5 business strategy frameworks for business growth
Business Strategy Framework #1 ANSOFF MATRIX ANALYSIS
The Ansoff Matrix is a business strategy framework and a planning tool that provides managers with a template to devise strategies for future growth.
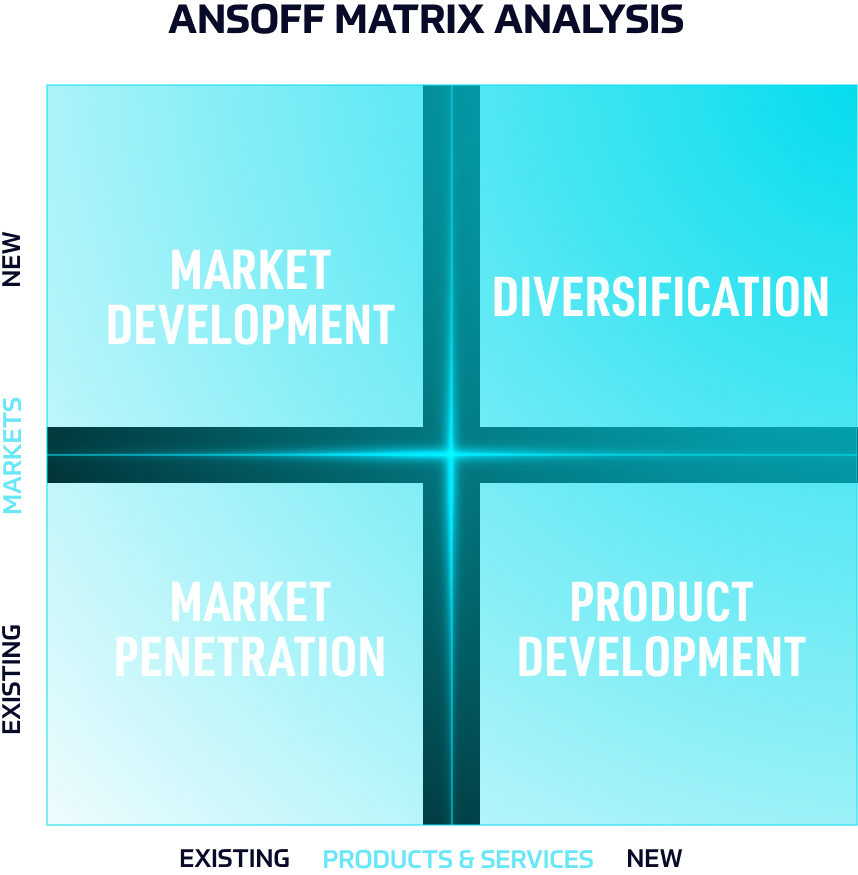
There are 4 growth strategies within the Ansoff Matrix:
- Market penetration strategy = in which the company seeks to improve business performance either; by increasing the volume of sales to its present customers or by finding new customers for present products;
- Market development strategy = in which the company sells its existing products to new markets;
- Product development strategy = in which the company develops new products for the same market;
- Diversification strategy = in which the company develops new products in a new market.
What growth strategies does Apple use?
Learn from our Ansoff Matris analysis of Apple.
Business Strategy Framework #2 BCG GROWTH-SHARE MATRIX
The BCG Growth-Share Matrix helps companies analyze their business units (i.e. their product lines) or any other cash-generating entities by their degree of profitability.
This business strategy framework provides the company with a four-quadrant chart where products are ranked on the basis of their relative market shares and growth rates:
“cash cows”,
“dogs”,
“question marks” and
“stars”.

Cash cows are products in low-growth areas for which the company has a high market share.
Products with a low market share in areas with slow growth are dogs.
Question marks are the products with a low market share in a high growth rate market.
Stars are products with a high market share in a high growth rate market.
To show how you can use the matrix for your business, read our analysis of e-commerce leader Amazon, specifically four of its products: Amazon AWS, Amazon Video, Amazon Live and Amazon Echo with Alexa.
