5 business strategy frameworks for business growth
Business Strategy Framework #1 ANSOFF MATRIX ANALYSIS
The Ansoff Matrix is a business strategy framework and a planning tool that provides managers with a template to devise strategies for future growth.
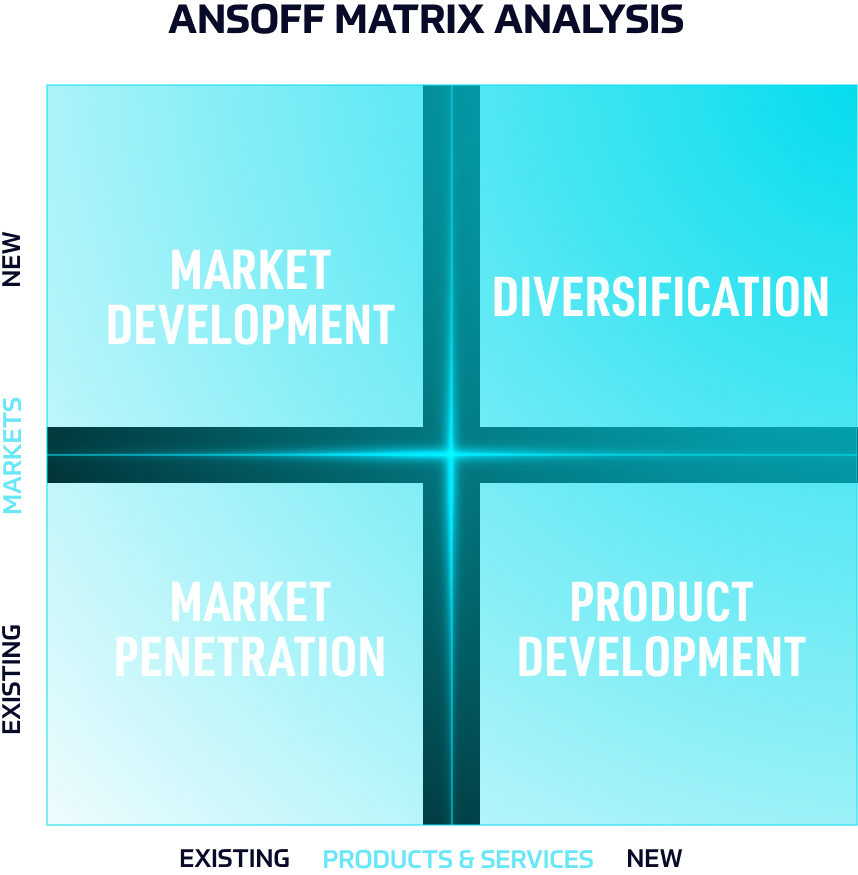
There are 4 growth strategies within the Ansoff Matrix:
- Market penetration strategy = in which the company seeks to improve business performance either; by increasing the volume of sales to its present customers or by finding new customers for present products;
- Market development strategy = in which the company sells its existing products to new markets;
- Product development strategy = in which the company develops new products for the same market;
- Diversification strategy = in which the company develops new products in a new market.
What growth strategies does Apple use?
Learn from our Ansoff Matris analysis of Apple.
Business Strategy Framework #2 BCG GROWTH-SHARE MATRIX
The BCG Growth-Share Matrix helps companies analyze their business units (i.e. their product lines) or any other cash-generating entities by their degree of profitability.
This business strategy framework provides the company with a four-quadrant chart where products are ranked on the basis of their relative market shares and growth rates:
“cash cows”,
“dogs”,
“question marks” and
“stars”.

Cash cows are products in low-growth areas for which the company has a high market share.
Products with a low market share in areas with slow growth are dogs.
Question marks are the products with a low market share in a high growth rate market.
Stars are products with a high market share in a high growth rate market.
To show how you can use the matrix for your business, read our analysis of e-commerce leader Amazon, specifically four of its products: Amazon AWS, Amazon Video, Amazon Live and Amazon Echo with Alexa.
Business Strategy Framework #3 PORTER DIAMOND MODEL
The Porter Diamond Model is a business framework that describes a nation’s competitive advantage in the international market.
It also refers to innovation and why certain companies based in certain nations are capable of consistent innovation.
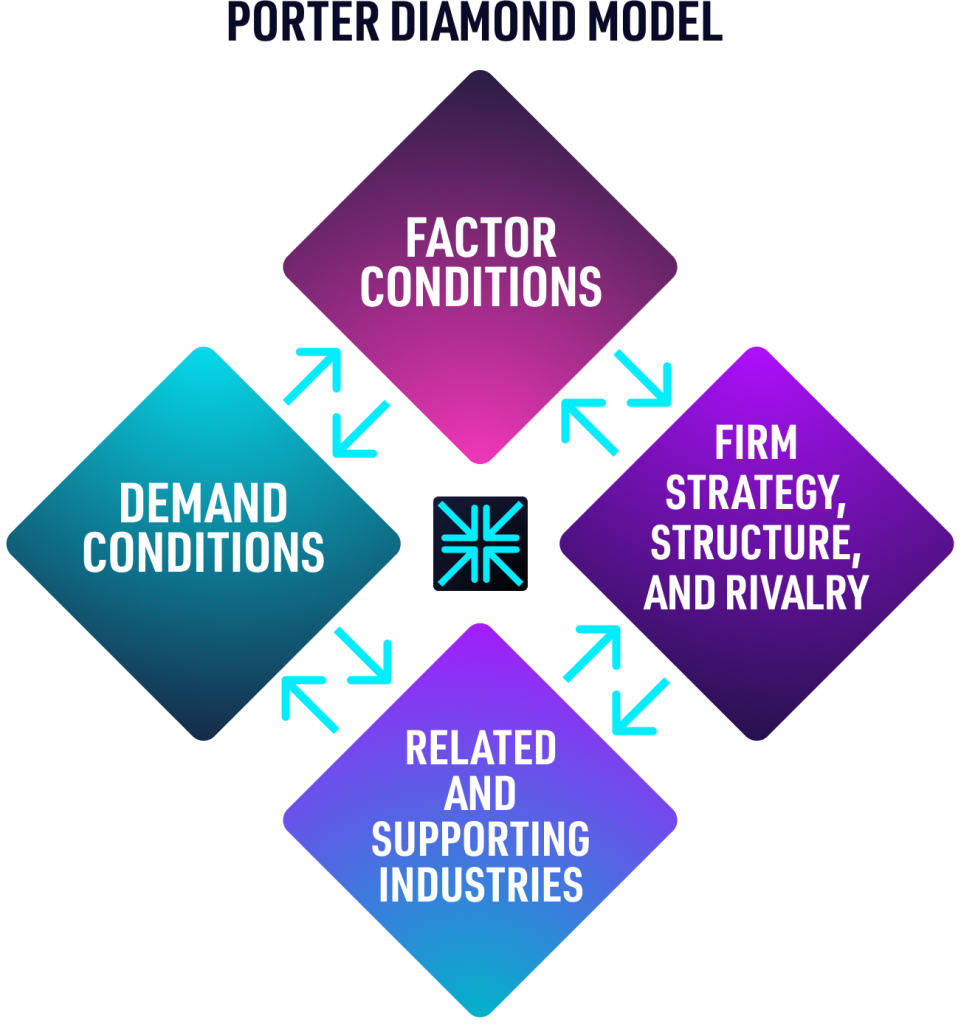
The 4 attributes of the Porter’s Diamond Model:
Factor Conditions = defines the nation’s position in factors of production, such as labour, land, natural resources, capital or infrastructure, necessary to compete in a given industry.
Demand Conditions = refers to the nature of home-market demand for the industry’s product or service.
Related and Supporting Industries = reveals the presence or absence in the nation of supplier industries and other related industries that are internationally competitive.
Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry = highlights the conditions in the nation governing how companies are created, organized, and managed, as well as the nature of domestic rivalry.
Curious to see Porter’s Diamond Model applied to two leading brands?
Read Porter’s Diamond Model Analysis – Louis Vuitton and BMW.
Business Strategy Framework #4 PESTEL
PESTEL business analysis is a framework for helping entrepreneurs and business people to understand the impact of macro-environmental factors on their businesses.
The PESTEL acronym stands for 6 factors: POLITICAL, ECONOMIC, SOCIAL, TECHNOLOGICAL, ENVIRONMENTAL, and LEGAL.
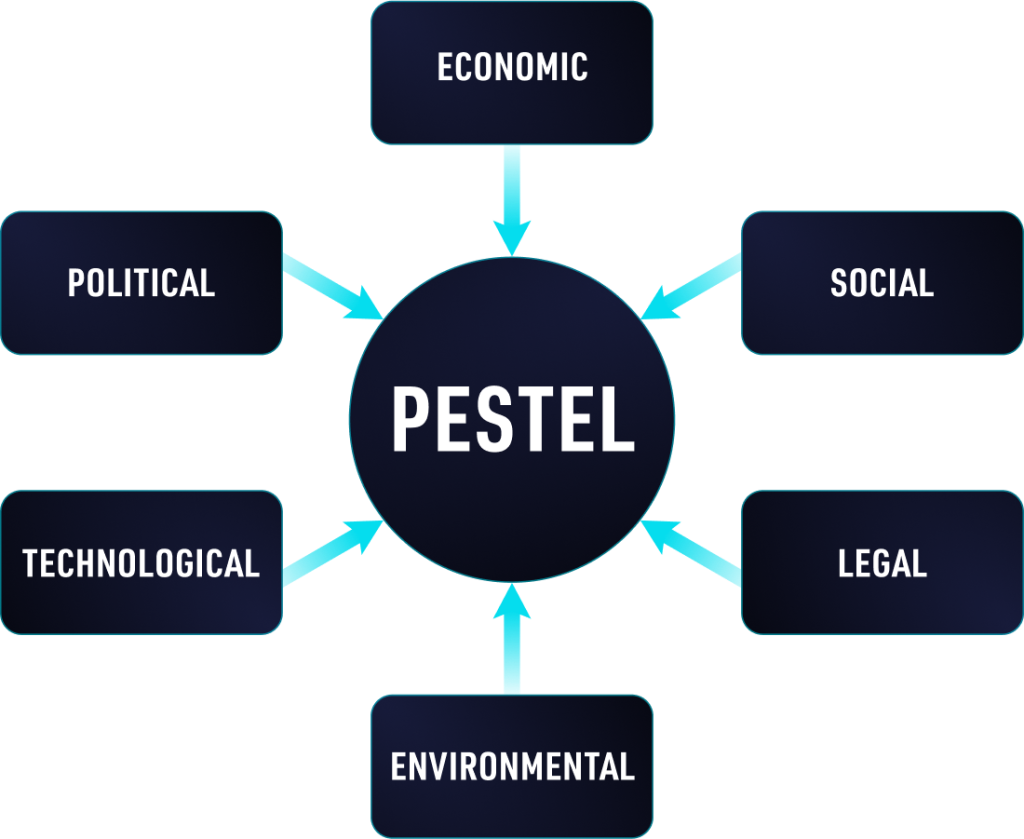
Political factor = helps you appraise the degree to which a government intervenes in the economy or a certain industry.
Economic factor = examines the economic growth, exchange rates, interest rates, unemployment rates, the state of the country’s infrastructure, and taxes.
Social factor = analyzes the profile and behaviour patterns of your customers.
Technological factor = lists the technologies impacting your industry and whether they are or not favourable.
Environmental factor = takes into account any negative impact your company operations have on the environment and prompts your company to reduce the carbon footprint, reduce waste and pollution, and preserve the environment.
Legal factor = looks into the laws and regulations of your industry.
Not sure how to apply the framework to your business?
Read A Pestel Analysis of Nike.
Business Strategy Framework #5 PORTER’S 5 FORCES
Porter’s 5 Forces framework is a valuable business tool that helps entrepreneurs shape their strategy to drive profitability.
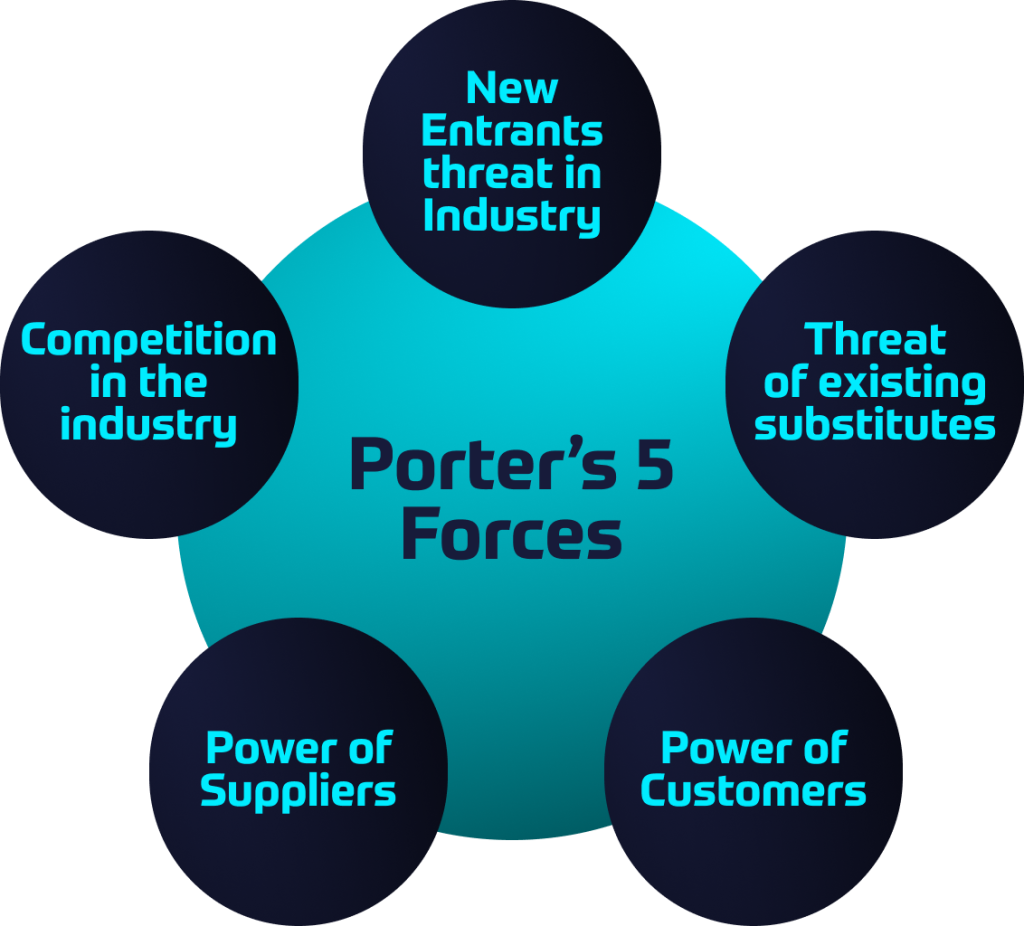
Porter’s 5 forces are:
1. Existing rivals = Evaluate the existing rivals by looking at the number of competitors, their size and power, the industry growth rate and product differentiation.
2. Buyers = The buyers are powerful and can influence the industry if they make purchases in large volumes. Are they price-sensitive? Do they have many alternatives to buy from?
3. Suppliers = Factors in determining supplier power: number of suppliers and concentration, switching costs, availability of substitutes, uniqueness of product, whether or not the industry is an important customer of the supplier and its availability to cut out the middleman.
4. Substitutes = Substitutes are alternative products that fulfil the same need by different means. In the airline industry, the substitutes are trains and cars.
5. New rivals = Is it easy for new rivals to enter the industry? If the entry barrier is low, which means requirements to enter the industry are affordable or readily accessible, then there are increasing chances of new entrants in great numbers. In this case, the threat is high.
Attend the BUSINESS STRATEGY MASTERCLASS, on October 27, and learn strategic business moves from Costas Markides, Professor of Strategy & Entrepreneurship at London Business School.

BUSINESS reSOURCES: Grow your business with Porter’s 5 Forces framework
On this page:
- What is Porter’s 5 Forces business framework?
- How to evaluate Porter’s 5 Forces (explained)
- 11 Benefits of applying Porter’s 5 Forces framework to grow your business
- 6 recommendations for a successful business strategy
What is Porter’s 5 Forces business framework?
Porter’s 5 forces is a holistic way of looking at any industry and understanding the structural underlining drivers of profitability and competition.
Porter’s 5 Forces framework is a valuable business tool that helps entrepreneurs shape their strategy to drive profitability.

Business strategist Michael E. Porter
The framework was created by Michael E. Porter, an economist, researcher, author and Harvard Business School professor. His expertise focuses on market competition and company strategy. His extensive research is widely recognized in governments, corporations, NGOs, and academic circles around the globe.
Strategy can be viewed as building defences against the competitive forces or as finding positions in the industry where the forces are weakest.
Michael E. Porter
How to evaluate Porter’s 5 Forces (explained)
1. Existing rivals
Evaluate the existing rivals by looking at the number of competitors. Are there many competitors? How do they rate in terms of size and power? Are they clearly differentiated or are their products almost identical?
What is the size of the competitors?
What is the industry growth rate: slow or fast?
Is product differentiation between competitors present?
What about exit barriers: are they high or low?
2. Buyers
The buyers are powerful and can influence the industry if they make purchases in large volumes.
Is the product undifferentiated? If that’s the case, the buyer will be price-sensitive and the digital environment allows the buyer to instantly compare prices and choose the cheapest.
Is there a large customer base? Do they have many alternatives to buy from? When the buyers are interested in high quality, they are not price-sensitive.
3. Suppliers
How much control does a supplier have over your business?
Does it influence your business by raising the cost of their products and lowering quality?
How many suppliers are in the industry? The fewer they are, the more powerful they are to control the industry and influence your profit margin.
Factors in determining supplier power: number of suppliers and concentration, switching costs, availability of substitutes, uniqueness of product, whether or not the industry is an important customer of the supplier and its availability to cut out the middle man.
4. Substitutes
Substitutes are alternative products that fulfil the same need by different means. In the airline industry, the substitutes are trains and cars.
Rule of thumb: don’t limit your analysis to your industry. Expand your approach to products that meet the same need but are in different industries.
How many alternatives to your product are on the market?
How can you rate the buyers’ willingness to switch and choose a substitute instead of your product?
What is the price-performance ratio of the substitutes?
5. New rivals
Is the entry barrier low or high?
If the entry barrier is low, which means requirements to enter the industry are affordable or readily accessible, then there are increasing chances of new entrants in great numbers. In this case, the threat is high.
There are six major sources of barriers to entry: economies of scale, product differentiation, capital requirements, cost disadvantages independent of size, access to distribution channels and government policy.
In a future envisioned by Elon Musk, people will fly from New York to Shanghai in a rocket, not an airplane and it will take only 10 minutes instead of 24 hours. The downside of this type of futuristic fast-travel may prove to have a high price.
A different way of fast and affordable transportation shines brightly in the near future: the hyperloop. Read about the hyperloop.
11 Benefits of applying Porter’s 5 Forces Business Framework
If you have a great idea, the next step is not product development, logo design, or assembling the best team.
If you’re contemplating starting a business, the first thing you should do is industry analysis and look at the competitor environment before anything else.
And that’s why Porter’s 5 Forces framework is of paramount importance to any entrepreneur: it helps to design a successful business strategy that will support the business to achieve its goals.
11 benefits of applying Porter’s 5 Forces Business Framework
- Evaluate the roots of long-term profitability in your industry.
- Discover the trends that are most likely to be significant in changing the game in the industry.
- Where are the constraints which if you can relax, it might allow you to find a really strong competitive position?
- Avoid getting trapped or tricked by the latest trend or technological sensation.
- Focus on the underlying fundamentals.
- Analyze your competition and how it is affecting the profit.
- Learn how to approach competition in your industry.
- Identify the structure of the industry.
- Find answers to the question How is the industry changing?
- Get the tools to understand industry dynamics.
- Position your business to find that spot in the industry where you can have a really good profit.
6 Recommendations for a successful business strategy
The goal of Porter’s business framework is not to find the weaknesses of your competitors in order to drive them out of the market.
As Michael Porter says, it’s not a zero-sum game. By applying this framework, you get valuable insights which in turn can help you identify a specific and unique way in which to delight your customers.
Your business can delight your customers in one way, the competitors can delight their customers in another way.
It’s a better strategy rather than engaging in price wars which is not a long-term strategy.
When creating your strategy based on insights gained by applying Porter’s 5 Forces framework, take into account the following recommendations:
- Choose a supplier group to buy from that exercises less power over your business;
- Perform buyer selection i.e. choose a buyer group to sell to that leverages a low power over your business;
- Your business can sell to powerful buyers if it partners with a low-cost supplier or the product is unique;
- When creating your strategy, factor in the substitutes that are subject to trends improving their price-performance tradeoff with the industry’s product;
- Devise a solution to not merely survive the forces, but change them;
- Keep a close eye on industry evolution.
The key to growth—even survival—is to stake out a position that is less vulnerable to attack from head-to-head opponents, whether established or new, and less vulnerable to erosion from the direction of buyers, suppliers, and substitute goods. Establishing such a position can take many forms—solidifying relationships with favourable customers, differentiating the product either substantively or psychologically through marketing, integrating forward or backwards, establishing technological leadership.
Michael E Porter
Conclusion
Porter’s 5 Forces Framework is a very robust framework, easily applicable to all industries, allowing entrepreneurs to position the business so as to be least vulnerable to the industry’s competitive forces.
Join the Conversation
We’d love to hear what you have to say.
Get in touch with us on our LinkedIn Page, Facebook Page, Twitter or TikTok.
Source: How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy by Michael E. Porter