So you want to start your own business.
You have written a solid business plan and raised the necessary capital. Before assembling your team and drawing your business logo, have you considered which country you should grow your business in?
Yes, business-wise some countries embrace and nurture the entrepreneurial initiative while other countries make it difficult for businesses to succeed.
Curious which are the best countries for business in 2018?
Forbes’ Best Countries for Business in 2018 is a list of 153 nations ranked on 15 different factors. These factors include: property rights, innovation, taxes, technology, corruption, freedom (personal, trade and monetary), red tape, investor protection, workforce, infrastructure, market size, quality of life and political risk.
Here is the Top 10 Best Countries for Business in 2018:
1. United Kingdom of Great Britain
The UK is the third largest economy in Europe after Germany and France, leading the world in the trading and financial sector. The UK produces about 60% of its food needs with less than 2% of the labor force. Beginning with 2005 the UK has been importing energy to meet population needs.
The key drivers of British GDP growth are services, particularly banking, insurance, and business services. Regarding its corporation tax, Britain has pledged to lower it from 20% to 17% by 2020.
technology – 4
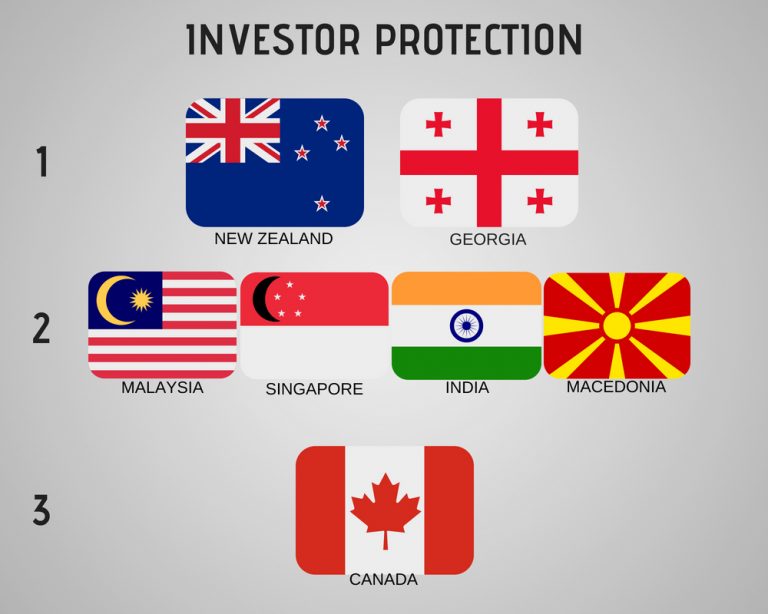
investor protection – 10
2. New Zealand
New Zealand is an industrialized, free market economy that can compete globally with other powerful countries.
The economy pulled out of recession in 2009, and achieved 2%-3% growth from 2011 to 2016. The New Zealand government’s continued programs include expanding export markets, developing capital markets, investing in innovation, raising productivity growth, and developing infrastructure, while easing its fiscal austerity. One of New Zealand’s top foreign policy priority is to expand the country’s network of free trade agreements.
investor protection – 2
tax burden – 9
3. Netherlands
The Netherlands is the sixth-largest economy in the European Union. The country plays an important role as a European transportation hub, with a persistently high trade surplus, stable industrial relations, and low unemployment.
Netherlands’ industry focuses on food processing, chemicals, petroleum refining, and electrical machinery. The country provides large surpluses for food-processing and underpins its status as the world’s second largest agricultural exporter.
technology – 3
innovation – 6
4. Sweden
Sweden’s enviable standard of living is the result of a combination of free-market capitalism and extensive welfare benefits. Sweden’s economy is heavily oriented toward foreign trade and is based upon resources such as timber, hydropower, and iron ore. Between 2014 and 2016 the country experienced modest growth, with real GDP growth above 2%, but continues to struggle with deflationary pressure.
technology – 5
innovation – 7
5. Canada
Following World War II, Canada turned its economy from a largely rural one into a primarily industrial and urban. The country’s growth was accelerated by manufacturing, mining, and service sectors. Canada has a large oil and natural gas sector with the majority of crude oil production derived from oil sands in the western provinces, especially Alberta. Canada now ranks third in the world in proved oil reserves behind Venezuela and Saudi Arabia and is the world’s sixth-largest oil producer. Canada is the largest foreign supplier of energy to the US, including oil, natural gas, and electric power, and a top source of US uranium imports.
