daily life. They won’t just be a gadget that only the tech-obsessed can’t live without. Amazon’s Alexa has all the chances to become the most popular piece of ADN Voice Technology, outpacing Siri and Google Assistant. To make driving safer, Alexa will be integrated into cars, therefore drivers can ask for directions or change the music without taking their hands off the wheel.
For added convenience, you can use Alexa and other ADN Voice Technology to control your Smart Home. You’ll be able to turn on your lights, adjust your thermostat, and much more.
Since it was founded in 2001, VoiceBox, a provider of contextual voice and natural language understanding (NLU) technologies, has partnered with car, smartphone and wearable manufacturers on its speech recognition technology, said Mike Kennewick, company co-founder, chairman and CEO, for http://internetofthingsagenda.techtarget.com.
5. Smart Cities
A 2016 survey from Daintree Networks,quoted by Business Insider, found that almost 60% of building managers in the U.S. are familiar with the IoT, and 43% believe the IoT would shape how they operate their buildings in the next two to three years. One area with massive potential for improvement is in lighting, as building managers could switch to LED bulbs in order to save money and energy.
Another area is elevators, where the need for greater efficiency is shocking. IBM noted that in 2010, people in New York City waited a total of 22.5 years for elevators. As a result, Allied Market Research expects the smart elevator market to nearly double from $12 billion in 2015 to $23 billion in 2020.
“The greatest implementation of smart architecture and infrastructure is smart grids, which help tremendously with resource conservation. The European Commission expects that 72% of consumers in the European Union will have smart electricity meters installed in their homes by 2020, and 40% will have a smart gas meter,” said Andrew Meola for Business Insider.
Moreover, as excellentwebworld.com points out, thanks to Smart City projects, delayed trains and sitting in hours of traffic may be a thing of the past. These technologies even use cameras to monitor the traffic flow. This means that traffic lights will operate according to the levels of congestion. Public transit riders will get real-time updates regarding when a bus or subway will arrive. Smart City technology will also influence the overall infrastructure of a city. This helps to improve predictive maintenance estimates. It also assists in the control of potential public health crises, and creates better city planning strategies.