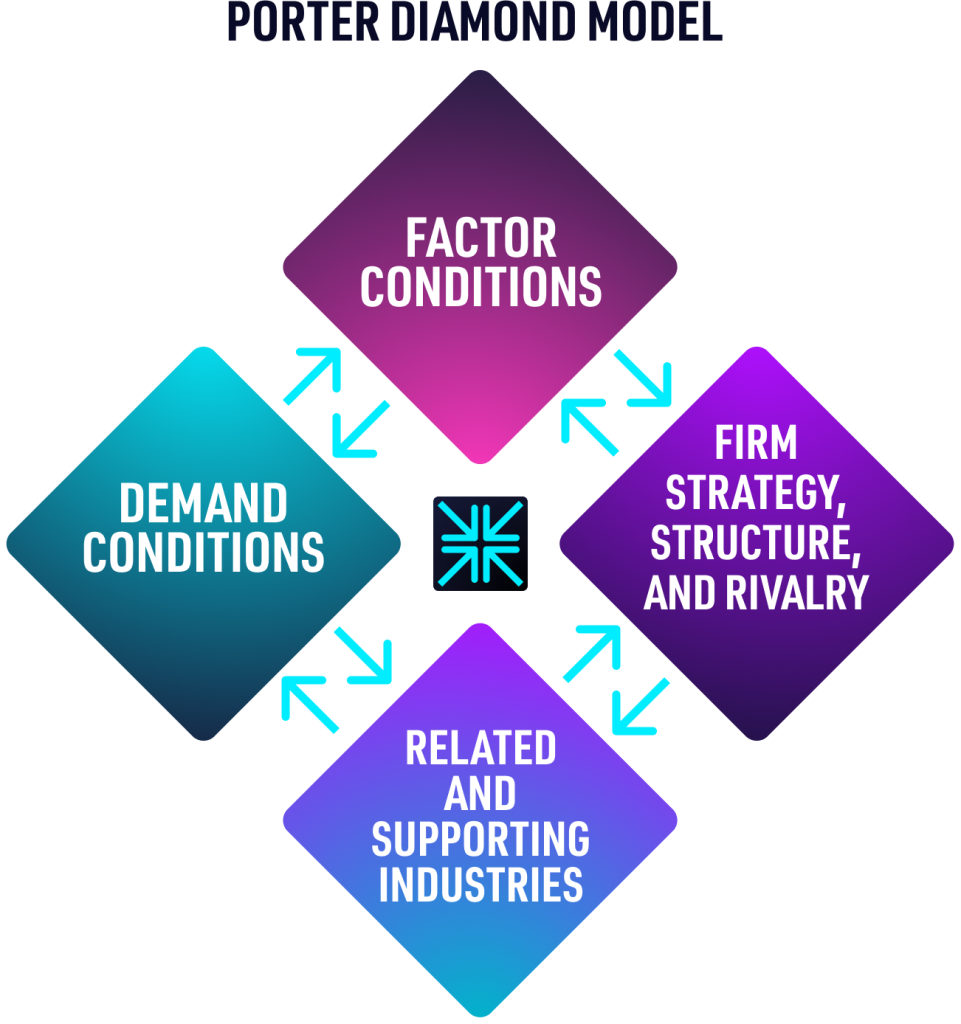
Business Strategy Framework #3 PORTER DIAMOND MODEL
The Porter Diamond Model is a business framework that describes a nation’s competitive advantage in the international market.
It also refers to innovation and why certain companies based in certain nations are capable of consistent innovation.
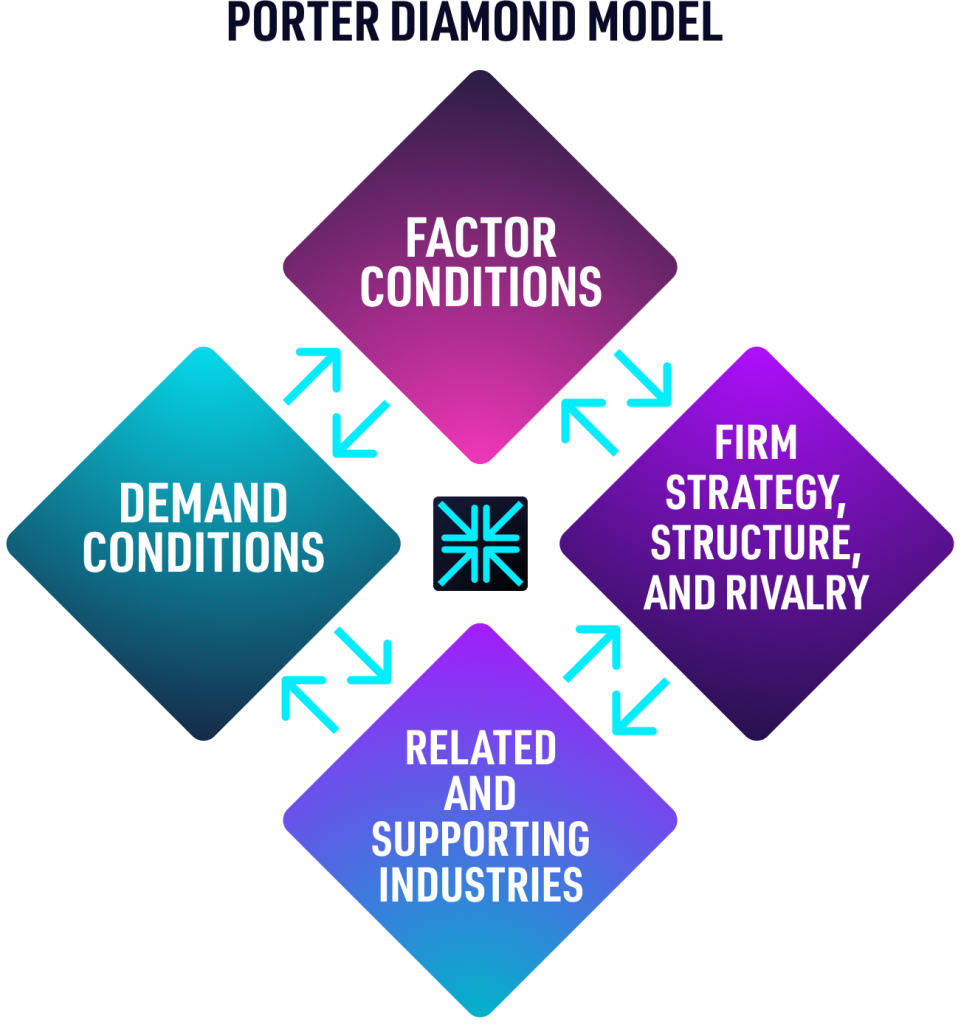
The 4 attributes of the Porter’s Diamond Model:
Factor Conditions = defines the nation’s position in factors of production, such as labour, land, natural resources, capital or infrastructure, necessary to compete in a given industry.
Demand Conditions = refers to the nature of home-market demand for the industry’s product or service.
Related and Supporting Industries = reveals the presence or absence in the nation of supplier industries and other related industries that are internationally competitive.
Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry = highlights the conditions in the nation governing how companies are created, organized, and managed, as well as the nature of domestic rivalry.
Curious to see Porter’s Diamond Model applied to two leading brands?
Read Porter’s Diamond Model Analysis – Louis Vuitton and BMW.
Business Strategy Framework #4 PESTEL
PESTEL business analysis is a framework for helping entrepreneurs and business people to understand the impact of macro-environmental factors on their businesses.
The PESTEL acronym stands for 6 factors: POLITICAL, ECONOMIC, SOCIAL, TECHNOLOGICAL, ENVIRONMENTAL, and LEGAL.
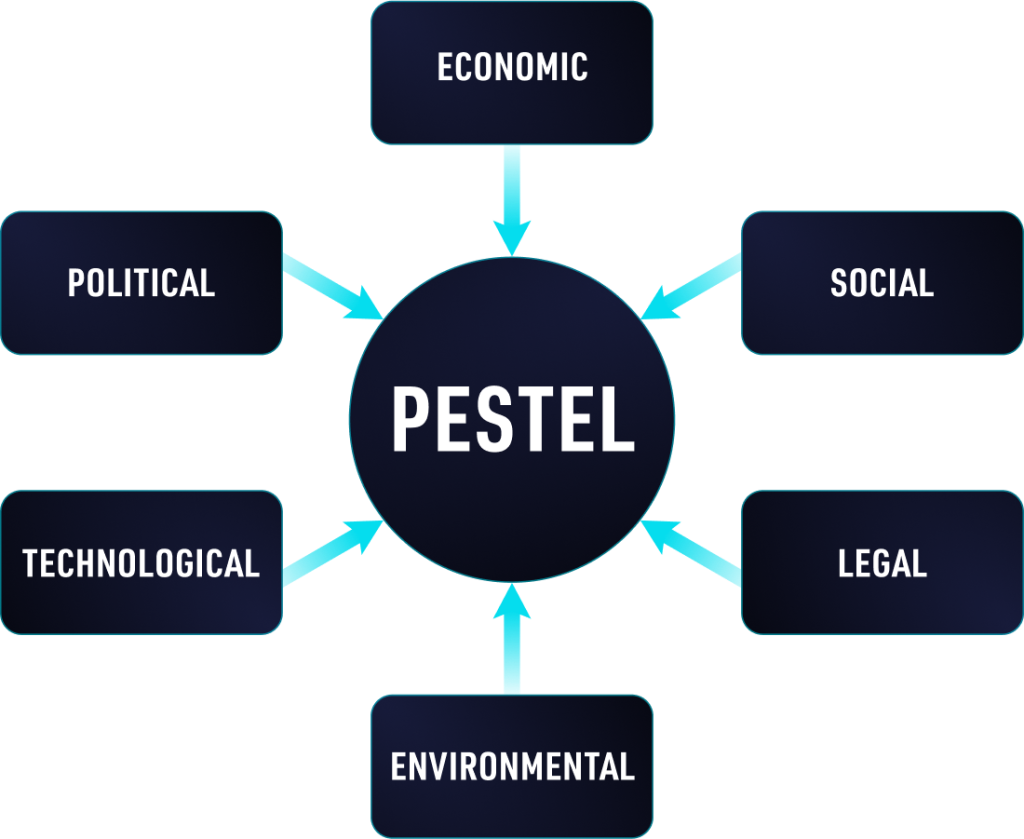
Political factor = helps you appraise the degree to which a government intervenes in the economy or a certain industry.
Economic factor = examines the economic growth, exchange rates, interest rates, unemployment rates, the state of the country’s infrastructure, and taxes.
Social factor = analyzes the profile and behaviour patterns of your customers.
Technological factor = lists the technologies impacting your industry and whether they are or not favourable.
Environmental factor = takes into account any negative impact your company operations have on the environment and prompts your company to reduce the carbon footprint, reduce waste and pollution, and preserve the environment.
Legal factor = looks into the laws and regulations of your industry.
Not sure how to apply the framework to your business?
Read A Pestel Analysis of Nike.
Business Strategy Framework #5 PORTER’S 5 FORCES
Porter’s 5 Forces framework is a valuable business tool that helps entrepreneurs shape their strategy to drive profitability.
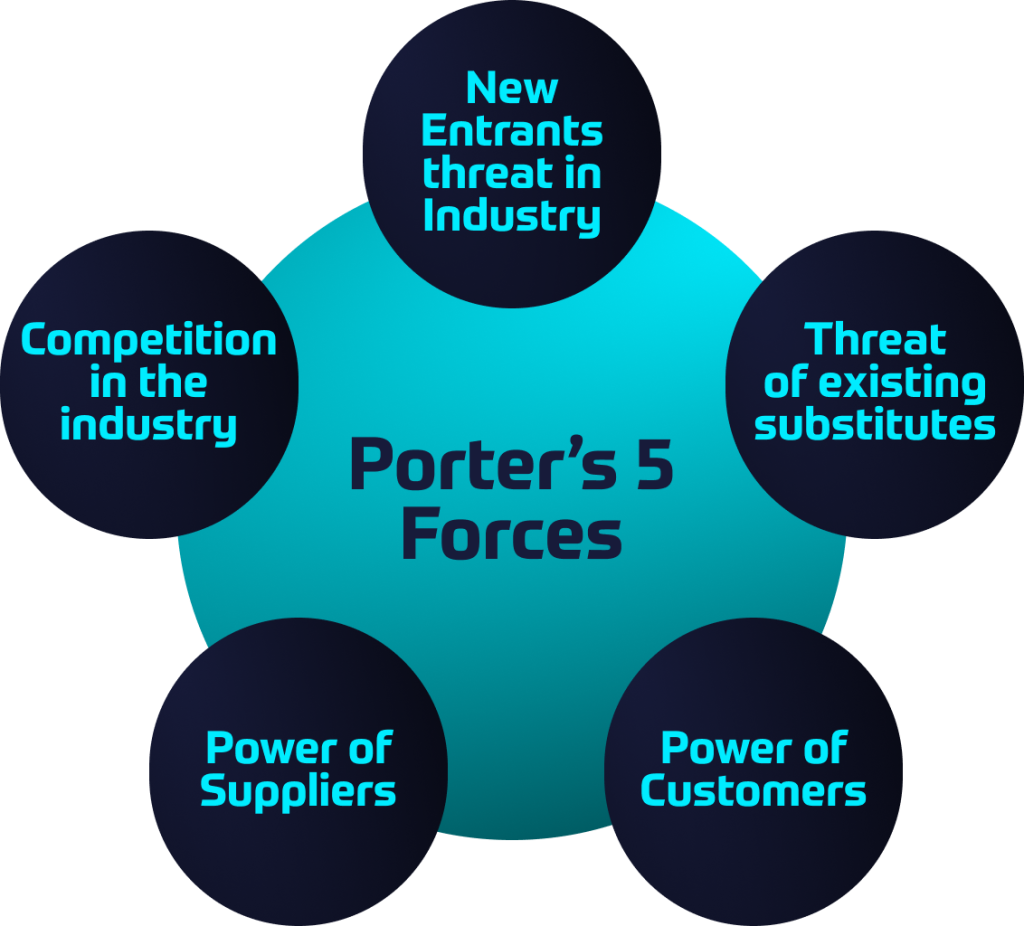
Porter’s 5 forces are:
1. Existing rivals = Evaluate the existing rivals by looking at the number of competitors, their size and power, the industry growth rate and product differentiation.
2. Buyers = The buyers are powerful and can influence the industry if they make purchases in large volumes. Are they price-sensitive? Do they have many alternatives to buy from?
3. Suppliers = Factors in determining supplier power: number of suppliers and concentration, switching costs, availability of substitutes, uniqueness of product, whether or not the industry is an important customer of the supplier and its availability to cut out the middleman.
4. Substitutes = Substitutes are alternative products that fulfil the same need by different means. In the airline industry, the substitutes are trains and cars.
5. New rivals = Is it easy for new rivals to enter the industry? If the entry barrier is low, which means requirements to enter the industry are affordable or readily accessible, then there are increasing chances of new entrants in great numbers. In this case, the threat is high.
Attend the BUSINESS STRATEGY MASTERCLASS, on October 27, and learn strategic business moves from Costas Markides, Professor of Strategy & Entrepreneurship at London Business School.

Porter’s Diamond Model analysis: Louis Vuitton and BMW
Learn about the business strategies used by Louis Vuitton and BMW from Porter’s Diamond Model analysis of these two successful and powerful organizations.
The Porter Diamond Model, also known as the Porter Diamond Theory of National Advantage is a business framework that describes a nation’s competitive advantage in the international market.
The model also highlights four factors that companies looking to expand their business internationally can take advantage of to achieve competitiveness in the market.
The Porter Diamond Model includes 4 attributes
The Porter Diamond Model analyzes a nation’s advantage against four broad attributes that each nation establishes and operates for its industries:
1.Factor Conditions
This attribute defines the nation’s position in factors of production, such as labour, land, natural resources, capital or infrastructure, necessary to compete in a given industry.
2. Demand Conditions
The second attribute of the Porter Diamond Model refers to the nature of home-market demand for the industry’s product or service.
3. Related and Supporting Industries
This attribute reveals the presence or absence in the nation of supplier industries and other related industries that are internationally competitive.
4. Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry
The Firm strategy, structure and rivalry attribute highlights the conditions in the nation governing how companies are created, organized, and managed, as well as the nature of the domestic competition.
For in-depth information on Porter’s Diamond Model, check out this article!
Theoretical knowledge is good but it’s only the starting point. Analyzing real-life examples is the best way to learn about a new business framework or model. It helps you put things in perspective.
For the purpose of this article, let’s look at two global brands and how the Porter Diamond Model is applied to them: Louis Vuitton and BMW.
Porter’s Diamond Model Analysis of Louis Vuitton

With a brand value of over $51 million in 2020, Louis Vuitton is the most valuable luxury brand in the world.
France is the company’s home base but since its inception more than 150 years ago, Louis Vuitton has expanded in 50 countries and has a retail network of over 4,910 stores worldwide.
What is the secret of Louis Vuitton’s success? Read Louis Vuitton: The story behind the brand.
Louis Vuitton: Factor and demand conditions
When you think of luxury, you think of France.
France is the world’s capital for luxury goods, haute-couture fashion, cosmetics, perfumes and accessories and the home for famous international houses such as Chanel, Dior, Givenchy, L’Oreal, Clarins, Lancome, Hermes, Celine, Louis Vuitton etc.
It’s not by chance that France has such a strong cluster of luxury brands.
The country’s luxury goods industry has a long history which began more than 500 years ago.
Eight hundred years ago, France was Europe’s silk centre with a booming silk industry.
King Louis XIV, the country’s most fashionable royalty recognized the importance of luxury goods to the national economy. Under his leadership, the country developed a powerful textile industry which in turn boosted trading and the country’s infrastructure.
Fast forward to the 21st century, France is synonymous with high fashion and luxury goods.
The fashion and luxury goods industry has a direct turnover of €150 billion. The share of French GDP generated by fashion is 2.7%. There are 1 million jobs in the fashion industry (source). The workforce in the industry is highly skilled. Experienced craftsmen or seamstresses sometimes receive an 18-month to 2-year training.
France was the perfect country for Louis Vuitton to be born in. The country provided the luxury brand with perfect factor conditions.
The French are known for their good taste and high fashion style so the brand had to work hard and innovate to meet the needs of such demanding customers (demand conditions).
This, in turn, helped them expand internationally and retain their competitive advantages.
With 37% of global sales, the Asian market is Louis Vuitton’s biggest revenue source.
Surveys show that 92% of Japanese women own a Louis Vuitton handbag and sales in China rose by more than 50% and in August last year when the brand reported record sales at its largest store in Shanghai.
Louis Vuitton: Related and Supporting Industries
The country also ranks high in the Related and Supporting Industries attribute for the luxury goods industry.
The industry’s development has been in close relationship with many subsectors such as textile and apparel, garments and embellishments, and sewing machinery. It’s an ecosystem whose members pressured each other to improve and innovate for mutual benefit.
Louis Vuitton: Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry
In France, the luxury goods industry is highly competitive.
With pressure from competitors, online sales increase and technology disruption, Louis Vuitton’s business strategy is to grow through acquisitions.
The brand is part of LVMH, the world’s largest conglomerate which came to be in 1987 when Louis Vuitton merged with champagne and cognac producer Moët Hennessy.
Over a period of 34 years, LVMH acquired more than 70 famous luxury brands. The latest acquisition is Tiffany & Co.
Porter’s Diamond Model Analysis of BMW
BMW: Factor and demand conditions
Germany played a major role in the history of the automotive industry.
It was Karl Benz, a German mechanical engineer who designed and, in 1885, built the world’s first practical automobile to be powered by an internal-combustion engine. Today, Germany is renowned for its powerful and innovative cars.
The largest industry sector in Germany is the automotive industry. Vehicles make up almost 17% of total exports.
The automobile industry generated roughly 426 billion euros in total sales in 2018.
With 882,000 manufacturing jobs in the automotive industry, Germany ranks first among European countries.
The country is a primary location for innovative car manufacturers and suppliers and is home to powerful brands such as BMW, Audi, Volkswagen, Mercedes etc.
One of the factors underlying German success is that the workforce is created. German students benefit from the country’s dual system of education where they combine vocational education with apprenticeships. This type of education supplies the country with a steady flow of highly skilled workers.
The German automotive industry benefits from a strong industrial core, first-class infrastructure, a highly-skilled workforce and cutting-edge research and development.
BMW has become a prestige global brand, operating 31 plants in 14 countries, including the largest car manufacturing plant in the world.
BMW has taken advantage of the factor conditions provided by the country. Ranked 2019’s 3rd most valuable car brand in the world, the company didn’t start as a car manufacturer, but as an aircraft engine manufacturer.
The brand’s success relies on its outstanding car design, technological innovation and workforce.
As the Porter Diamond Model recommends, the brand grows its own workforce. The BMW Manufacturer-Specific Advanced Training (MSAT) program provides students with extensive training on BMW vehicles thus preparing them to work for the company.
BMW: Related and Supporting Industries
BMW cars are high-quality automobiles.
The brand carefully selects suppliers in subsectors of the automotive industry such as parts and components, heating, ventilation, air conditioning, electronics etc. BMW depends upon a network of over 100 auto parts suppliers from all over the globe, though approximately 50% of its suppliers are either located in Germany or are subsidiaries of German-based companies (source).
BMW: Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry
BMW faces tough competition both domestically and internationally.
The company’s competitors are legacy brands much like itself.
On the local market, car automakers differentiate themselves through brand positioning.
In recent years, German car manufacturers have been struggling to adapt to new technological challenges (car connectivity, e-mobility), environmental challenges (green technology) and new entrants such as Tesla.
To stay ahead of the competition, BMW is using a competitive strategy which builds on market relevance, competitive services and research and development.
And it continues to make cars that consumers can emotionally relate to.
Attend the BUSINESS STRATEGY MASTERCLASS, on October 27 and learn future-proof business strategies for your organization from Costas Markides, Professor of Strategy & Entrepreneurship at London Business School.
Limited number of seats. Get your tickets today!

Achieve competitive advantage with the Porter Diamond Model
Looking to achieve a competitive advantage in international markets? Apply the Porter Diamond Model!
On this page:
- What is the Porter Diamond Model?
- What are the four attributes discussed in Porter’s Diamond Model (with examples)?
- How do you use Porter’s Diamond?
1. What is the Porter Diamond Model?
The Porter Diamond Model, also known as the Porter Diamond Theory of National Advantage is a business framework that describes a nation’s competitive advantage in the international market.
The Porter Diamond Model also refers to innovation and why certain companies based in certain nations are capable of consistent innovation.
The model was created by economist and researcher Michael Porter whose expertise focuses on market competition and company strategy.
If you follow this blog, you are already familiar with Mr Porter and his earlier business framework, Porter’s 5 Forces.
2. What are the 4 attributes discussed in Porter’s Diamond Model?
The Porter Diamond Model analyzes a nation’s advantage against four broad attributes that each nation establishes and operates for its industries:
- Factor Conditions
- Demand Conditions
- Related and Supporting Industries
- Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry
Porter Diamond Model – Attribute #1 – Factor Conditions
This attribute defines the nation’s position in factors of production, such as labour, land, natural resources, capital or infrastructure, necessary to compete in a given industry.
It is worth noting that these factors are not inherited, but created.
According to the Porter Diamond Model, having a general workforce that is high school or even college-educated doesn’t constitute a competitive advantage.
To become competitive in the industry, a nation’s workforce must be highly specialized in an industry’s particular needs.

In Germany, the largest industry sector is the automotive industry.
The country is a primary location for innovative car manufacturers and suppliers and home to powerful car manufacturers such as BMW, Audi, Volkswagen, Mercedes etc.
The German automotive industry benefits from a strong industrial core, first-class infrastructure, a highly-skilled workforce and cutting edge research and development.
One of the factors underlying the German success is that the workforce is created. German students benefit from the country’s dual system of education where they combine vocational education with apprenticeships. This type of education supplies the country with a steady flow of highly skilled workers.
Nations succeed in industries where they are particularly good at factor creation. Competitive advantage results from the presence of world-class institutions that first create specialized factors and then continually work to upgrade them.
Michael Porter
Porter Diamond Model – Attribute #2 – Demand Conditions
The second attribute of the Porter Diamond Model refers to the nature of home-market demand for the industry’s product or service.
Demand conditions include the nature of domestic buyers and of emerging buyer needs.
In a nation where the domestic buyers are the world’s most sophisticated and demanding buyers for the product or service, the nation’s companies gain competitive advantage.
Demanding domestic buyers pressure companies to improve, innovate and upgrade their products. Thus preparing them to rise to the challenges of buyers in other nations.

Amazon is leading the eCommerce industry in the US and worldwide.
What makes Amazon so successful on both domestic and international markets? The company’s focus on customer satisfaction.
Every product and service developed by Amazon is designed to delight customers and build a system around true customer obsession. Read this article to learn more.

Denmark is the world’s leading country in cleantech.
40% of Denmark’s total power consumption is covered by wind turbines with the goal of raising to 55% by 2030.
Everyone in Denmark is working to achieve this goal: the government, local authorities, corporations and the public.
Denmark’s energy transformation started in the 1970s when the country faced a severe energy crisis which left Denmark crippled. In just a few decades, the country veered from fossil fuels to clean energy.
Today Denmark holds exceptional cleantech opportunities with a collaborative business environment, government support and attractive framework conditions.
Nations gain competitive advantage in industries where the home demand gives their companies a clearer or earlier picture of emerging buyer needs, and where demanding buyers pressure companies to innovate faster and achieve more sophisticated competitive advantages than their foreign rivals.
Michael Porter
Porter Diamond Model – Attribute #3 – Related and Supporting Industries
This attribute reveals the presence or absence in the nation of supplier industries and other related industries that are internationally competitive.
Internationally competitive home-based suppliers create advantages by delivering the most cost-effective inputs in an efficient, early, rapid, and sometimes preferential way. Developing a close relationship between your company and its home-based suppliers is mutually beneficial.

South Korea is the world’s largest producer of semiconductors. The semiconductors industry is a supplier for a wide range of other tech-oriented industries such as smartphone manufacturers, CCTV cameras, car manufacturers etc.
The country is home to leading high-tech companies such as Samsung, Hyundai or LG.
Porter Diamond Model – Attribute #4 – Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry
The Firm strategy, structure and rivalry attribute highlights the conditions in the nation governing how companies are created, organized, and managed, as well as the nature of the domestic rivalry.

In Italy, for example, successful companies are often small or medium-sized family-run companies.

In China, 85% of enterprises are state-owned and lacking in market flexibility.

In the United Arab Emirates, the law required foreign companies to set up their businesses in partnership with an Emirati sponsor. Starting in November 2020, the government changed the law to allow 100% foreign ownership of businesses.
These four attributes make up the foundation upon which nations build their business environment. This environment determines how companies are born and how they learn to compete.
3. How do you use Porter’s Diamond?
Is your company looking to achieve international competitive success?
Here are 6 main insights provided by the Porter Diamond model:
- availability of resources necessary for competitive advantage in the industry of your choice;
- availability of skills necessary for competitive advantage in the industry of your choice;
- information that shapes the opportunities;
- directions in which companies deploy their resources and skills;
- goals of the owners, managers, and individuals in companies;
- the pressures on companies to invest and innovate.
If your company is planning to achieve a competitive advantage in the industry, investigate to which extent the national environment supports the rapid accumulation of specialized assets and skills.
Or whether or not the national environment affords better ongoing information and insight into product and process needs.
Does the national environment pressure companies to innovate and invest?
If the answers to these questions are affirmative, then your company could gain a competitive advantage and upgrade those advantages over time.
Join the Conversation
We’d love to hear what you have to say.
Get in touch with us on our LinkedIn Page, Facebook Page, Twitter or TikTok.