trade freedom – 7
investor protection – 8
6. Hong Kong
Hong Kong has a free market economy, highly dependent on international trade and finance. The value of goods and services trade is about four times GDP. Hong Kong has no tariffs on imported goods and it levies excise duties on only four commodities, whether imported or produced locally: hard alcohol, tobacco, hydrocarbon oil and methyl alcohol. Hong Kong is vulnerable to renewed global financial market volatility or a slowdown in the global economy due to its continued reliance on foreign trade and investment. Hong Kong’s natural resources are limited, and food and raw materials must be imported.
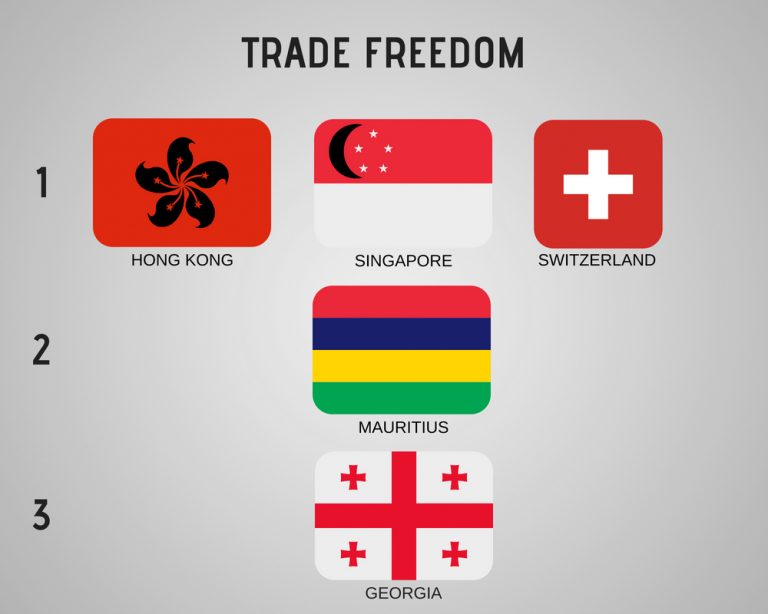
trade freedom – 1
tax burden – 3
investor protection – 9
technology – 9
7. Denmark
Denmark’s modern market economy features a high-tech agricultural sector, advanced industry with world-leading firms in pharmaceuticals, maritime shipping, and in renewable energy. As Hong Kong, the country is highly dependent on foreign trade. Denmark is a net exporter of food, oil, and gas and enjoys a comfortable balance of payments surplus, but depends on imports of raw materials for the manufacturing sector. Danish economy is characterised by extensive government welfare measures and an equitable distribution of income. Denmark is among the strongest supporters of trade liberalisation.
tax burden – 8
innovation – 10
8. Ireland
Ireland is a small, modern, trade-dependent economy. In 2014, the economy rapidly picked up and GDP grew by 5.2%. The recovering economy assisted lowering the deficit to 2.5% of GDP. Ireland government has encouraged business investment by lowering corporation tax to 12.5% and nurturing a talented pool of high-tech laborers. Ireland’s tax residency requirements are loose which makes the country a common destination for international firms seeking to avoid taxation.
tax burden – 4
investor protection – 10
9. Singapore
Singapore has a highly developed and successful free-market economy. It enjoys a remarkably open and corruption-free environment, stable prices and a per capita GDP higher than that of most developed countries. Unemployment is very low and the economy depends heavily on exports, particularly of consumer electronics, information technology products, medical and optical devices. Singapore’s economy benefits from rapid development of its transportation, business and financial services sectors.
trade freedom – 1
investor protection – 4
tax burden – 7
innovation – 9
10. Switzerland
Switzerland is a prosperous and modern market economy with low unemployment, a highly skilled labor force, and a per capita GDP among the highest in the world. Switzerland’s economy benefits from a highly developed service sector, led by financial services and a manufacturing industry that specializes in high-technology and knowledge-based production. Switzerland enjoys economic and political stability, transparent legal system, exceptional infrastructure and efficient capital markets. Low corporate tax rates also make Switzerland one of the world’s most competitive economies.
trade freedom – 1
innovation – 1
technology – 2
Here is our list of Top 3 countries ranked by the following factors: